Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
let e = e(t) [C] be the temperature of a graphics processing unit (GPU), a component of a computer. the computations performed by the GPU
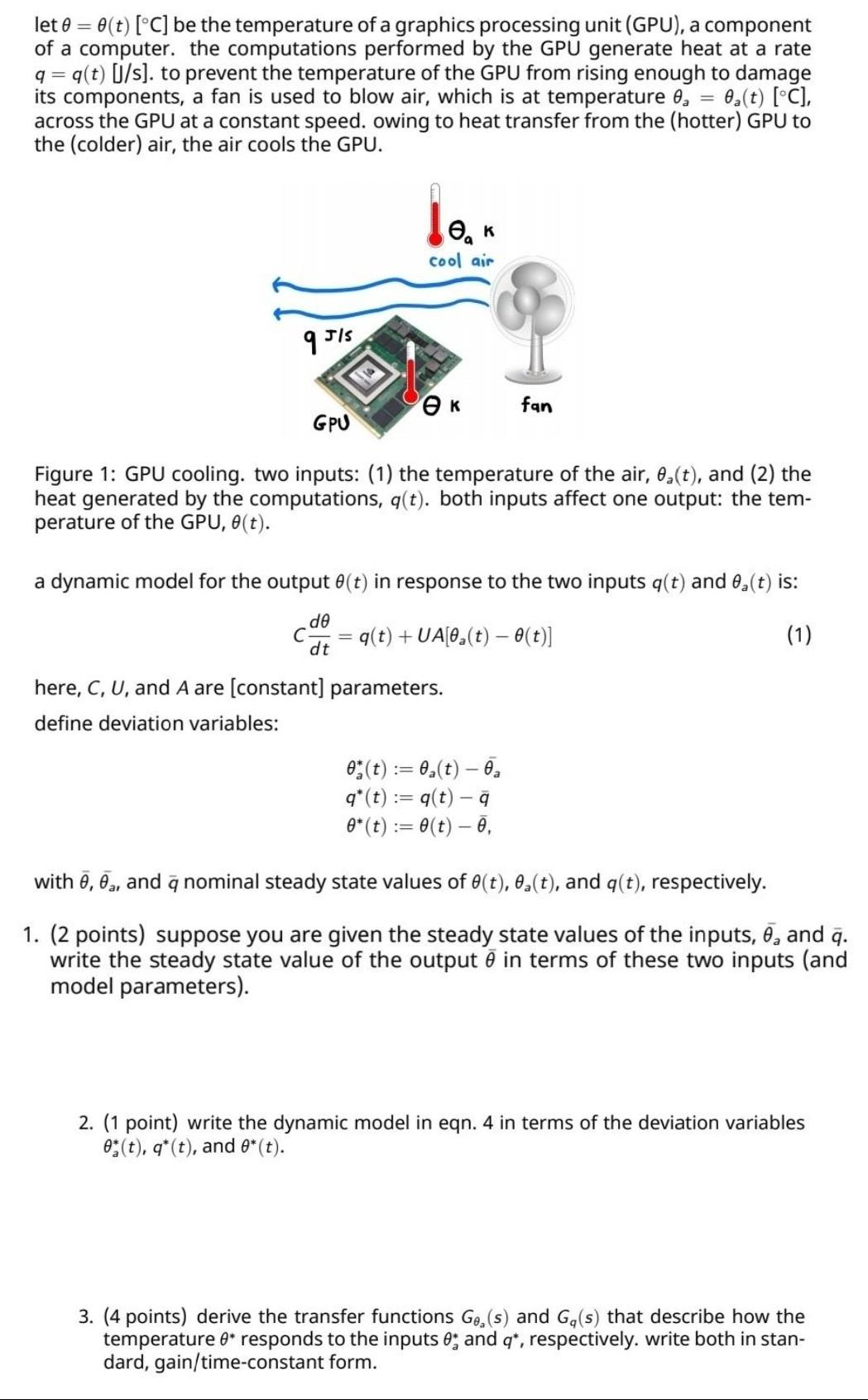
let e = e(t) [C] be the temperature of a graphics processing unit (GPU), a component of a computer. the computations performed by the GPU generate heat at a rate q=g(t) [/s]. to prevent the temperature of the GPU from rising enough to damage its components, a fan is used to blow air, which is at temperature , 0.(t) [C], across the GPU at a constant speed. owing to heat transfer from the (hotter) GPU to the (colder) air, the air cools the GPU. lear cool air 9 Jls fan GPU Figure 1: GPU cooling. two inputs: (1) the temperature of the air, 0.(t), and (2) the heat generated by the computations, q(t). both inputs affect one output: the tem- perature of the GPU, 0(t). a dynamic model for the output (t) in response to the two inputs q(t) and 0.(t) is: de dt q(t) + UA[0.(t)-0(t)] (1) here, C, U, and A are [constant] parameters. define deviation variables: 0 (t) := 0(t) - 2 q*(t) := g(t) - 9 0*(t) == 0(t) - 7, with 7, 7., and q nominal steady state values of (t), 0,(t), and qt), respectively. 9 1. (2 points) suppose you are given the steady state values of the inputs, 7, and q. write the steady state value of the output 7 in terms of these two inputs (and model parameters). 2. (1 point) write the dynamic model in eqn. 4 in terms of the deviation variables 0;(t), q*(t), and e*(t). 3. (4 points) derive the transfer functions Ge, (s) and G (s) that describe how the temperature 8* responds to the inputs e; and q*, respectively. write both in stan- dard, gain/time-constant form
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


