A system of acetone-benzene at 318.15 K forms a non-ideal solution. Its vapor-liquid equilibrium is given in Figure Q3 for partial and total vapor
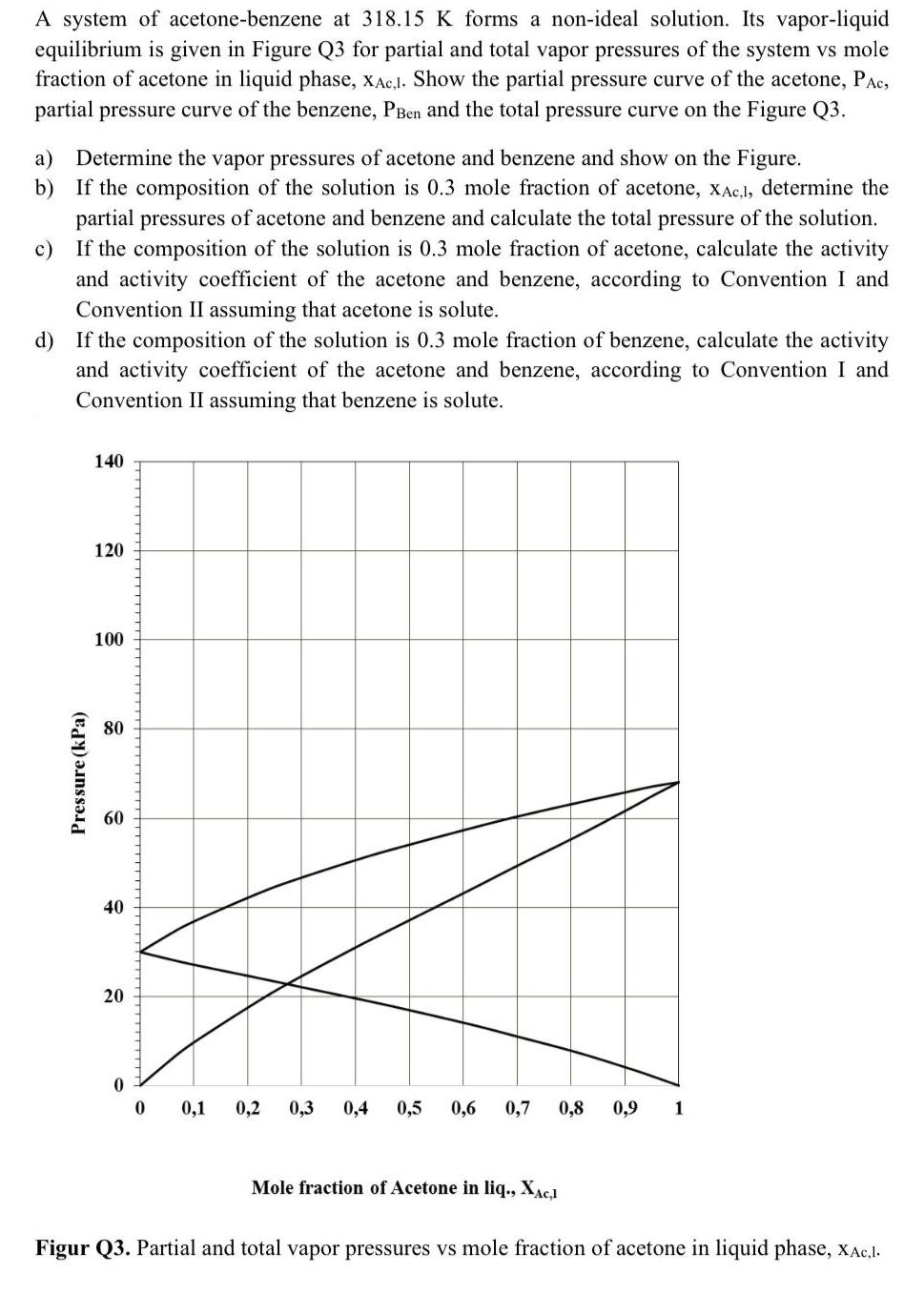
A system of acetone-benzene at 318.15 K forms a non-ideal solution. Its vapor-liquid equilibrium is given in Figure Q3 for partial and total vapor pressures of the system vs mole fraction of acetone in liquid phase, xAc,I. Show the partial pressure curve of the acetone, PAc, partial pressure curve of the benzene, PBen and the total pressure curve on the Figure Q3. a) Determine the vapor pressures of acetone and benzene and show on the Figure. b) If the composition of the solution is 0.3 mole fraction of acetone, xAc,l, determine the partial pressures of acetone and benzene and calculate the total pressure of the solution. If the composition of the solution is 0.3 mole fraction of acetone, calculate the activity and activity coefficient of the acetone and benzene, according to Convention I and c) Convention II assuming that acetone is solute. d) If the composition of the solution is 0.3 mole fraction of benzene, calculate the activity and activity coefficient of the acetone and benzene, according to Convention I and Convention II assuming that benzene is solute. 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0,1 0,2 0,3 0,4 0,5 0,6 0,7 0,8 0,9 1 Mole fraction of Acetone in liq., XAC1 Figur Q3. Partial and total vapor pressures vs mole fraction of acetone in liquid phase, xAc,1. Pressure (kPa)
Step by Step Solution
3.51 Rating (164 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Document Format ( 2 attachments)
60915c5db153d_209836.pdf
180 KBs PDF File
60915c5db153d_209836.docx
120 KBs Word File
Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


