I have shared with a starter Code

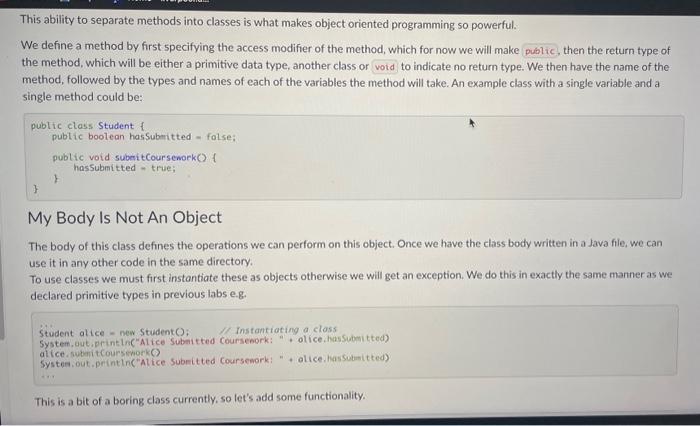
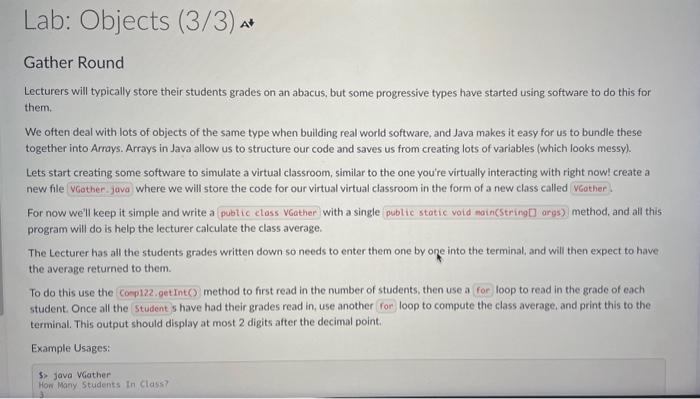
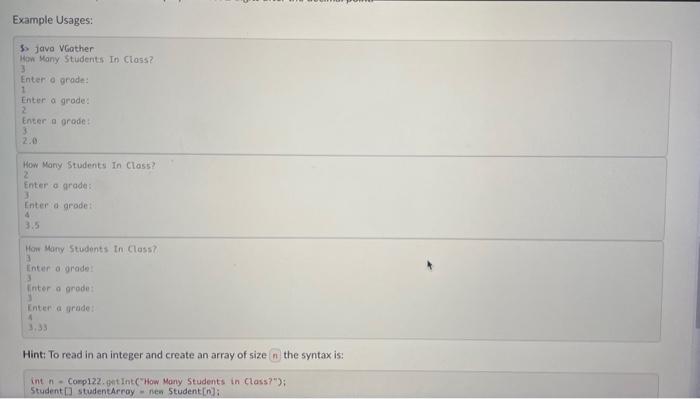
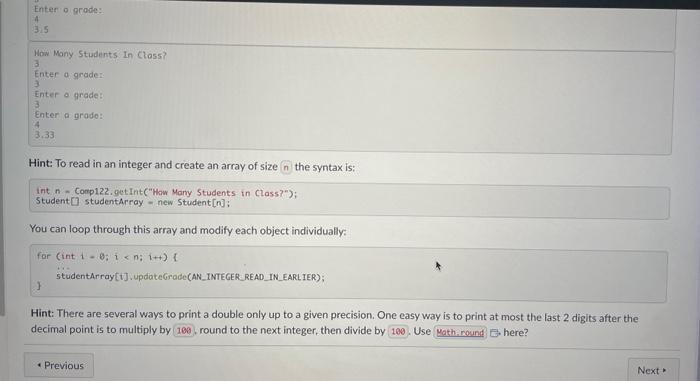
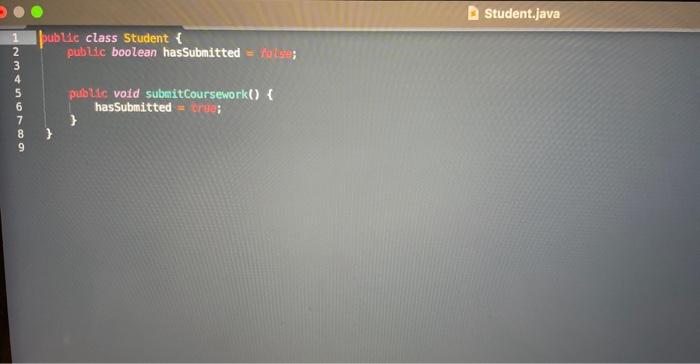
A louch of Class All of the variables we have used so far (with the exception of arrays and the inputhelper) have been primitive data types. There's an awful lot you can do with primitive data types, in languages such as C we only have primitive data types (and people have done an awful lot with C). In Java however we have the option of creating more complex data types, classes! Programs of can get complex very quickly, in large pieces of software it is simply impossible to keep track of tens of thousands of lines of code when they are in a single file. To make life much easier for ourselves (honestly), we separate our code into separate functional classes. Class Half Full You may have noticed that you have been using classes in every single Java program you have written in this course so far, nice job! We define a class using the keyword, which you may note has been near the start of each of your submissions. Each of our programs have been quite short, so we haven't used many of the features apart from a single function where we have put all of our code. Each of our classes can contain a number of variables, as well as functions to operate on those variables. From now on, variables when they belong to a class will be referred to as attributes, and a function which belongs to a class is called a method. This ability to separate methods into classes is what makes object oriented programming so powerful. We define a method by first specifying the access modifier of the method, which for now we will make then the return type of the method, which will be either a primitive data type, another class or to indicate no return type. We then have the name of the method, followed by the types and names of each of the variables the method will take. An example class with a single variable and a single method could be: public class Student f pubtic boolean hassuberitted - folse; public void subeitcoursenorkO f h hassubmitted - true; My Body Is Not An Object The body of this class defines the operations we can perform on this object. Once we have the class body written in a Java file, we can use it in any other code in the same directory. To use classes we must first instantiate these as objects otherwise we will get an exception. We do this in exactly the same manner as we declared primitive types in previous labs e.g. Student alice - new Student( ) ; Instantioting a class System, aut,println("Alice Subaitted Coursenork: " olice. hassubmitted) alice. SubenitCoursmorkC Systes,out,printlnc"Alice Subeitted Coursenork: " + olice.hassubeitted) This is a bit of a boring class currently, so let's add some functionality. Lab: Objects (2/3) What's in a Name? Let's change the given starter code a bit, and add more attributes as follows. - Most students have a name, so at the top of the class add a variable - Similarly, add a attribute called - an attribute called - an attribute called - and an attribute called - Finally, an to the class to keep track of the students score, called initilly equal to Now add a new method called "updateGrade", that takes an parameter (and returns nothing = "that can be used to set a student's grade. After each of the assignments, the lecturer will update the students score with a method which will return a void called , which will add the students grade for that assignment to their grade.' The automarker will be using these terms, so make sure to follow this specification closely (capitalisation matters)! Gather Round Lecturers will typically store their students grades on an abacus, but some progressive types have started using software to do this for them. We often deal with lots of objects of the same type when building real world software, and Java makes it easy for us to bundle these together into Arrays. Arrays in Java allow us to structure our code and saves us from creating lots of variables (which looks messy). Lets start creating some software to simulate a virtual classroom, similar to the one you're virtually interacting with right now! create a new file where we will store the code for our virtual virtual ciassroom in the form of a new class called For now we'l keep it simple and write a with a single method, and all this program will do is help the lecturer calculate the class average. The Lecturer has all the students grades written down so needs to enter them one by one into the terminal, and will then expect to have the average returned to them. To do this use the method to first read in the number of students, then use a loop to read in the grade of each student. Once all the 5 have had their grades read in, use another for) loop to compute the class average, and print this to the terminal. This output should display at most 2 digits after the decimal point. Example Usages: 5. Java VGather Example Usages: 5. java VGather Han Many Students In Class? 3 Enterio acode: 1 Enter a grade: 2 Enter: a prode: 33 How Many Students In Class? 2. Enter a grade: Enteria arode: 4.5 3.5 How Mary Stodents In Class? 3 Inter a grade: 3 Pinter a grode: Enter a grude: 4 3,33 Hint: To read in an integer and create an array of size the syntax is: int n - Conp122, gnt Ink( How Many Students in (lass?"); Student [] studentArroy = nen 5 tudent [n]; Hint: There are several ways to print a double only up to a given precision. One easy way is to print at most the last 2 digits after the decimal point is to multiply by round to the next integer, then divide by Use here? Publuc class Student f public boolean hasSubmitted = /alici; puibluc vold subaitCoursework() \{ hasSubmitted = Irie; 3