Question
Ivanhoe Inc. is a retailer operating in Centralia. Ivanhoe uses the perpetual inventory method. All sales returns from customers result in the goods being returned
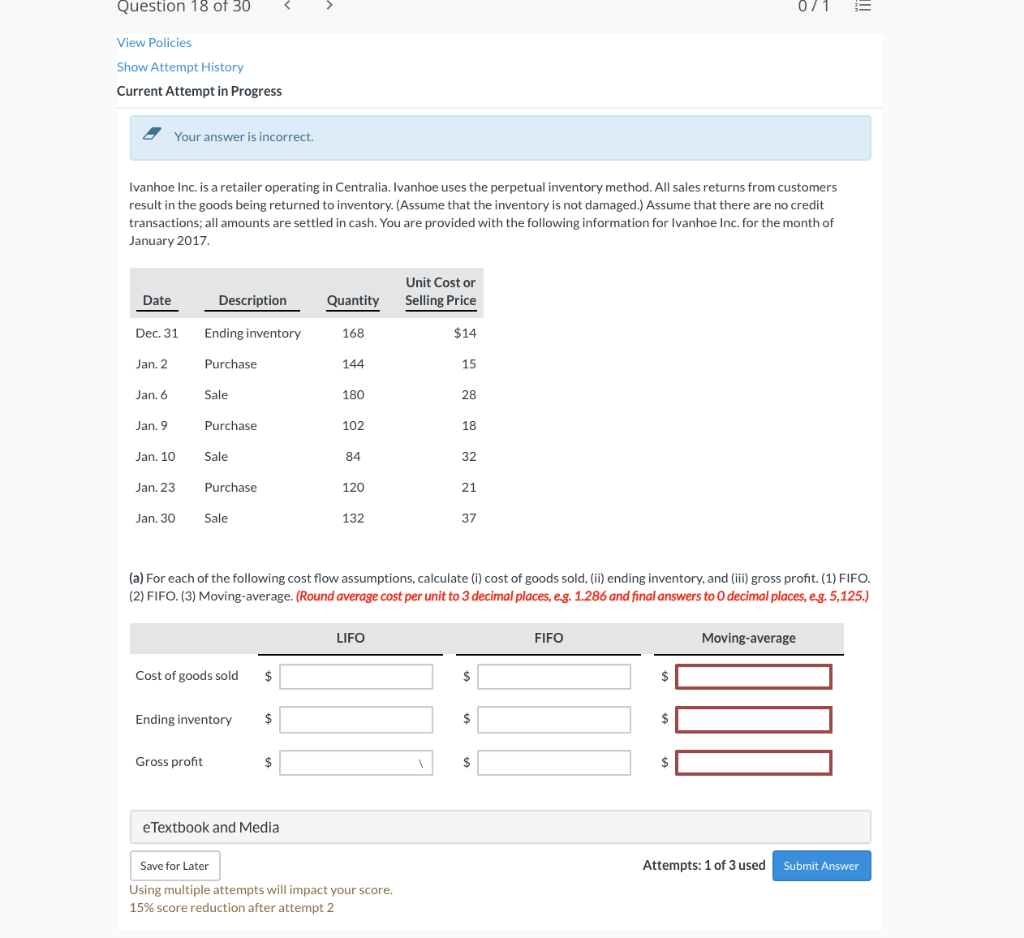
Ivanhoe Inc. is a retailer operating in Centralia. Ivanhoe uses the perpetual inventory method. All sales returns from customers result in the goods being returned to inventory. (Assume that the inventory is not damaged.) Assume that there are no credit transactions; all amounts are settled in cash. You are provided with the following information for Ivanhoe Inc. for the month of January 2017.
| Date | Description | Quantity | Unit Cost or Selling Price | |||
| Dec. 31 | Ending inventory | 168 | $14 | |||
| Jan. 2 | Purchase | 144 | 15 | |||
| Jan. 6 | Sale | 180 | 28 | |||
| Jan. 9 | Purchase | 102 | 18 | |||
| Jan. 10 | Sale | 84 | 32 | |||
| Jan. 23 | Purchase | 120 | 21 | |||
| Jan. 30 | Sale | 132 | 37 |
(a) For each of the following cost flow assumptions, calculate (i) cost of goods sold, (ii) ending inventory, and (iii) gross profit. (1) FIFO. (2) FIFO. (3) Moving-average. (Round average cost per unit to 3 decimal places, e.g. 1.286 and final answers to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,125.)
| LIFO | FIFO | Moving-average | ||||
| Cost of goods sold | $ | $ | $ | |||
| Ending inventory | $ | $ | $ | |||
| Gross profit | $ | $ | $ |
Question 18 of 30 0/1 View Policies Show Attempt History Current Attempt in Progress Your answer is incorrect. Ivanhoe Inc. is a retailer operating in Centralia. Ivanhoe uses the perpetual inventory method. All sales returns from customers result in the goods being returned to inventory. (Assume that the inventory is not damaged.) Assume that there are no credit transactions; all amounts are settled in cash. You are provided with the following information for Ivanhoe Inc. for the month of January 2017 Date Description Unit Cost or Selling Price Quantity Dec. 31 Ending inventory 168 $14 Jan. 2 Purchase 144 15 Jan. 6 Sale 180 28 Jan. 9 Purchase 102 18 Jan 10 Sale 84 32 Jan. 23 Purchase 120 21 Jan. 30 Sale 132 37 (a) For each of the following cost flow assumptions, calculate (i) cost of goods sold, (ii) ending inventory, and (iii) gross profit. (1) FIFO. (2) FIFO. (3) Moving-average. (Round average cost per unit to 3 decimal places, eg. 1.286 and final answers to decimal places, eg. 5,125.) LIFO FIFO Moving-average Cost of goods sold $ $ Ending inventory $ $ $ Gross profit $ $ e Textbook and Media Attempts: 1 of 3 used Submit Answer Save for Later Using multiple attempts will impact your score. 15% score reduction after attempt 2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


