Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1-2. Derive the relationships stated in Eqs. 1.6, 1.7, and 1.8. the two ends. As we will see, many of the limb movements of

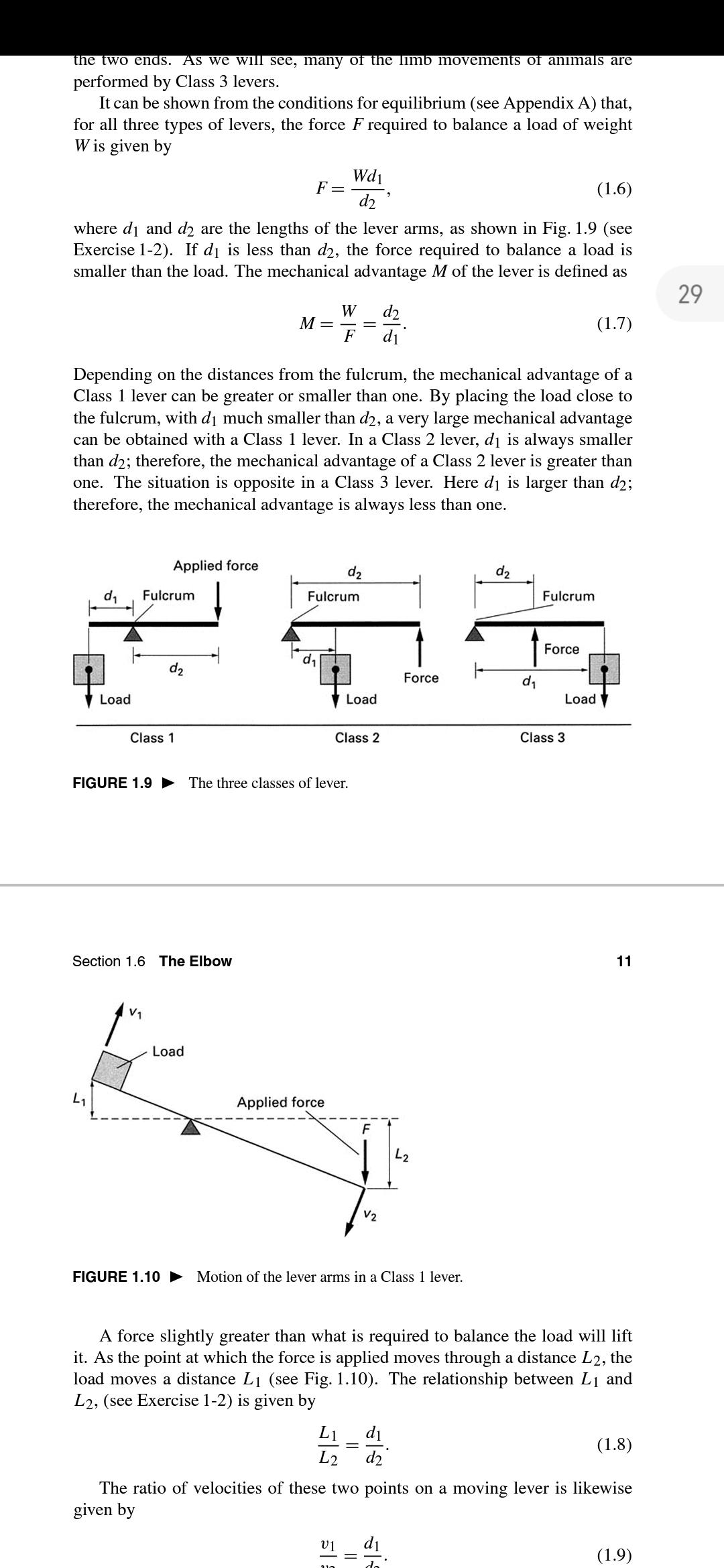
1-2. Derive the relationships stated in Eqs. 1.6, 1.7, and 1.8. the two ends. As we will see, many of the limb movements of animals are performed by Class 3 levers. It can be shown from the conditions for equilibrium (see Appendix A) that, for all three types of levers, the force F required to balance a load of weight W is given by Wdi F = d2 (1.6) where di and d2 are the lengths of the lever arms, as shown in Fig. 1.9 (see Exercise 1-2). If di is less than d2, the force required to balance a load is smaller than the load. The mechanical advantage M of the lever is defined as 29 d2 W M = F (1.7) di Depending on the distances from the fulcrum, the mechanical advantage of a Class 1 lever can be greater or smaller than one. By placing the load close to the fulcrum, with di much smaller than d2, a very large mechanical advantage can be obtained with a Class 1 lever. In a Class 2 lever, di is always smaller than d2; therefore, the mechanical advantage of a Class 2 lever is greater than one. The situation is opposite in a Class 3 lever. Here d is larger than d2; therefore, the mechanical advantage is always less than one. Applied force d2 Fulcrum Fulcrum Fulcrum Force d, d2 Force d, Load Load Load Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 FIGURE 1.9 > The three classes of lever. Section 1.6 The Elbow 11 V1 Load L1 Applied force L2 V2 FIGURE 1.10 > Motion of the lever arms in a Class 1 lever. A force slightly greater than what is required to balance the load will lift it. As the point at which the force is applied moves through a distance L2, the load moves a distance L1 (see Fig. 1.10). The relationship between L1 and L2, (see Exercise 1-2) is given by L1 di (1.8) L2 d2 The ratio of velocities of these two points on a moving lever is likewise given by (1.9)
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.44 Rating (147 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Derivation of equation 16 De...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Document Format ( 2 attachments)
635d8acc469a7_176584.pdf
180 KBs PDF File
635d8acc469a7_176584.docx
120 KBs Word File
Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


