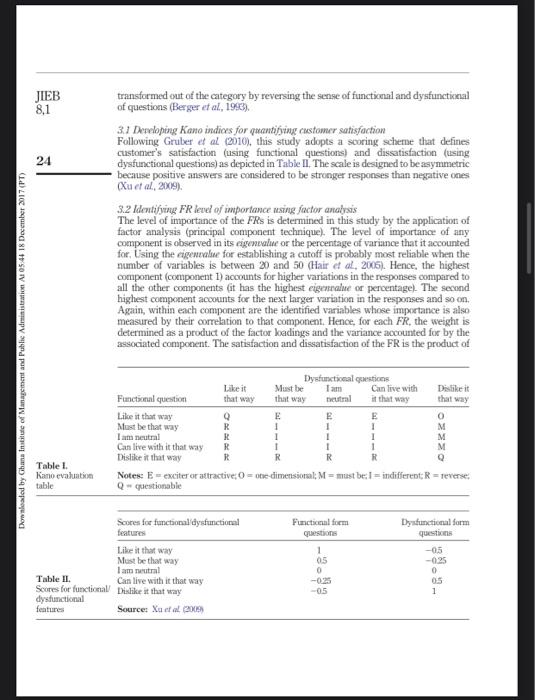
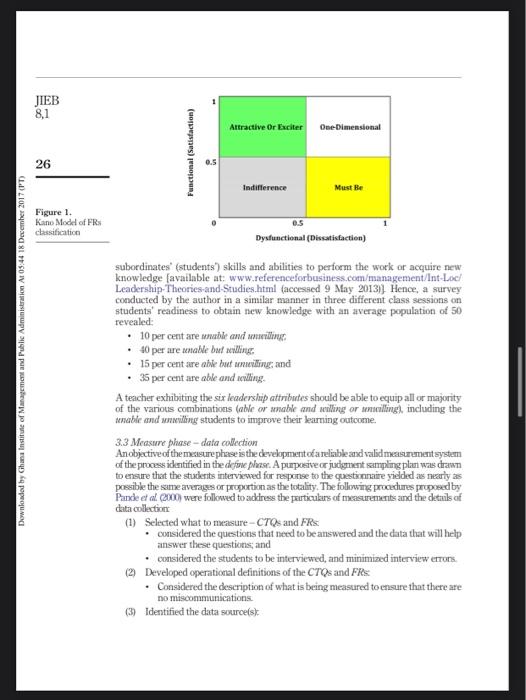
Question: kindly reviewed this article The current issue and full text archive of this journal is available de Emerald Insight at www.emeraldinsight.com/2016-469x.htm Downloaded by Ghana Institute
kindly reviewed this article
The current issue and full text archive of this journal is available de Emerald Insight at www.emeraldinsight.com/2016-469x.htm Downloaded by Ghana Institute of Management and Public Administratie Atos 44 18 December 2017 (PT) JIEB Improving learning outcome 8,1 using Six Sigma methodology Godson Tetteh 18 Ghana Institute of Management and Public Administration (GIMPA), Accra, Ghana Newb300 Red February 2014 Apted 1730 Abstract Purpose - The purpose of this research paper is to apply the Sax Sp methodology to identify the attributes of a lectures that will help impece a student's prior knowledge of a discipline from an initial Yowledge to a higher premtolewwindig Design/methodology/approach - The data collection method involved a conca in depth interview based on the Kano questionnaire with a sample of 170 undergraduate and graduate students aged between 3 and 40 years in two Glamin universities. The ano questionnaire contained the critical to quality (CTO) and the functional requirements (FR). The analytical Kano Kano) questionnaire was adopted for the purpose of improving leaming outcome with a student lecturer interaction. The CTOs in this study, from the customer student) perspective will correspond to Bloom's (1956) categories in the cognitive domain made up of remember, understand apply, analyze evaluate and create. The configuration index, which provides a decision factor for selecting the 25 FRs that centribute to improving kaming outcome made up of the American Society of Quality's six keadership cuerpetencies navigator, communicator, mente, amer, builder and motivator) and 19 attributes from previous research studies on service quality in higher education. This study used the varim and quartimax factor analysis rotation methods to get the principal company PC Findings - Out of the 25 FRs, four communicator, mentor, builder and motivator) of the American Soekty of Quality (ASQleadership competencies were found to be excites e attractive and when applied by the lectures would exceed customer student expectation Research limitations implications - The study involved only a judgment sample of 170 undergraduate and graduate students from two miversities drawn in Aara. Glanchence the outcome cannot be generalized to the entire student population in Ghana as a whole Practical implications - The Kuro results from this stady corroborates with previous finding that students perceive "Fostering of Team Work. Expertise in Other Subject As, Variety of Teching Method Friendliness and Humoras either excites attractive attributes Social implications - Some of the benefits from this study include the fact that lectures may improve classroom experience knowing what their students regard as satisfactory and dissatisfactory attributes or they may have a better understanding of the student's perspective. The concept of student satisfactice addressed in this study should there always been a means to an end, waththe end being the transformation of students Emerald Originality/value - This study contributes to the literature by camining bow the student's approach to leaming or acquiring new knew ledge has a significant elfect on the learning some using factor analysis rotatic methods to generate the PC and Keywords Six Sigtra methodology Student satisfaction. Educational services Effective and efficient lecturer. Factor analysis, Kanoe evaluation that Paper type Research paper Downloaded by Ghana Institute of Management and Public Administration A 05:44 18 December 2017 (PT) 1. Introduction Six Sigma Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology of defining measuring, analyzing, nonproeting methodology and controlling the quality in an institution's products, processes transactions and services so that the product or service quality and reliability meets and exceeds customer requirements. This research problem statement is defined as Dr Baker, a professor of physics at a university in the USA, confessed that when he entered the teaching profession, he had a set of attitudes toward instruction and student-university 19 teacher interaction. At the beginning of the semester, he would declare, in the presence of his students that only 50 per cent would pass his class and his predictions, most of the time, came true. Unfortunately, other university professors or teachers shared the same philosophy, and they would laugh over the number of their students who have failed in their respective classes. (Schuller, 1993). The research question is, do college professors or teachers have a role to play in the learning outcome or is the learning outcome the sole responsibility of the student? What are the attitudes of the umiversity teacher that will improve learning outcomes? This study contributes to literature by examining how the attitudes) of the university teacher has a significant effect on the leaming outcome using the Six Sigma methodology. In Six Sigma methodology, an effective quality management, is built on a foundational concept known as customer focus Identifying one's customers and understanding their expectations are fundamental to achieving customer satisfaction The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the American Society for Quality (ASQ) standardized offical definition of quality is the totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bears on its ability to satisfy given needs (Evans, 2012). Also quality has been defined as meeting or exceeding customer expectations. When an institution is operating in a total quality setting the customers define quality. Therefore, customer satisfaction must be the highest priority of the higher education institution. To understand this definition, one must first understand the meaning of the term "customer". The conceptual framework behind this definition requires an understanding and integration of many concepts and principles that are part of the total quality philosophy. Customer satisfaction is achieved by producing high quality products or services that meet or exceed expectations. For example, Watson (2003) and Narasimhan (2001) maintained that fee-paying students expect value for money and behave more like customers. Customer driven quality is fundamental to high performing organizations and institutions, Reliable customers are the most important customers. Customers who are satisfied with the quality of their purchases from an organization become reliable customers. Continual improvement is the only way to keep austomer satisfied and loyal. Arambewela et al (2005) and Maringe (2005) urged institutions that want to retain existing students, and recruit new students to regard students as customers in need of higher education services (Helgesen and Nesset, 2007). Hence, there is a need for university teachers to treat students as customers. If students are considered as customers, the university teacher must then meet or exceed their expectations to motivate them to acquire new knowledge. Because the customers (students) define quality and value, it is imperative to clearly identify the attributes for critical to quality [CTO) and Functional Requirements [FR] that provide satisfaction to the customer (student) when achieved fully, but do not cause dissatisfaction when not fulfilled. To JIEB 81 20 . Downed by Ghana Institute of Management and Public Administration At 05.44 18 December 2017 (PT) fulfill this requirement, we will use the Kano Model to explore the critical elements or attributes, CTQs and FR of a teacher that will help improve the learning outcome. The Kano Model theorized by Kano dal (1981) is one of the quality management tools used in many models of customer satisfaction. The model uniquely classifies product or service attributes based on how they are perceived by customers and their effect on customer satisfaction Kano et al. (1985) considered two aspects of any given quality attribute - an objective aspect involving the fulfillment of quality and a subjective aspect involving the customers' perception of satisfaction. Using this model, quality attributes can be divided into five categories as follows (1) Attractive quality attribute. An attribute that gives satisfaction if present but that produces no dissatisfaction if absent. (2) One-dimensional quality attribute. An attribute that is positively and linearly related to customer satisfaction that is the greater the degree of fulfillment of the attribute the greater the degree of customer satisfaction (3) Micr-de quality attribute . An attribute whose absence will result in customer dissatisfaction but whose presence does not significantly contribute to customes satisfaction (4) Indifferent quality attribute. An attribute whose presence or absence does not cause any satisfaction or dissatisfaction to customers (5) Kerese quality attribute. An attribute whose presence Giuses customer dissatisfaction and whose absence results in customer satisfaction It is assumed in this study that a university teacher needs to exhibit these attributes in the classroom to make an impact to improve learning outcome. We continue this paper by reviewing the literature on the students approach to learning, teachers approach to teaching, students treated as customers, leadership attributes and the Kano Model 2. Literature review Bloom et al. (1956) define knowledge involving the recall of specifics and universale; the recall of methods and processes of the recall of a pattern, structure or setting Bloom dal, 1956 p. 201). Bloom's Taxonomy has three classifications of domains that university teachers set as learning objectives for students to acquire knowledge. The three classifications or domains are cognitive domain, affective domain and psychomotor domain. The main objective or goal of university teachers is to equip the students to achieve these three main classifications or domains. Nonetheless, there are several studies on the teacher's approach to teaching (that is - how they teach) and the conceptions they hold about teaching (what they believe about teaching), and the approach to learning from the student's perspective which needs to be investigated. 2.1 Student's approach to learning A number of research studies have been carried out on learning styles -how adults learn, study preferences and how psychologists with an interest in learning styles have developed methods to help students and teachers. The most popular learning-style schemes include the Dunn and Dunn learning-styles model for example, as expressed by Dunn (1990), Kolb (1981, 1965) and Honey and Mumford (1992)]Pishler d al. (2008) concluded that there is no significant evidence base to the widespread "meshing Six Sigma methodology 21 Downloaded by Ghana Institute of Management and Public Administration At 05:44 18 December 2017 (PT) hypothesis, which implies a student will leam best if taught in ain) (audituey, vital tactile or kinesthetic) into the general educational practice. Notwithstanding, there is a major gap in most of these research cases, as a teacher assigned to teach a group of students has no control whatsoever on the selection of the students, whether they are visual, auditory or kinesthetic learners (Omrod, 2008). Most students in a tertiary institution may have acquired a minimum qualification to enable them to be admitted for a particular discipline. The Yale Graduate School (2013) Web site, for instance, offers advice to their teachers that college students enter our classrooms with a wide variety of learning styles. Teachers are therefore to determine their own "modality of learning method" and also assess their students learning styles to optimize the instructional methods Students have studied textbooks on their own without a teacher of teacher intervention and have been able to acquire the requisite knowledge in several disciplines, the author of this study is one of them. Is it possible for students to acquire new knowledge without a classroom teacher's intervention? Several papers have been written about how students' performances have been falling over the years (Ravitch (1995), Clift (2011), and Party (2011). Clift (2011), in "From Students, a Misplaced Sense of Entitlement". stated that students pass through a deeply flawed education system and they are only interested in what they can do to make the teachers give them a "pass. Notwithstanding, interventions made by teachers to improve learning outcome sometimes lead to undesirable results. For example, in an article published in The Chronide of Higher Education, Party (2011), vowed never to probe cheating in the classroom again, after his yearly teaching evaluations fell below average of 53 out of 7.0 and his yearly salary took a dive 22 Teacher's approach to teaching Researchers have investigated both qualitative and quantitative studies about teachers approach to teaching and the consequential students' approach to learning to improve learning outcome. Trgwell and Presses (1991). and Triguell et al. (1999) in their study concluded that so called 'deep' approach to teaching created awareness a student learning. However, a "surface approach teaching encourages students to memorize and recall the subject matter. The results of the qualitative study were used to establish the approaches to teaching inventory (Trigwell and Prosser, 1996; Prosser and Trigwell. 1999). The methodologies used by these teachers have some relationship with their conceptions of teaching (Trigwell and Prosset. 1999) and also to their perceptions of their teaching context (Drosser and Trigwell, 1997). Teachers who conceive learning as information accumulation to meet external demands also conceive teaching as transmitting information to students, and approach their teaching in terms of teacher focused strategies Conversely, teachers who conceive learning as developing and changing students' conceptions approach teaching in terms of helping students to develop and change their conceptions in a student-focused way (Prosser and Trigwell, 1998). However, Meyer and Malcolm (2006) have criticized "The Approaches to Teaching Inventory published by Trigwell et al. (1999) with the purpose of measuring the ways teachers approach their teaching and of exploring the way academics go about teaching in a specific context or subject as having serious and irreversible concerns with the rigor and the methodology employed in the psychometric development JIEB 8,1 22 2.3 Students treated as customers Gruber et al. (2010), in their research paper, treated students as customers in the service industry and stated that higher education institutions must focus more on meeting or exceeding students' (customers') expectation from a total quality management perspective. Also Harnash-Glezer and Meyer (1991) and Hill et al. (2003) have concluded the importance of the teaching staff and the quality of the teacher as important factors in the delivery of high-quality education. Correspondingly, Poxo Munoz et al. (2000) and Marzo-Navarro d al. (2006) conjectured that teaching staff are the main players in a university, and having the largest positive influence on student satisfaction. For this reason, the students' (customers') satisfaction in a university could be influenced by the quality and attitude of the teacher. Hence, in this study, the student is considered as a customer of the teacher. The teacher must meet or exceed the students' expectations to motivate them to acquire new knowledge Downloaded by Chania Institute of Management and Public Administration At 05:44 18 December 2017 (PT) 24 Leadersluip attributes Swanson et al . (2005), in their study, found that knowledgeable, empathetic, friendly, helpful , reliable, responsive and expressive attributes are some of the characteristics of an effective teacher Harrison and Killion (2007) have verified how teachers could exhibit leadership qualities to support school and student success, hence, teachers are expected to exhibit leadership qualities. Similarly, the American Society of Quality (ASQ, 2014) has summarized six leadership competencies or attributes (navigator, commenticator, mentor, learner, bilder and motivator) based on more than 50 authors thoughts on quality leadership (Hirzel, 2004) which will be investigated in this study. It is assumed in this study that a teacher needs to exhibit these six leadership attributes in the classroom to make an impact to improve learning outcome. The six leadership attributes or construct to be exhibited by the teacher are defined as (1) Navigator. To create a shared meaning and provide direction toward a vision, mission, goal or end-result for students. (2) Communicator: To effectively listen and articulate messages to provide shared meaning. (The teacher should break down barriers and foster open, honest and honorable communication with the students) (3) Mentor. To guide the students in their actions and be a role model including ethical decision-making (Learner. To continuously through his or her formal study and experience develop a personal knowledge, skills, abilities and capabilities of the students. 65 Builder: To establish learning processes and structures to allow for the achievement of goals and outcomes using all resources available. 6 Motivator. To influence students to take action in a desirable manner In support of our adaptation of these six leadership constructs, Clayson (1999) and Curran and Rosen (2006) have demonstrated the importance of the personality of the teacher as the strongest contributing factor of the student's evaluation of the teacher's teaching effectiveness. These six leadershup construct measures have a good theoretical foundation and a strong indication of construct validity and reliability (Delucchi, 2000, Moore and Kuol, 2007) Downloaded by Ghana Institute of Management and Public Administration A05:44 18 December 2017 (PT) To that end, the Kano Model (Kano et al, 1984) would be used in this study to reveal Six Sigma the preferred six leadership attributes (natrigator, communicator, mentor, Karner, builder methodology and motivator) of the teacher that needs to be exhibited in the classroom to improve the leaming outcome 25 Six Sigma methodology - the Kano Model The Kano Model is used to identify the critical elements or attributes, CTQs and FRX, of 23 a teacher that will help improve the learning Outcome. The traditional Kano Model (Kano et al., 1984) is an approximate estimate of the customer's satisfaction in relation to the service provided or performance level. Hence, it only allows attributes of qualitative assessment of the service provided (Wassenaar d al. 2x6). It will be convenient to incorporate quantitative measures to assign some sales in terms of the levels of customer satisfaction or dissatisfaction (Matzler and Hinterhuber, 1998). However, the resulting Kano category is still qualitative in nature, which could not precisely reflect the extent to which the customers are satisfied Berger et al, 1996). Hence, Xu et al. (2009), in an effort to address the inherent deficiencies of the traditional Kano et al. (1981) method, proposed an analytical Kano (A.Kano) Model with a focus on customer need analysis. The A Kano Model extends traditional Kano indices which are quantitative measurements of customer satisfaction derived from Kano questionnaires and surveys. Kano classifiers, which consist of a set of criteria to classify customer CTOs based on the Kano indices. The A Kano was adopted for the purpose of improving leaming outcome with a student-university teacher interaction. However, we do not agree that the importance of the FRs or the leadership attributes should be self stated. Our contribution to literature is to use the factor analysis method to determine the level of importance instead of the self-stated importance as stated by Xu et al. (2009). 3. Methodology This study replicates that of Xu et al's (2009) Kano indices model for quantification of customer satisfaction. Let denote the university students which is made up of students (respondents), so that = {ty-1.27]). The set of FRs is identified as F=V-1.27...). The respondents evaluations are denoted by (V1-1.2...10 as per the functional and dysfunctional forms of Kano Model questions for each respondent, is (V- 1.21.) ..the evalution (Vi-1.2[...] D is represented as efter where is the score given to an FR for the dysfunctional form question, y, is the score given to an FR for the functional form question, and, for we do not agree that it should be a self-stated importance, which is the respondent's perception or the importance of an FR. However, we assume, in this study, that the level of importance of the FR should be determined by the application of factor analysis (principal component technique). Based on the Kano Model, the FRs of each variable were initially classified using the functional and dysfunctional form of Kano questions) as exciter or attractive al must be (m. one-dimensional () and indifferent as depicted in Table L. For each variable, a contingency output was generated between functional and dysfunctional questions) and the frequencies of respondents summed according to the classification structure (where the letters represent the Kano customer groups). A Questionable Category will not be included in the averages, and a Reverse (R) category can be JIEB 8,1 24 Downloaded by Ghana Institute of Management and Public Administration AL 05:44 18 December 2017 (PT) transformed out of the category by reversing the sense of functional and dysfunctional of questions (Berger et al., 1993) 3.1 Developing Kano indices for quantifying customer satisfaction Following Gruber d al (2010), this study adopts a scoring scheme that defines customer's satisfaction (using functional questions and dissatisfaction using dysfunctional questions) as depicted in Table Il. The scale is designed to be asymmetric because positive answers are considered to be stronger responses than negative ones (Xu et al., 2009). 3.2 Identifying FR level of importance using factor analysis The level of importance of the FRs is determined in this study by the application of factor analysis (principal component technique). The level of importance of any component is observed in its egenvalue or the percentage of variance that it accounted for. Using the eigenvalue for establishing a cutoff is probably most reliable when the number of variables is between 20 and 50 (Hair & al. 2005). Hence, the highest component component 1) accounts for higher variations in the responses compared to all the other components (it has the highest eigenalue or percentagel. The second highest component accounts for the next larger variation in the responses and so on. Again, within each component are the identified variables whose importance is also measured by their correlation to that component. Hence, for each FR, the weight is determined as a product of the factor kadings and the variance accounted for by the associated component. The satisfaction and dissatisfaction of the FR is the product of that way Dysfunctional questions Like it Must be Tam Can live with Dislike it Functional question that way neutral it that way Like it that way Q E E E Must be that way R 1 1 1 M I am neutral R 1 1 1 Can live with it that way R 1 1 1 M Dislike it that way R R R R Notes E-exciteror attractive = obe-dimensional M=must be indifferent: R=reverse Questionable OZRZO Table 1 Kano evaluation table Sences for functional dysfunctional features Like it that way Must be that way I am rutal Table II. Can live with it that way Scores for functional Dislike it that way dysfunctional features Source: Xuet el 2009 Function form questions 1 05 0 -025 -0.5 Dysfunctional form questi -0.5 -0.25 0 05 1 Downloaded by Chana Institute of Management and Public Administration A 05:44 18 December 2017 (PT) the variable mean and its weight. Based on the study by Xu et al 2009), for each FR.the Six Sigma average level of satisfaction for the dysfunctional form question within the university methodology students s is defined as x, and the average level of satisfaction for the functional form question within the same university students sis defined as y, so that ***, and Y (1) 25 For each FR, the mean of the satisfaction (a) and dissatisfaction (x) is computed. This is however weighted by the level of importance associated with that functional variable. Multivariate factor analysis was used to identify the underlying evaluative dimensions for the weight we, of the level of importance. The use of factor analysis method demands the existence of correlation among the variables of interest and also the adequacy of the sample for the factors formed to account for higher variation in the variables. The high statistics of Bartlett's Test of Sphericity (1493.860) with the corresponding small significant value (0.0005) confirmed the existence of strong correlation among the responses, and the Kaiser-Meyer Olkin (KMO) statistics of 0.702 which is greater than 0.500 indicated a strong sampling adequacy and hence reliability of the data (sample) for the factor analysis technique The analysis was repeated for the dysfunctional form questions to identify the weight associated with the dysfunctional variables. The Bartlett's Test of Sphericity (2047.007) with the corresponding small significant value (0.0005) confirmed the existence of strong correlation among the responses and the KMO statistics of 0.737. Specific items that correlate highly are assumed to be a member of that broader dimension. These dimensions become composites of specific variables, which in turn, allow the dimensions to be interpreted and described. In this study, the principal objective is to identify the weight we associated with the FR (variables) and not to identify the factors that account for the variations in each variable (as explained in most factor analysis. This is more of a principal component analysis (because we are interested in the components formed and the correlated variables in each component). The functional component matrix identifies the set of variables that are highly correlated with the principal component formed. A FR variable can belong to only one principal component, and this is determined by its leading the FR variable is allocated to a component where the loading is the highest. The weight se of any variable is therefore the product of its loadings and the percentage variance (in decimals) of the principal components that it belongs to For each FR. the customer's average satisfaction dissatisfaction with respect to the functional/dysfunctional form question is computed, resulting in the data point XY) with respect to equation (1) and the Kano configuration index for each FRiscomputedas Exciter or Attractive, Must-be. One-dimensional e indifferent as depicted in Figure 1 based on a methodl proposed by Berger et al (1990) It has been speculated that a fairly large percentage of tertiary students in a class are only interested in acquiring the certificate and not necessarily acquiring knowledge during class sessions. A total of 50 graduate students were interviewed to determine the appropriateness of the six leadership constructas quality attributes an overwhelming majority concluded they were applicable. The situational leadership model suggested leadership styles may depend on the "readiness of JIEB 8,1 Attractive Or Exciter One Dimensional Functional (Satisfaction) 26 Indifference Must Be Figure 1. Kano Model of FR classification 0.5 Dysfunctional (Dissatisfaction) Downloaded by Chase Institute of Management and Public Administration At 05:44 18 December 2017 (IT) subordinates' (students') skills and abilities to perform the work or acquire new knowledge (available at: www.referenceforbusiness.com/management/Int-Loc/ Leadership Theories and Studies.html (accessed 9 May 2013)) Hence, a survey conducted by the author in a similar manner in three different class sessions on students' readiness to obtain new knowledge with an average population of 50 revealed 10 per cent are able and many 40 per are unable but willing 15 per cent are able buat semmiling, and 35 per cent are able and evilling A teacher exhibiting the six leadershup attributes should be able to equip all or majority of the various combinations Calle or unable and willing or millingincluding the unable and willing students to improve their leaming outcome 3.3 Measure phase - data collection An objective of the measure phase is the development of a reliable and valid measurement system of the process identified in the defore purse. A purposive or judgment sampling plan was drawn to ensure that the students interviewed for response to the questinnaire yielded as nearly as possible the same averages or proportion as the totality. The following procedures proposed by Pande et al. (2000) were followed to adiress the particulars of measurements and the details of data collection (1) Selected what to measure - CTQs and FRS . considered the questions that need to be answered and the data that will help answer these questions and considered the students to be interviewed, and minimized interview errors. (2) Developed operational definitions of the CTQ and FRS Considered the description of what is being measured to ensure that there are no miscommunications 3 Identified the data sources Six Sigma methodology 27 Downloaded by Ghana Institute of Management and Public Administration At05:44 18 December 2017 (PT) Considered where someone can obtain data and whether historical data can be used (4) Prepared the collection and sampling plan considered who will collect and compile the data and the tools that are necessary to capture the data and created a data-sampling plan that addresses any potential data integrity issues 6) Implemented and refined the measurement system Considered what could be done to assess an initial set of measures and procedures for collecting the data before expending a lot of resource collecting compiling questionable data As the data were collected and analyzed, an interpretative framework was constructed, so the sampling strategy changed from largely judgment to largely theoretical to build on the leaming theory (Marshall, 1996). The data collection involved an in-depth interview based on the Kano questionnaire with a sample of 170 undergraduate and graduate students aged between 25 to 40 years in two Ghanaian universities. The respondents were divided into two groups depending on their age and undergraduate or graduate levels, representing the two market segments (). Each respondent was required to respond to the Kano questionnaire with respect to every FR. The respondents were interviewed in classrooms and libraries and were not given any incentive for participation. The Kano questionnaire contained the CTQs and the 25 FRS. The CTO in this study from the customer's (student's) perspective will correspond to Bloom et el's (1956) categories in the cognitive domain (Anderson and Krathwohl, 2001) made up of remember, understand, apply, analar, caluate and create. The configuration index, which provides a decision factor for selecting the 25 FRs that contribute to improve the learning outcome are made up of the American Society of Quality's six leadership (teacher) attributes (natrigator.communicator, mentor, Iranner, builder and motivator) and 19 other attributes from previous research studies on service quality in higher education (Voss et al. 2007). For each teacher attribute in the Kano questionnaire, students had to respond to a question consisting of two parts for instance (1) "ti a teacher possesses good communication skills how do you feel (functional form of the question and (2) "If a teacher does not possess good communication skills, how do you feel? (Dysfunctional form of the question) For each question, respondents could then answer in five different ways following a five point Likert scale (Likert, 1902) I like it that way. (2) It must be that way: (3) I am neutral (6) I can live with it that way, and 5) I dislike it that way JIEB 8,1 28 Downloaded by Ghana Institute of Management and Public Administration AL 05:44 18 December 2017 (PT) The form of Kano questionnaire used in this survey is shown in Table III, including both the functional and dysfunctional forms. 3.4 Analyze phase - results and sensitieuty analysis This research study set out to identify the 25 FRs that contribute to improving learning outcomes from the perspective of the customer (students). We would like to test if the relationship between the 25 FR and the 6 Kano Classifications (exciter or attractive, must-br, one-dimensional, indifferent and reverse categories) are statistically significant in the sense that it is too strong to happen by chance. We applied the chi-square test to test the null hypothesis-indicating there is no relationship between the two (25FR and 6 Kano Classifications) categorical variables. The observed chi square - 2258.521 and purvaline -0.0005; hence, we have an overwhelming evidence that the 25 FR's are associated or related to the 6 Kano Classifications. The internal reliability tests indicated strong Cronbach alphas between 0.72 and 0.95 when the sample of 170 students was split randomly and recalculated This study used the varimax and quartimax factor analysis rotation methods to generate the principal components (PCs). For the first trial (Varinux Eigen), eigenvalues greater than 1.0 were selected to generate the PCs. Based on this rule, the functional questions form established 11 PCs with a cumulative variance of 666 per cent as depicted in Table AL The factor loadings are depicted in Table AV. For the second trial using the varimax method and restricting the number of principal components to 11. the data produced the same results as specified in the first trial depicted in Table Al Similar trials were conducted, varying the principal components to 7 and 13 for the varimax and quartimax factor analysis rotation methods, respectively, using the names Varimax 13. Varimax7. QuartimaxEigen. Quartimax13 and Quartimax7. A similar method was applied to the dysfunctional questions. The PCs after Varinax13 rotation are depicted in Table All. For the Varimax 13 rotation, two components (12 and 13) were included that had less than 1 eigenvalues even though the cumulative variance explained was 71.8 per cent. It will be recalled that only factors with latent roots or eigenalines greater than 1 are regarded as significant; those less than 1 are insignificant and disregarded (Hair et al, 2005), hence, Varimax!3 rotation method was disregarded, The PCs after Varimax7 rotation are depicted in Table Alll. The PCs after Quartimax Eigen, Quartimax 13 and Quartimax rotation extracts are depicted in Table AIV. I like it It must be l am I can live with I dislike it that way that way neutralit that way that way How do you feel if your teacher 1 Niger Provides direction toward your vision, mission and goal as a student (Functional form of question) DOES NOT provide direction toward your vision, Mission and goal as a student Dysfunctional form of question) Table III. Kano questionnaire The details of the PCs after QuartimaxEigen, Quartimax13, and Quartimax rotatica Six Sigma are similar to the results for the VarimaxEigen rotation method in Table Al methodology Notwithstanding, the varimax rotation method minimines the number of variables that have high loadings on each factor which satisfies our main objective and the quartimax Totation method merely minimizes the number of factors needed to explain each variable Hence, we settled on the Varimax Eigen rotation method factor loadings as depicted in Table AV. The component matrix in Table AV identifies the set of variables 29 that are highly correlated with the PC formed. A variable aan belong to only one PC and this is determined by its ladings. The FR variable is allocated to a component wherethe loading is the highest. The weight (w) of level of importance of any variable is therefore the product of its loadings and the percentage varance in decimals) of the PCs that it belongs to. For each FR, the mean of the satisfaction dissatisfaction (x) and the weight (10) of level of importance were computed, satisfying equation (): The Kano indices were computed to obtain the configuration index for each FR as exciter or attractive, must be one-dimensional or indifferent as depicted in Table AVI based on a model proposed by Berger et al. (1993). Our assumption of using the factor analysis method conformed to McNaught & al . (2007) testing the validity of the recovery assessment scale (RAS). McNaught et al. (2007) used the application of factor analysis with a rotation method to confirm the studies of Corrigan et al. (2001) that the factors of the RAS are consistent with the consumer literature can mental patient recovery. Downloaded by Chan Institute of Management and Public Administraties At 05:44 18 December 2017 (PT) 4. Conclusion The main purpose of this research study is to use the Six Sigma methodology to identify the 25 FRs that contributed to improve laiming outomne from the perspective of the customers (students). Out of the 25 FRS, four out of the six romicator, mentor, Older and motivator of the ASQ (2014) keaderslup attributes were found to be either exciters or attractive and when applied by the university teacher would exceed customer student) expectation Seven other FR from other studies were also found to exate the students However, nine other FRS - [that is, university teacher presenting information in a coherent way, ensures strict, firm and fair principles, practices and procedures understands and share the feelings of a student encourages team work and participation in class discussion; is willing to assist you when in need, isable to relate the course to practical issues, encourages students to ask good and tangible questions, is flexible (does not adhere to strict timeliness and focuses more on knowledge acquisition) are a must-be quality of a university teacher. These mest be qualities must be taken into consideration to avoid dissatisfaction of the students 4.1 Theoretical and practical implications This study examined how to identify the university teacher's attributes that need to be exhibited in the classroom to improve the leaming outcome from the perspective of the students. The Kano results also corroborate with previous findings that students perceive "Fostering of Team Work", "Expertise in Other Subject Areas", "Variety of Teaching Methods", "Friendliness" and "Humor" as Exciters or Attractive attributes (Gruber et al. 2010). University teachers may improve classroom experience knowing what their students regard as satisfactory and dissatisfactory attributes or they may have a better The current issue and full text archive of this journal is available de Emerald Insight at www.emeraldinsight.com/2016-469x.htm Downloaded by Ghana Institute of Management and Public Administratie Atos 44 18 December 2017 (PT) JIEB Improving learning outcome 8,1 using Six Sigma methodology Godson Tetteh 18 Ghana Institute of Management and Public Administration (GIMPA), Accra, Ghana Newb300 Red February 2014 Apted 1730 Abstract Purpose - The purpose of this research paper is to apply the Sax Sp methodology to identify the attributes of a lectures that will help impece a student's prior knowledge of a discipline from an initial Yowledge to a higher premtolewwindig Design/methodology/approach - The data collection method involved a conca in depth interview based on the Kano questionnaire with a sample of 170 undergraduate and graduate students aged between 3 and 40 years in two Glamin universities. The ano questionnaire contained the critical to quality (CTO) and the functional requirements (FR). The analytical Kano Kano) questionnaire was adopted for the purpose of improving leaming outcome with a student lecturer interaction. The CTOs in this study, from the customer student) perspective will correspond to Bloom's (1956) categories in the cognitive domain made up of remember, understand apply, analyze evaluate and create. The configuration index, which provides a decision factor for selecting the 25 FRs that centribute to improving kaming outcome made up of the American Society of Quality's six keadership cuerpetencies navigator, communicator, mente, amer, builder and motivator) and 19 attributes from previous research studies on service quality in higher education. This study used the varim and quartimax factor analysis rotation methods to get the principal company PC Findings - Out of the 25 FRs, four communicator, mentor, builder and motivator) of the American Soekty of Quality (ASQleadership competencies were found to be excites e attractive and when applied by the lectures would exceed customer student expectation Research limitations implications - The study involved only a judgment sample of 170 undergraduate and graduate students from two miversities drawn in Aara. Glanchence the outcome cannot be generalized to the entire student population in Ghana as a whole Practical implications - The Kuro results from this stady corroborates with previous finding that students perceive "Fostering of Team Work. Expertise in Other Subject As, Variety of Teching Method Friendliness and Humoras either excites attractive attributes Social implications - Some of the benefits from this study include the fact that lectures may improve classroom experience knowing what their students regard as satisfactory and dissatisfactory attributes or they may have a better understanding of the student's perspective. The concept of student satisfactice addressed in this study should there always been a means to an end, waththe end being the transformation of students Emerald Originality/value - This study contributes to the literature by camining bow the student's approach to leaming or acquiring new knew ledge has a significant elfect on the learning some using factor analysis rotatic methods to generate the PC and Keywords Six Sigtra methodology Student satisfaction. Educational services Effective and efficient lecturer. Factor analysis, Kanoe evaluation that Paper type Research paper Downloaded by Ghana Institute of Management and Public Administration A 05:44 18 December 2017 (PT) 1. Introduction Six Sigma Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology of defining measuring, analyzing, nonproeting methodology and controlling the quality in an institution's products, processes transactions and services so that the product or service quality and reliability meets and exceeds customer requirements. This research problem statement is defined as Dr Baker, a professor of physics at a university in the USA, confessed that when he entered the teaching profession, he had a set of attitudes toward instruction and student-university 19 teacher interaction. At the beginning of the semester, he would declare, in the presence of his students that only 50 per cent would pass his class and his predictions, most of the time, came true. Unfortunately, other university professors or teachers shared the same philosophy, and they would laugh over the number of their students who have failed in their respective classes. (Schuller, 1993). The research question is, do college professors or teachers have a role to play in the learning outcome or is the learning outcome the sole responsibility of the student? What are the attitudes of the umiversity teacher that will improve learning outcomes? This study contributes to literature by examining how the attitudes) of the university teacher has a significant effect on the leaming outcome using the Six Sigma methodology. In Six Sigma methodology, an effective quality management, is built on a foundational concept known as customer focus Identifying one's customers and understanding their expectations are fundamental to achieving customer satisfaction The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the American Society for Quality (ASQ) standardized offical definition of quality is the totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bears on its ability to satisfy given needs (Evans, 2012). Also quality has been defined as meeting or exceeding customer expectations. When an institution is operating in a total quality setting the customers define quality. Therefore, customer satisfaction must be the highest priority of the higher education institution. To understand this definition, one must first understand the meaning of the term "customer". The conceptual framework behind this definition requires an understanding and integration of many concepts and principles that are part of the total quality philosophy. Customer satisfaction is achieved by producing high quality products or services that meet or exceed expectations. For example, Watson (2003) and Narasimhan (2001) maintained that fee-paying students expect value for money and behave more like customers. Customer driven quality is fundamental to high performing organizations and institutions, Reliable customers are the most important customers. Customers who are satisfied with the quality of their purchases from an organization become reliable customers. Continual improvement is the only way to keep austomer satisfied and loyal. Arambewela et al (2005) and Maringe (2005) urged institutions that want to retain existing students, and recruit new students to regard students as customers in need of higher education services (Helgesen and Nesset, 2007). Hence, there is a need for university teachers to treat students as customers. If students are considered as customers, the university teacher must then meet or exceed their expectations to motivate them to acquire new knowledge. Because the customers (students) define quality and value, it is imperative to clearly identify the attributes for critical to quality [CTO) and Functional Requirements [FR] that provide satisfaction to the customer (student) when achieved fully, but do not cause dissatisfaction when not fulfilled. To JIEB 81 20 . Downed by Ghana Institute of Management and Public Administration At 05.44 18 December 2017 (PT) fulfill this requirement, we will use the Kano Model to explore the critical elements or attributes, CTQs and FR of a teacher that will help improve the learning outcome. The Kano Model theorized by Kano dal (1981) is one of the quality management tools used in many models of customer satisfaction. The model uniquely classifies product or service attributes based on how they are perceived by customers and their effect on customer satisfaction Kano et al. (1985) considered two aspects of any given quality attribute - an objective aspect involving the fulfillment of quality and a subjective aspect involving the customers' perception of satisfaction. Using this model, quality attributes can be divided into five categories as follows (1) Attractive quality attribute. An attribute that gives satisfaction if present but that produces no dissatisfaction if absent. (2) One-dimensional quality attribute. An attribute that is positively and linearly related to customer satisfaction that is the greater the degree of fulfillment of the attribute the greater the degree of customer satisfaction (3) Micr-de quality attribute . An attribute whose absence will result in customer dissatisfaction but whose presence does not significantly contribute to customes satisfaction (4) Indifferent quality attribute. An attribute whose presence or absence does not cause any satisfaction or dissatisfaction to customers (5) Kerese quality attribute. An attribute whose presence Giuses customer dissatisfaction and whose absence results in customer satisfaction It is assumed in this study that a university teacher needs to exhibit these attributes in the classroom to make an impact to improve learning outcome. We continue this paper by reviewing the literature on the students approach to learning, teachers approach to teaching, students treated as customers, leadership attributes and the Kano Model 2. Literature review Bloom et al. (1956) define knowledge involving the recall of specifics and universale; the recall of methods and processes of the recall of a pattern, structure or setting Bloom dal, 1956 p. 201). Bloom's Taxonomy has three classifications of domains that university teachers set as learning objectives for students to acquire knowledge. The three classifications or domains are cognitive domain, affective domain and psychomotor domain. The main objective or goal of university teachers is to equip the students to achieve these three main classifications or domains. Nonetheless, there are several studies on the teacher's approach to teaching (that is - how they teach) and the conceptions they hold about teaching (what they believe about teaching), and the approach to learning from the student's perspective which needs to be investigated. 2.1 Student's approach to learning A number of research studies have been carried out on learning styles -how adults learn, study preferences and how psychologists with an interest in learning styles have developed methods to help students and teachers. The most popular learning-style schemes include the Dunn and Dunn learning-styles model for example, as expressed by Dunn (1990), Kolb (1981, 1965) and Honey and Mumford (1992)]Pishler d al. (2008) concluded that there is no significant evidence base to the widespread "meshing Six Sigma methodology 21 Downloaded by Ghana Institute of Management and Public Administration At 05:44 18 December 2017 (PT) hypothesis, which implies a student will leam best if taught in ain) (audituey, vital tactile or kinesthetic) into the general educational practice. Notwithstanding, there is a major gap in most of these research cases, as a teacher assigned to teach a group of students has no control whatsoever on the selection of the students, whether they are visual, auditory or kinesthetic learners (Omrod, 2008). Most students in a tertiary institution may have acquired a minimum qualification to enable them to be admitted for a particular discipline. The Yale Graduate School (2013) Web site, for instance, offers advice to their teachers that college students enter our classrooms with a wide variety of learning styles. Teachers are therefore to determine their own "modality of learning method" and also assess their students learning styles to optimize the instructional methods Students have studied textbooks on their own without a teacher of teacher intervention and have been able to acquire the requisite knowledge in several disciplines, the author of this study is one of them. Is it possible for students to acquire new knowledge without a classroom teacher's intervention? Several papers have been written about how students' performances have been falling over the years (Ravitch (1995), Clift (2011), and Party (2011). Clift (2011), in "From Students, a Misplaced Sense of Entitlement". stated that students pass through a deeply flawed education system and they are only interested in what they can do to make the teachers give them a "pass. Notwithstanding, interventions made by teachers to improve learning outcome sometimes lead to undesirable results. For example, in an article published in The Chronide of Higher Education, Party (2011), vowed never to probe cheating in the classroom again, after his yearly teaching evaluations fell below average of 53 out of 7.0 and his yearly salary took a dive 22 Teacher's approach to teaching Researchers have investigated both qualitative and quantitative studies about teachers approach to teaching and the consequential students' approach to learning to improve learning outcome. Trgwell and Presses (1991). and Triguell et al. (1999) in their study concluded that so called 'deep' approach to teaching created awareness a student learning. However, a "surface approach teaching encourages students to memorize and recall the subject matter. The results of the qualitative study were used to establish the approaches to teaching inventory (Trigwell and Prosser, 1996; Prosser and Trigwell. 1999). The methodologies used by these teachers have some relationship with their conceptions of teaching (Trigwell and Prosset. 1999) and also to their perceptions of their teaching context (Drosser and Trigwell, 1997). Teachers who conceive learning as information accumulation to meet external demands also conceive teaching as transmitting information to students, and approach their teaching in terms of teacher focused strategies Conversely, teachers who conceive learning as developing and changing students' conceptions approach teaching in terms of helping students to develop and change their conceptions in a student-focused way (Prosser and Trigwell, 1998). However, Meyer and Malcolm (2006) have criticized "The Approaches to Teaching Inventory published by Trigwell et al. (1999) with the purpose of measuring the ways teachers approach their teaching and of exploring the way academics go about teaching in a specific context or subject as having serious and irreversible concerns with the rigor and the methodology employed in the psychometric development JIEB 8,1 22 2.3 Students treated as customers Gruber et al. (2010), in their research paper, treated students as customers in the service industry and stated that higher education institutions must focus more on meeting or exceeding students' (customers') expectation from a total quality management perspective. Also Harnash-Glezer and Meyer (1991) and Hill et al. (2003) have concluded the importance of the teaching staff and the quality of the teacher as important factors in the delivery of high-quality education. Correspondingly, Poxo Munoz et al. (2000) and Marzo-Navarro d al. (2006) conjectured that teaching staff are the main players in a university, and having the largest positive influence on student satisfaction. For this reason, the students' (customers') satisfaction in a university could be influenced by the quality and attitude of the teacher. Hence, in this study, the student is considered as a customer of the teacher. The teacher must meet or exceed the students' expectations to motivate them to acquire new knowledge Downloaded by Chania Institute of Management and Public Administration At 05:44 18 December 2017 (PT) 24 Leadersluip attributes Swanson et al . (2005), in their study, found that knowledgeable, empathetic, friendly, helpful , reliable, responsive and expressive attributes are some of the characteristics of an effective teacher Harrison and Killion (2007) have verified how teachers could exhibit leadership qualities to support school and student success, hence, teachers are expected to exhibit leadership qualities. Similarly, the American Society of Quality (ASQ, 2014) has summarized six leadership competencies or attributes (navigator, commenticator, mentor, learner, bilder and motivator) based on more than 50 authors thoughts on quality leadership (Hirzel, 2004) which will be investigated in this study. It is assumed in this study that a teacher needs to exhibit these six leadership attributes in the classroom to make an impact to improve learning outcome. The six leadership attributes or construct to be exhibited by the teacher are defined as (1) Navigator. To create a shared meaning and provide direction toward a vision, mission, goal or end-result for students. (2) Communicator: To effectively listen and articulate messages to provide shared meaning. (The teacher should break down barriers and foster open, honest and honorable communication with the students) (3) Mentor. To guide the students in their actions and be a role model including ethical decision-making (Learner. To continuously through his or her formal study and experience develop a personal knowledge, skills, abilities and capabilities of the students. 65 Builder: To establish learning processes and structures to allow for the achievement of goals and outcomes using all resources available. 6 Motivator. To influence students to take action in a desirable manner In support of our adaptation of these six leadership constructs, Clayson (1999) and Curran and Rosen (2006) have demonstrated the importance of the personality of the teacher as the strongest contributing factor of the student's evaluation of the teacher's teaching effectiveness. These six leadershup construct measures have a good theoretical foundation and a strong indication of construct validity and reliability (Delucchi, 2000, Moore and Kuol, 2007) Downloaded by Ghana Institute of Management and Public Administration A05:44 18 December 2017 (PT) To that end, the Kano Model (Kano et al, 1984) would be used in this study to reveal Six Sigma the preferred six leadership attributes (natrigator, communicator, mentor, Karner, builder methodology and motivator) of the teacher that needs to be exhibited in the classroom to improve the leaming outcome 25 Six Sigma methodology - the Kano Model The Kano Model is used to identify the critical elements or attributes, CTQs and FRX, of 23 a teacher that will help improve the learning Outcome. The traditional Kano Model (Kano et al., 1984) is an approximate estimate of the customer's satisfaction in relation to the service provided or performance level. Hence, it only allows attributes of qualitative assessment of the service provided (Wassenaar d al. 2x6). It will be convenient to incorporate quantitative measures to assign some sales in terms of the levels of customer satisfaction or dissatisfaction (Matzler and Hinterhuber, 1998). However, the resulting Kano category is still qualitative in nature, which could not precisely reflect the extent to which the customers are satisfied Berger et al, 1996). Hence, Xu et al. (2009), in an effort to address the inherent deficiencies of the traditional Kano et al. (1981) method, proposed an analytical Kano (A.Kano) Model with a focus on customer need analysis. The A Kano Model extends traditional Kano indices which are quantitative measurements of customer satisfaction derived from Kano questionnaires and surveys. Kano classifiers, which consist of a set of criteria to classify customer CTOs based on the Kano indices. The A Kano was adopted for the purpose of improving leaming outcome with a student-university teacher interaction. However, we do not agree that the importance of the FRs or the leadership attributes should be self stated. Our contribution to literature is to use the factor analysis method to determine the level of importance instead of the self-stated importance as stated by Xu et al. (2009). 3. Methodology This study replicates that of Xu et al's (2009) Kano indices model for quantification of customer satisfaction. Let denote the university students which is made up of students (respondents), so that = {ty-1.27]). The set of FRs is identified as F=V-1.27...). The respondents evaluations are denoted by (V1-1.2...10 as per the functional and dysfunctional forms of Kano Model questions for each respondent, is (V- 1.21.) ..the evalution (Vi-1.2[...] D is represented as efter where is the score given to an FR for the dysfunctional form question, y, is the score given to an FR for the functional form question, and, for we do not agree that it should be a self-stated importance, which is the respondent's perception or the importance of an FR. However, we assume, in this study, that the level of importance of the FR should be determined by the application of factor analysis (principal component technique). Based on the Kano Model, the FRs of each variable were initially classified using the functional and dysfunctional form of Kano questions) as exciter or attractive al must be (m. one-dimensional () and indifferent as depicted in Table L. For each variable, a contingency output was generated between functional and dysfunctional questions) and the frequencies of respondents summed according to the classification structure (where the letters represent the Kano customer groups). A Questionable Category will not be included in the averages, and a Reverse (R) category can be JIEB 8,1 24 Downloaded by Ghana Institute of Management and Public Administration AL 05:44 18 December 2017 (PT) transformed out of the category by reversing the sense of functional and dysfunctional of questions (Berger et al., 1993) 3.1 Developing Kano indices for quantifying customer satisfaction Following Gruber d al (2010), this study adopts a scoring scheme that defines customer's satisfaction (using functional questions and dissatisfaction using dysfunctional questions) as depicted in Table Il. The scale is designed to be asymmetric because positive answers are considered to be stronger responses than negative ones (Xu et al., 2009). 3.2 Identifying FR level of importance using factor analysis The level of importance of the FRs is determined in this study by the application of factor analysis (principal component technique). The level of importance of any component is observed in its egenvalue or the percentage of variance that it accounted for. Using the eigenvalue for establishing a cutoff is probably most reliable when the number of variables is between 20 and 50 (Hair & al. 2005). Hence, the highest component component 1) accounts for higher variations in the responses compared to all the other components (it has the highest eigenalue or percentagel. The second highest component accounts for the next larger variation in the responses and so on. Again, within each component are the identified variables whose importance is also measured by their correlation to that component. Hence, for each FR, the weight is determined as a product of the factor kadings and the variance accounted for by the associated component. The satisfaction and dissatisfaction of the FR is the product of that way Dysfunctional questions Like it Must be Tam Can live with Dislike it Functional question that way neutral it that way Like it that way Q E E E Must be that way R 1 1 1 M I am neutral R 1 1 1 Can live with it that way R 1 1 1 M Dislike it that way R R R R Notes E-exciteror attractive = obe-dimensional M=must be indifferent: R=reverse Questionable OZRZO Table 1 Kano evaluation table Sences for functional dysfunctional features Like it that way Must be that way I am rutal Table II. Can live with it that way Scores for functional Dislike it that way dysfunctional features Source: Xuet el 2009 Function form questions 1 05 0 -025 -0.5 Dysfunctional form questi -0.5 -0.25 0 05 1 Downloaded by Chana Institute of Management and Public Administration A 05:44 18 December 2017 (PT) the variable mean and its weight. Based on the study by Xu et al 2009), for each FR.the Six Sigma average level of satisfaction for the dysfunctional form question within the university methodology students s is defined as x, and the average level of satisfaction for the functional form question within the same university students sis defined as y, so that ***, and Y (1) 25 For each FR, the mean of the satisfaction (a) and dissatisfaction (x) is computed. This is however weighted by the level of importance associated with that functional variable. Multivariate factor analysis was used to identify the underlying evaluati