Haskell
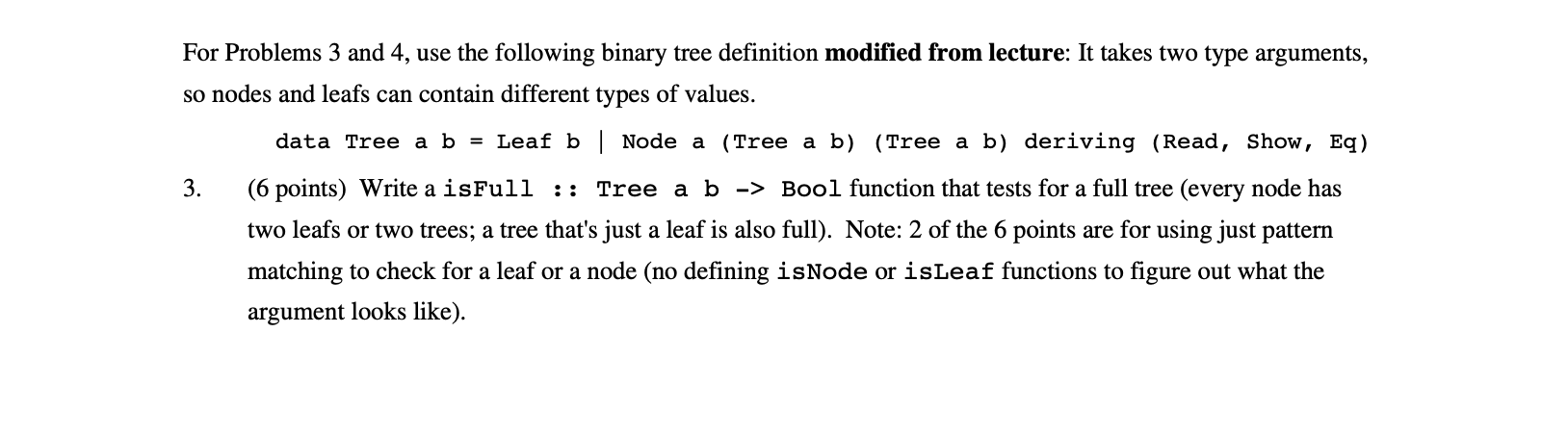

For Problems 3 and 4, use the following binary tree definition modified from lecture: It takes two type arguments, so nodes and leafs can contain different types of values. data Tree a b = Leaf b | Node a (Tree a b) (Tree a b) deriving (Read, Show, Eq) 3. (6 points) Write a isFull :: Tree a b -> Bool function that tests for a full tree (every node has two leafs or two trees; a tree that's just a leaf is also full). Note: 2 of the 6 points are for using just pattern matching to check for a leaf or a node (no defining isnode or isLeaf functions to figure out what the argument looks like). 4. (12 points) For this problem, let's call an expression tree a Tree String b tree where all of the node data are strings from the set "+", "-", "*", and "/", and the leafs hold numbers. Write an eval function routine that evaluates an expression tree. Division requires fractional numbers, so the type of eval is Fractional t => Tree String b-> b. Examples: Let el = Node "+" (Leaf 2) (Leaf 4), e2 = Node "-" (Leaf 11) (Leaf 8), and e3 = Node "/" (Node "*" el e2) (Leaf 36). Then eval el = 6.0; eval e2 = 3.0; and eval e3 = 0.5. For Problems 3 and 4, use the following binary tree definition modified from lecture: It takes two type arguments, so nodes and leafs can contain different types of values. data Tree a b = Leaf b | Node a (Tree a b) (Tree a b) deriving (Read, Show, Eq) 3. (6 points) Write a isFull :: Tree a b -> Bool function that tests for a full tree (every node has two leafs or two trees; a tree that's just a leaf is also full). Note: 2 of the 6 points are for using just pattern matching to check for a leaf or a node (no defining isnode or isLeaf functions to figure out what the argument looks like). 4. (12 points) For this problem, let's call an expression tree a Tree String b tree where all of the node data are strings from the set "+", "-", "*", and "/", and the leafs hold numbers. Write an eval function routine that evaluates an expression tree. Division requires fractional numbers, so the type of eval is Fractional t => Tree String b-> b. Examples: Let el = Node "+" (Leaf 2) (Leaf 4), e2 = Node "-" (Leaf 11) (Leaf 8), and e3 = Node "/" (Node "*" el e2) (Leaf 36). Then eval el = 6.0; eval e2 = 3.0; and eval e3 = 0.5








