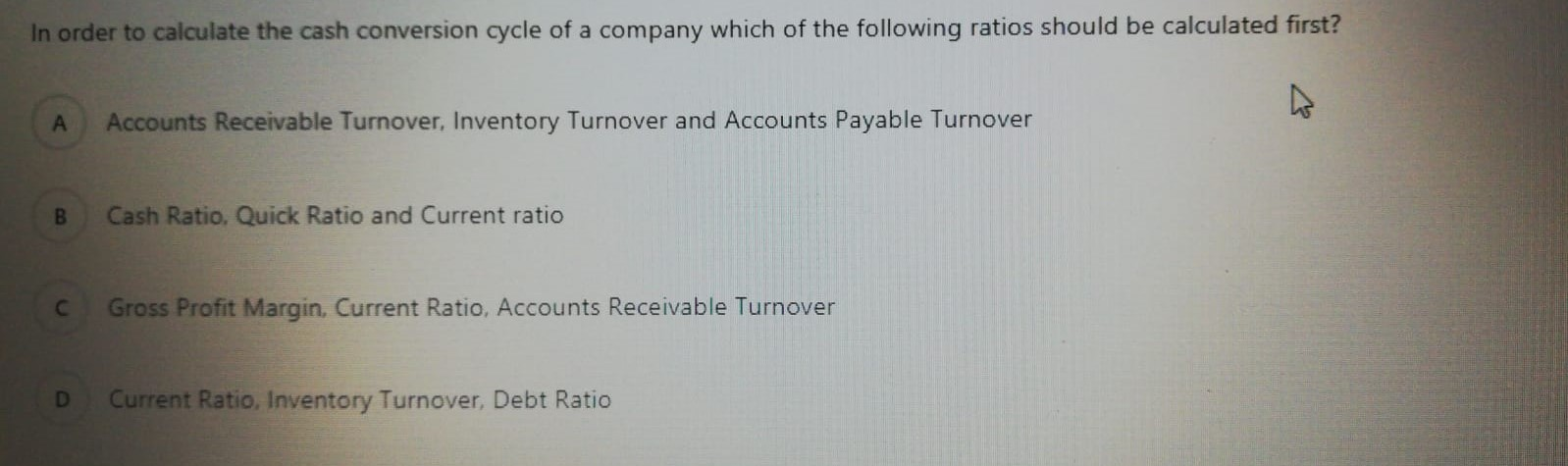
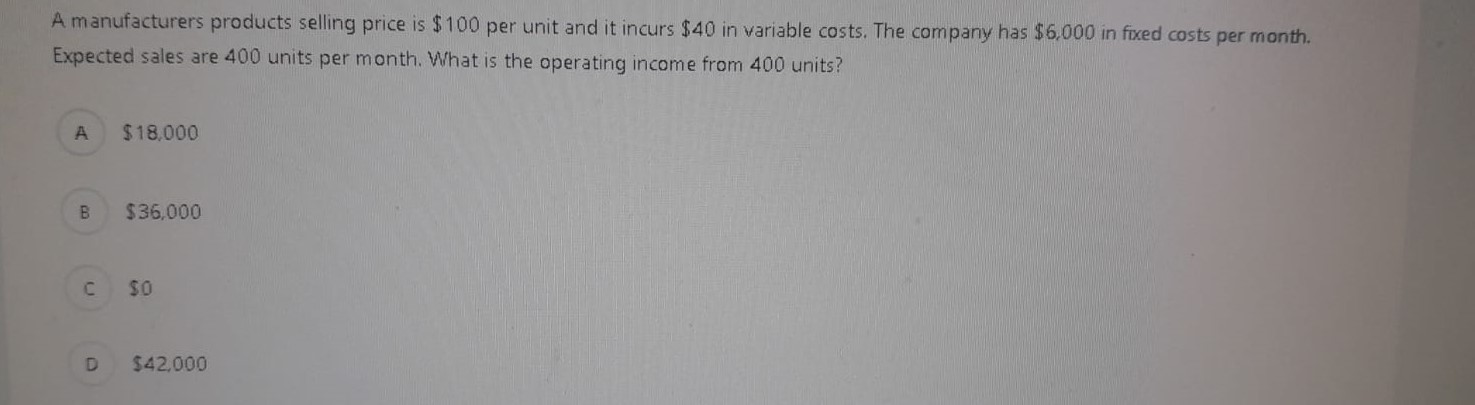
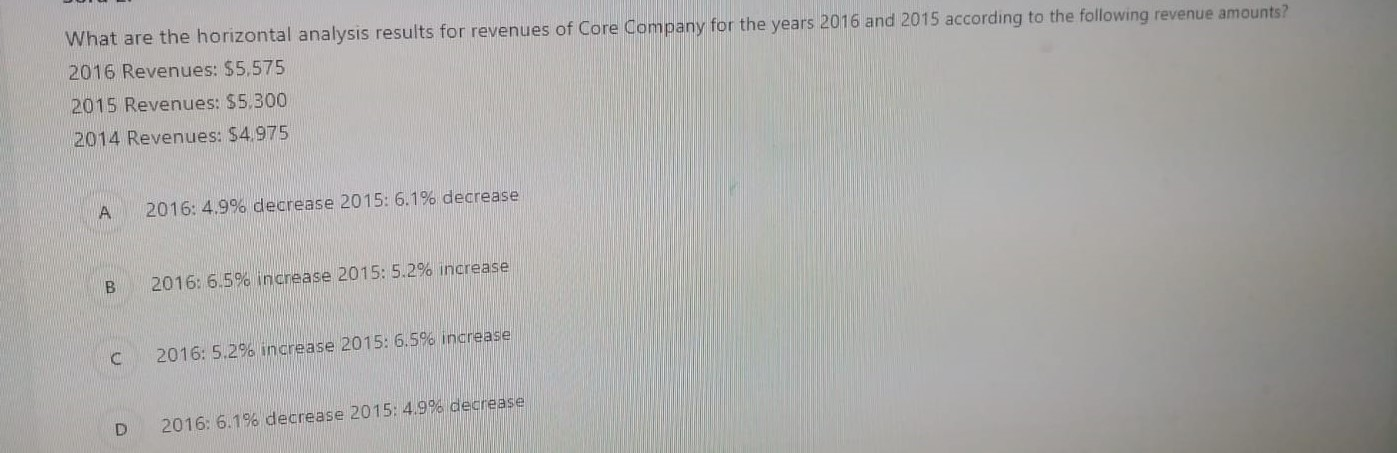
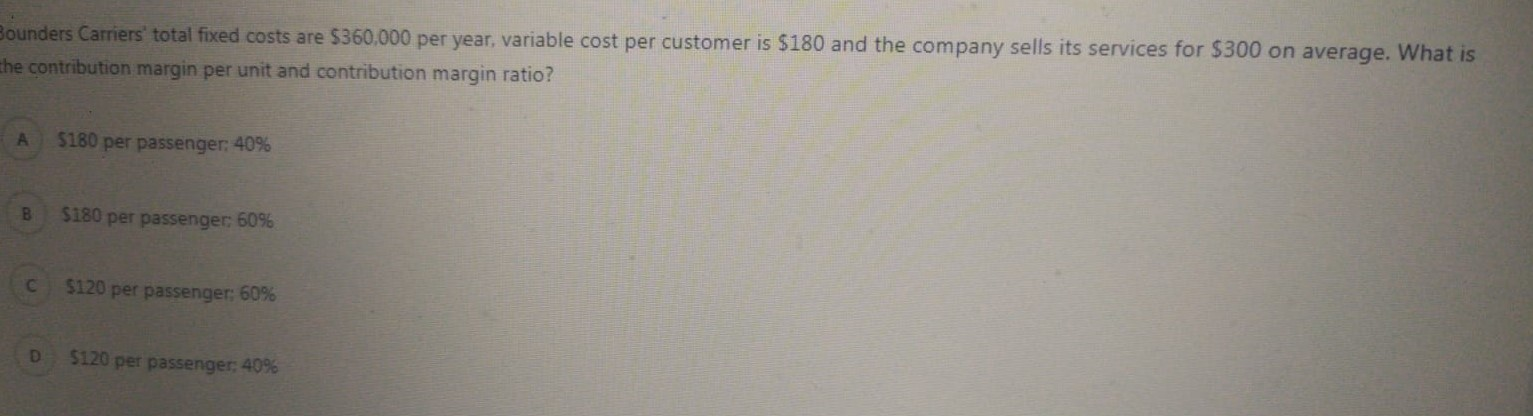
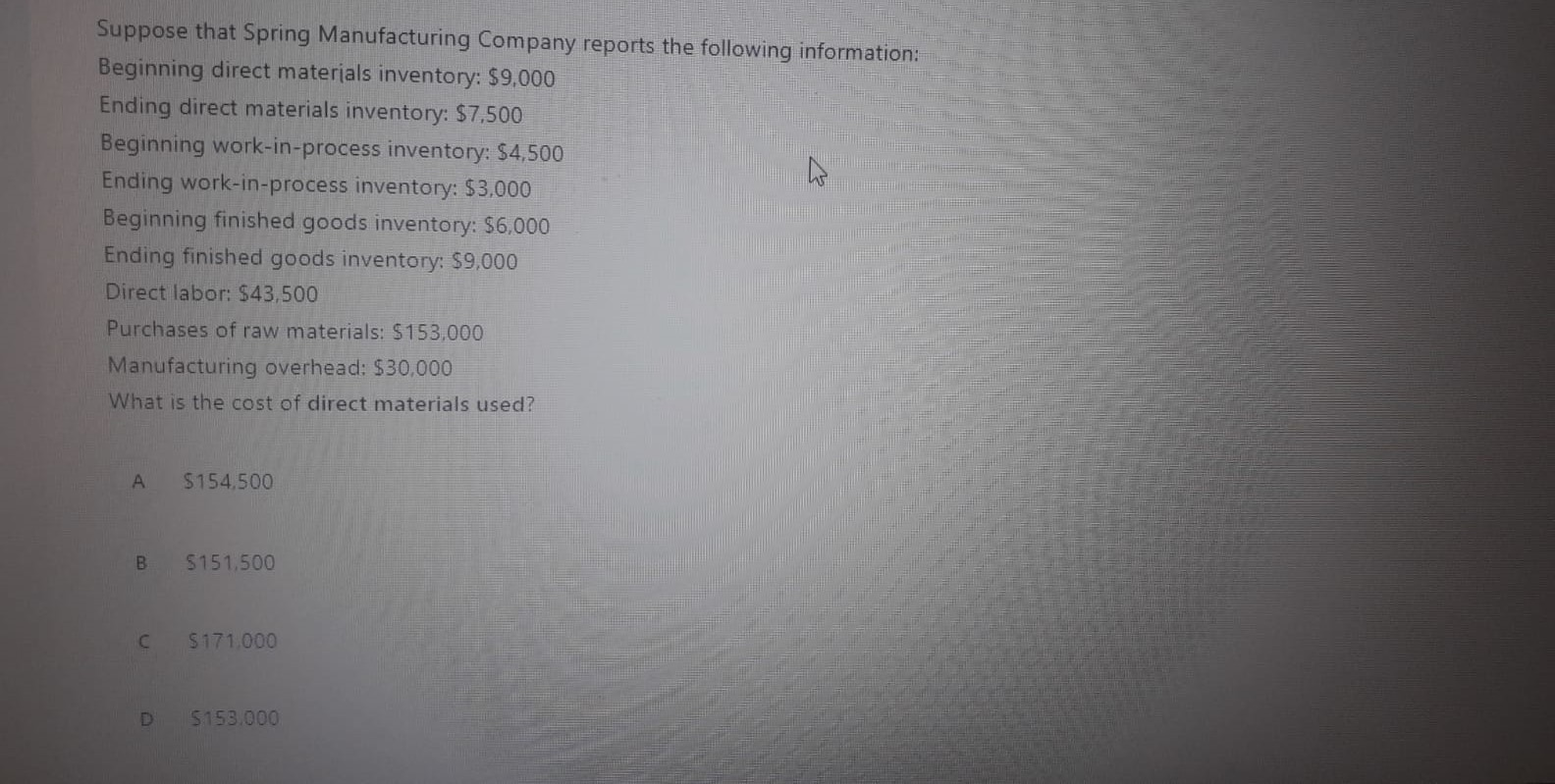
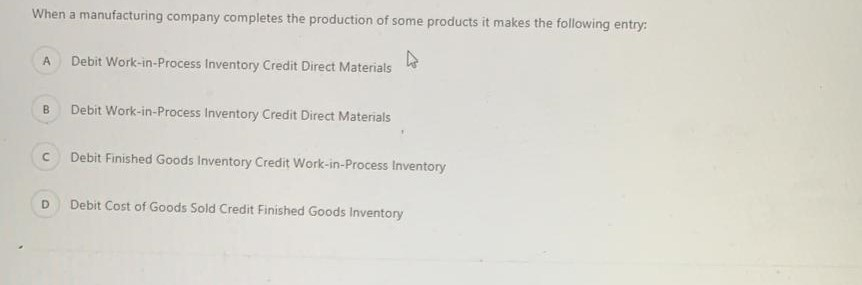

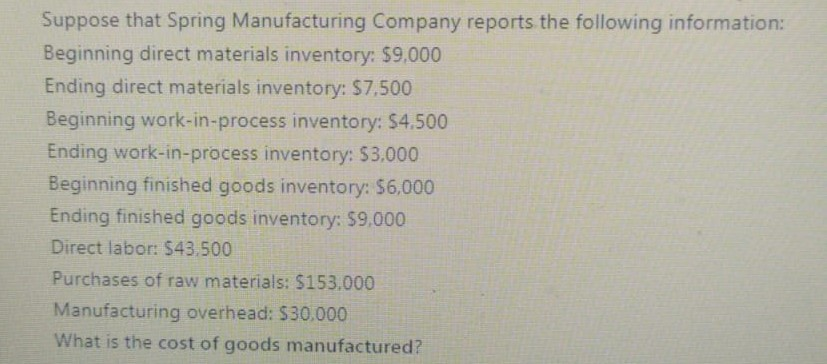
In order to calculate the cash conversion cycle of a company which of the following ratios should be calculated first? Accounts Receivable Turnover, Inventory Turnover and Accounts Payable Turnover B Cash Ratio. Quick Ratio and Current ratio Gross Profit Margin. Current Ratio, Accounts Receivable Turnover D Current Ratio, Inventory Turnover, Debt Ratio A manufacturers products selling price is $100 per unit and it incurs $40 in variable costs. The company has $6,000 in fixed costs per month. Expected sales are 400 units per month. What is the operating income from 400 units? $18,000 B $36,000 so D $42.000 What are the horizontal analysis results for revenues of Core Company for the years 2016 and 2015 according to the following revenue amounts? 2016 Revenues: $5.575 2015 Revenues: $5,300 2014 Revenues: $4.975 A 2016: 4.9% decrease 2015: 6.1% decrease B 2016: 6.5% increase 2015: 5.2% increase C 2016: 5.2% increase 2015: 6.5% increase D 2016: 6.1% decrease 2015: 4.9% decrease Bounders Carriers' total fixed costs are $360,000 per year, variable cost per customer is $180 and the company sells its services for $300 on average. What is the contribution margin per unit and contribution margin ratio? A $180 per passenger: 40% B $180 per passenger: 60% $120 per passenger: 60% D $120 per passenger: 40% Suppose that Spring Manufacturing Company reports the following information: Beginning direct materials inventory: $9,000 Ending direct materials inventory: $7,500 Beginning work-in-process inventory: $4,500 Ending work-in-process inventory: $3.000 Beginning finished goods inventory: $6,000 Ending finished goods inventory: $9,000 Direct labor: $43,500 Purchases of raw materials: $ 153,000 Manufacturing overhead: $30,000 What is the cost of direct materials used? A $154.500 B 5151.500 $ 171.000 $150.000 When a manufacturing company completes the production of some products it makes the following entry: A Debit Work-in-Process Inventory Credit Direct Materials B Debit Work-in-Process Inventory Credit Direct Materials Debit Finished Goods Inventory Credit Work-in-Process Inventory Debit Cost of Goods Sold Credit Finished Goods Inventory A transportation company has the following overhead costs pooled in its activities: Activity 1: Materials Handling Estimated Overhead Cost: $230,000 Allocation Base: Kilograms Estimated Quantity of the Allocation Bade: 46.000 kilograms Activity 2: Packaging Estimated Overhead Cost: $416,000 Allocation Base: Number of DL Hours Estimated Quantity of the Allocation Base: 6,400 hours What is the predetermined overhead rate for the two activities? Suppose that Spring Manufacturing Company reports the following information: Beginning direct materials inventory: $9,000 Ending direct materials inventory: $7,500 Beginning work-in-process inventory: $4.500 Ending work-in-process inventory: 53,000 Beginning finished goods inventory: $6,000 Ending finished goods inventory: $9,000 Direct labor: $43.500 Purchases of raw materials: $153.000 Manufacturing overhead: 530.000 What is the cost of goods manufactured














