
need all parts please
this is all the information you you are given and ita all you should need
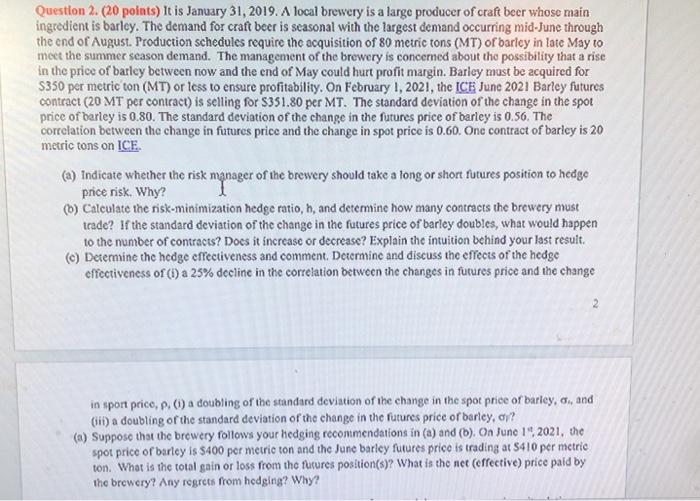
Question 2. (20 points) It is January 31, 2019. A local brewery is a large producer of craft beer whose main ingredient is barley. The demand for craft beer is seasonal with the largest demand occurring mid-June through the end of August. Production schedules require the acquisition of 80 metric tons (MT) of barley in late May to meet the summer season demand. The management of the brewery is concemed about the possibility that a rise in the price of barley between now and the end of May could hurt profit margin. Barley must be acquired for $350 per metric ton (MT) or less to ensure profitability. On February 1, 2021, the ICE June 2021 Barley futures contract (20 MT per contract) is selling for $351.80 per MT. The standard deviation of the change in the spot price of barley is 0.80. The standard deviation of the change in the futures price of bariey is 0.56. The correlation between the change in futures price and the change in spot price is 0.60. One contract of barley is 20 metric tons on ICE (a) Indicate whether the risk manager of the brewery should take a long or short futures position to hedge price risk. Why? 6) Calculate the risk-minimization hedge ratio, h, and determine how many contracts the brewery must trade? If the standard deviation of the change in the futures price of barley doubles, what would happen to the number of contracts? Does it increase or decrease? Explain the intuition behind your last result. (e) Determine the hedge effectiveness and comment. Determine and discuss the effects of the hedge effectiveness of (1) a 25% decline in the correlation between the changes in futures price and the change 2 in sport price, p. (i) a doubling of the standard deviation of the change in the spot price of barley, 0, and (ii) a doubling of the standard deviation of the change in the futures price of barley, or? (a) Suppose that the brewery follows your hedging recommendations in (a) and (b). On June 15,2021, the spot price of barley is $400 per metric ton and the Junc barley futures price is trading at $410 per metric ton. What is the total gain or loss from the futures position(s)? What is the net (effective) price paid by the brewery? Any regrets from hedging? Why? Question 2. (20 points) It is January 31, 2019. A local brewery is a large producer of craft beer whose main ingredient is barley. The demand for craft beer is seasonal with the largest demand occurring mid-June through the end of August. Production schedules require the acquisition of 80 metric tons (MT) of barley in late May to meet the summer season demand. The management of the brewery is concerned about tho possibility that a rise in the price of barley between now and the end of May could hurt profit margin. Barley must be acquired for S350 per metric ton (MT) or less to ensure profitability. On February 1, 2021, the ICE June 2021 Barley futures contract (20 MT per contract) is selling for S351.80 per MT. The standard deviation of the change in the spot price of barley is 0.80. The standard deviation of the change in the futures price of barley is 0.56. The correlation between the change in futures price and the change in spot price is 0.60. One contract of barley is 20 metric tons on ICE (2) Indicate whether the risk manager of the brewery should take a tong or short futures position to hedge e price risk. Why? ) Calculate the risk-minimization hedge ratio, n, and determine how many contracts the brewery must trade? If the standard deviation of the change in the futures price of barley doubles, what would happen 10 the number of contracts? Does it increase or decrease? Explain the intuition behind your last result (e) Determine the hedge effectiveness and comment. Determine and discuss the effects of the hedge effectiveness of (1) a 25% decline in the correlation between the changes in futures price and the change in spon price,p.) a doubling of the standard deviation of the change in the spot price of barley, o, and (it) a doubling of the standard deviation of the change in the futures price or barley, oy? (a) Suppose that the brewery follows your hedging recommendations in (a) and (b). On June 1", 2021, the spot price of barley is $400 per metric ton and the June barley futures price is trading at $410 per metric ton. What is the total gain or loss from the futures position(s)? What is the net (effective) price paid by the brewery? Any regrets from hedging? Why? Question 2. (20 points) It is January 31, 2019. A local brewery is a large producer of craft beer whose main ingredient is barley. The demand for craft beer is seasonal with the largest demand occurring mid-June through the end of August. Production schedules require the acquisition of 80 metric tons (MT) of barley in late May to meet the summer season demand. The management of the brewery is concemed about the possibility that a rise in the price of barley between now and the end of May could hurt profit margin. Barley must be acquired for $350 per metric ton (MT) or less to ensure profitability. On February 1, 2021, the ICE June 2021 Barley futures contract (20 MT per contract) is selling for $351.80 per MT. The standard deviation of the change in the spot price of barley is 0.80. The standard deviation of the change in the futures price of bariey is 0.56. The correlation between the change in futures price and the change in spot price is 0.60. One contract of barley is 20 metric tons on ICE (a) Indicate whether the risk manager of the brewery should take a long or short futures position to hedge price risk. Why? 6) Calculate the risk-minimization hedge ratio, h, and determine how many contracts the brewery must trade? If the standard deviation of the change in the futures price of barley doubles, what would happen to the number of contracts? Does it increase or decrease? Explain the intuition behind your last result. (e) Determine the hedge effectiveness and comment. Determine and discuss the effects of the hedge effectiveness of (1) a 25% decline in the correlation between the changes in futures price and the change 2 in sport price, p. (i) a doubling of the standard deviation of the change in the spot price of barley, 0, and (ii) a doubling of the standard deviation of the change in the futures price of barley, or? (a) Suppose that the brewery follows your hedging recommendations in (a) and (b). On June 15,2021, the spot price of barley is $400 per metric ton and the Junc barley futures price is trading at $410 per metric ton. What is the total gain or loss from the futures position(s)? What is the net (effective) price paid by the brewery? Any regrets from hedging? Why? Question 2. (20 points) It is January 31, 2019. A local brewery is a large producer of craft beer whose main ingredient is barley. The demand for craft beer is seasonal with the largest demand occurring mid-June through the end of August. Production schedules require the acquisition of 80 metric tons (MT) of barley in late May to meet the summer season demand. The management of the brewery is concerned about tho possibility that a rise in the price of barley between now and the end of May could hurt profit margin. Barley must be acquired for S350 per metric ton (MT) or less to ensure profitability. On February 1, 2021, the ICE June 2021 Barley futures contract (20 MT per contract) is selling for S351.80 per MT. The standard deviation of the change in the spot price of barley is 0.80. The standard deviation of the change in the futures price of barley is 0.56. The correlation between the change in futures price and the change in spot price is 0.60. One contract of barley is 20 metric tons on ICE (2) Indicate whether the risk manager of the brewery should take a tong or short futures position to hedge e price risk. Why? ) Calculate the risk-minimization hedge ratio, n, and determine how many contracts the brewery must trade? If the standard deviation of the change in the futures price of barley doubles, what would happen 10 the number of contracts? Does it increase or decrease? Explain the intuition behind your last result (e) Determine the hedge effectiveness and comment. Determine and discuss the effects of the hedge effectiveness of (1) a 25% decline in the correlation between the changes in futures price and the change in spon price,p.) a doubling of the standard deviation of the change in the spot price of barley, o, and (it) a doubling of the standard deviation of the change in the futures price or barley, oy? (a) Suppose that the brewery follows your hedging recommendations in (a) and (b). On June 1", 2021, the spot price of barley is $400 per metric ton and the June barley futures price is trading at $410 per metric ton. What is the total gain or loss from the futures position(s)? What is the net (effective) price paid by the brewery? Any regrets from hedging? Why
 need all parts please
need all parts please  this is all the information you you are given and ita all you should need
this is all the information you you are given and ita all you should need 





