Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Part A The equilibrium constant, K, of a reaction at a particular temperature is determined by the concentrations or pressures of the reactants and
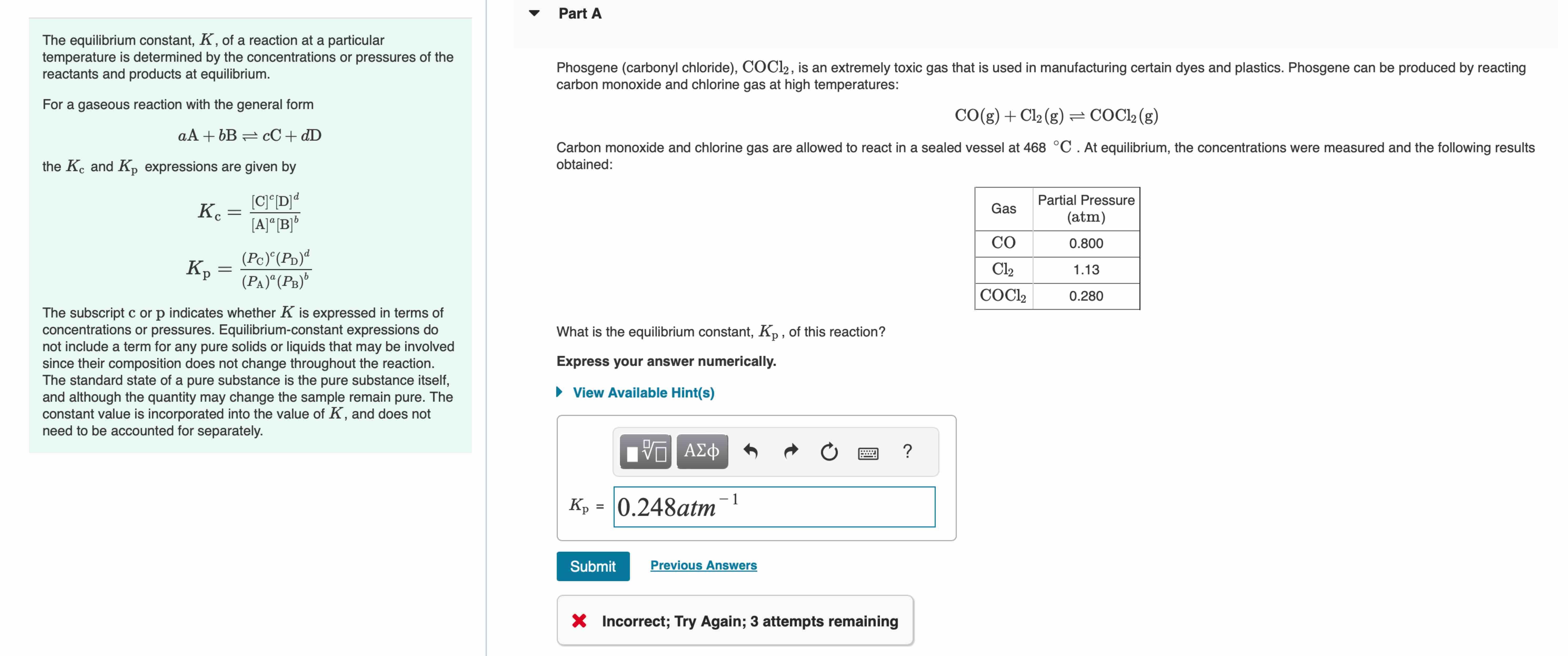
Part A The equilibrium constant, K, of a reaction at a particular temperature is determined by the concentrations or pressures of the reactants and products at equilibrium. For a gaseous reaction with the general form aA+bB = cC+dD the Kc and Kp expressions are given by Kc K = [C]c[D] d [A][B]b (Pc) (PD)d (PA)a (PB) The subscript c or p indicates whether K is expressed in terms of concentrations or pressures. Equilibrium-constant expressions do not include a term for any pure solids or liquids that may be involved since their composition does not change throughout the reaction. The standard state of a pure substance is the pure substance itself, and although the quantity may change the sample remain pure. The constant value is incorporated into the value of K, and does not need to be accounted for separately. Phosgene (carbonyl chloride), COC12, is an extremely toxic gas that is used in manufacturing certain dyes and plastics. Phosgene can be produced by reacting carbon monoxide and chlorine gas at high temperatures: CO(g) + Cl2(g) = COCl2(g) Carbon monoxide and chlorine gas are allowed to react in a sealed vessel at 468 C. At equilibrium, the concentrations were measured and the following results obtained: What is the equilibrium constant, Kp, of this reaction? Express your answer numerically. View Available Hint(s) 0 ? Gas Partial Pressure (atm) CO 0.800 Cl 1.13 COCl2 0.280 1 Kp = 0.248atm Submit Previous Answers Incorrect; Try Again; 3 attempts remaining
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


