Question: in c++ Statement Purpose: Purpose of this Lab is to familiarize the students with Linked List data structure. Another aim is to teach the students





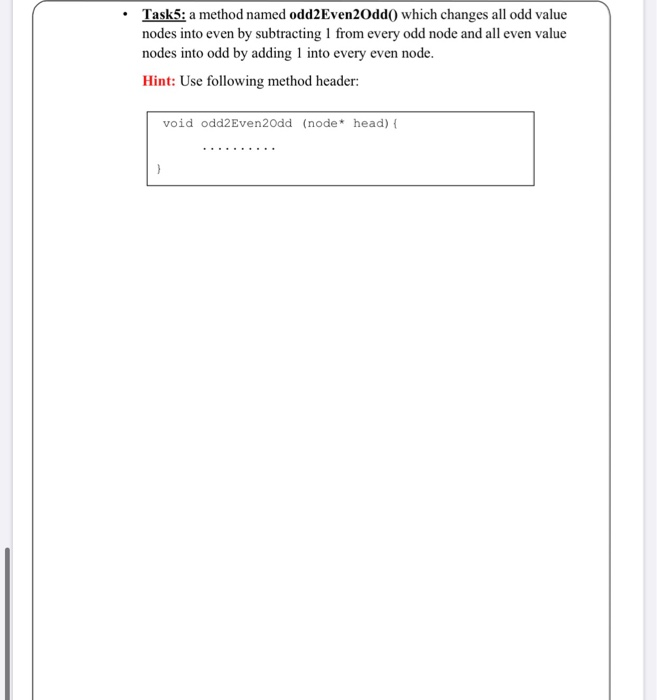
Statement Purpose: Purpose of this Lab is to familiarize the students with Linked List data structure. Another aim is to teach the students the disadvantages of using arrays and advantages of using linked lists as well as the difference between these two data structures. The students are given small tasks related to linked list which they complete during the lab session under the supervision of the lab instructor. This helps them understand the concepts well which they learn in their lectures. Activity Outcomes: The students will learn how to write code for various methods which work with linked lists. They will also understand how to construct nodes and link them together find the largest value in the list return data of second node present in the linked list. return data of second last node present in the linked list. delete last node in the existing linked list. modify the values of the nodes Theory Review: Linked List: A linked list is an ordered collection of data, where each element (generally called nodes) contains the location of the next element in the list. Each node essentially has two parts: 1. The data part. If this was a list of student records, for example, the data here may consist of a name, PID, social security number, address, phone, email, etc. 2. The link part. This link is used to chain the nodes together. It simply contains a reference that points to the next node in the linked list. Variable is often called "next". Disadvantages of Arrays Arrays are fixed size i.e. static. Arrays can store homogeneous (same) data. Inserting and deleting elements is expensive because it requires shifting of remaining elements. Advantages of Linked List Linked list is not fixed size i.e. they are dynamic which means that their size can be increased or decreased during the execution of program. Linked list can store heterogeneous (different) data. Inserting and deleting elements is very cheap because it does not require shifting of remaining elements. Visiting all elements of linked list In case of linked list, a reference variable, generally called head points to the first node of the linked list. In order to visit each and every node of linked list, we need to move the reference variable (may also be called pointer) from first node to the last node. We cannot move the head reference variable (unless it is required in order to delete the first node), otherwise we shall lose some nodes of the linked list. . For this purpose, we take a copy of the reference variable head and call it as help Ptr which is moved from first node to the last node using while loop. It is depicted in the following method, which displays all nodes of a linked list. This is the class that is used to define a node: struct node int data; node *next; Code for printAIINodes( Method //This method is called from main() and it visits each and every node of linked list and displays the value stored in data field. void printAllNodes (node *head) { node *helpPtr = new node (); helpPtr= head; while (helpPtr != NULL) { // Print the data value of the node coutdata next; LAB EXERCISE: 1. Create a new project with the name Lab3_LinkList Project. 2. Create a C++ file with name LinkedList and copy struct node class into it. 3. Add main method and complete the balnk with suitable statements int main() { // construct four linked list nodes and add their values( see output) // display the nodes values using printAllNodes() Il print the largest value in the linked list // print the value of the second node // print the value of the second last node // delete the last node // display the nodes values using printAllNodes() // modify the nodes values by using odd2Even2Odd method // display the nodes values using printAllNodes() return 0; 4. Add the following methods to the file: Taskl: a method named findLargest() which finds the largest value in the linked list and returns its data to the calling main() method. Hint: Use following method header: int findLargest (node* head) { Task 2: a method named data2ndNode() which returns the data of second node in the linked list, to the calling main() method. Hint: Use following method header: node* data2ndNode (node* head) { Task3: a method named data2ndLastNode() which returns the data of second last node in the linked list, to the calling main() method. Hint: Use following method header: node* data2ndLastNode (node* head ) { Task4: a method named deleteLastNode() which deletes last node in the existing linked list. Hint: Use following method header: void deleteLastNode (node* head) { .......... Task5: a method named odd2Even20dd() which changes all odd value nodes into even by subtracting 1 from every odd node and all even value nodes into odd by adding 1 into every even node. Hint: Use following method header: void odd2 Even20dd (node* head) {
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


