In studying the purchase of durable goods Y (Y = 1 if purchased, Y = 0 if no purchase) as a function of several
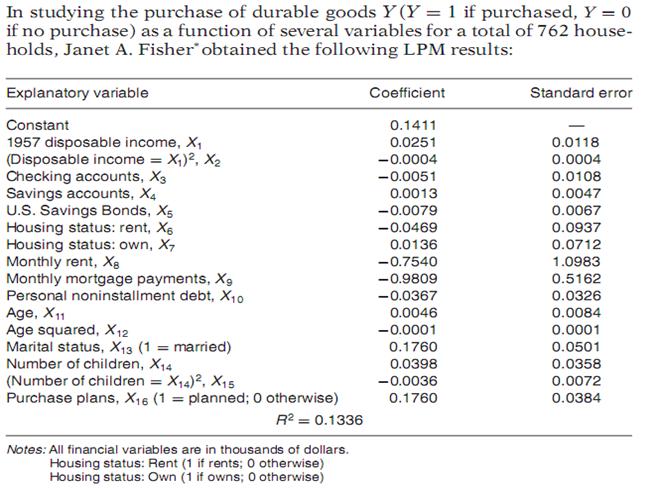

In studying the purchase of durable goods Y (Y = 1 if purchased, Y = 0 if no purchase) as a function of several variables for a total of 762 house- holds, Janet A. Fisher obtained the following LPM results: Explanatory variable Coefficient Standard error Constant 0.1411 1957 disposable income, X, (Disposable income = X,)2, X2 Checking accounts, X3 Savings accounts, X4 U.S. Savings Bonds, X5 Housing status: rent, X6 Housing status: own, X7 Monthly rent, X8 Monthly mortgage payments, Xg Personal noninstallment debt, X10 Age, X11 Age squared, X12 Marital status, X13 (1 = married) Number of children, X14 (Number of children = X14)2, X15 Purchase plans, X16 (1 = planned; 0 otherwise) 0.0251 0.0118 -0.0004 0.0004 -0.0051 0.0108 0.0013 0.0047 -0.0079 0.0067 0.0937 0.0712 -0.0469 0.0136 -0.7540 1.0983 0.5162 -0.9809 -0.0367 0.0326 0.0046 0.0084 -0.0001 0.0001 0.1760 0.0501 0.0398 0.0358 -0.0036 0.0072 0.1760 0.0384 R? = 0.1336 Notes: All financial variables are in thousands of dollars. Housing status: Rent (1 if rents; 0 otherwise) Housing status: Own (1 if owns; O otherwise) Source: Janet A. Fisher, "An Analysis of Consumer Good Expenditure," The Review of Economics and Statistics, vol. 64, no. 1, Table 1, 1962, p. 67. a. Comment generally on the fit of the equation. b. How would you interpret the coefficient of -0.0051 attached to checking account variable? How would you rationalize the negative sign for this variable? c. What is the rationale behind introducing the age-squared and number of children-squared variables? Why is the sign negative in both cases? d. Assuming values of zero for all but the income variable, find out the conditional probability of a household whose income is $20,000 pur- chasing a durable good. e. Estimate the conditional probability of owning durable good(s), given: X1 = $15,000, X3 = $3000, X4 = $5000, X6 = 0, X7 = 1, Xg = $500, X9 = $300, X10 = 0, X11 = 35, X13 = 1, X14 = 2, X16 = 0.
Step by Step Solution
3.40 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
the solu...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


