please solve completely, clearly and with understandable solutions, PLEASEE
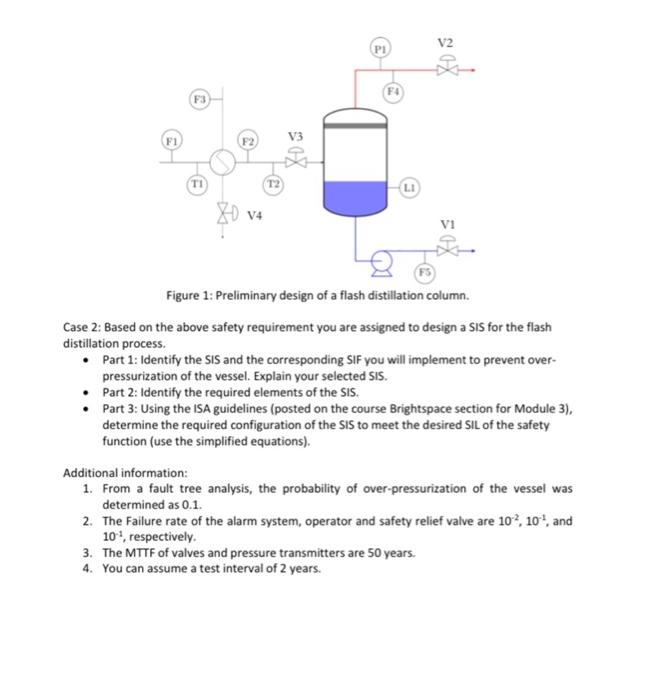
Case 1: Coseider the flash dict llation probiem as llustrated below. The liquid and vapor ander tonsiferation are farmable. A hich level of liquid in the vesel may tesult in overpressuriation of the vessel. - The following basic process control sptems are implemented in the proceis: Transmitter 11 measures the level and manbulates the outlet flow watve frake vi) to maintais the kevel 9. Transmitters F4 and P1 meapure the owerhead line fow and pressere respectively and masipulate the overhead ovtlet flow valve (watre vas to maritain the flow and pressure - A high-pressure alarm (not shown in the dagram) is also implemented to alet the operator to take appropriate action. - If the operator fails to respond, a presure relef walme is inutalied inot shome in the diagramb to release the materibk in the vassel to the atmosghere ind than grevent the vessel's failure. The management seecifies the safety taget level as the "probebility of rebase to the atmosohele to be not greater than 104 per vear". The release inta the atmosphere can cause Lerious permanent injury ta ote or more persont and can retult in the deuth of ene peras at well as causing temporary damage to the environment. The vessel is not holated, and slant personne! we aways exposed to possable accidents. There are no other meallerei in place 10 avoid or minimine the expasure of plant personnet. The frequency of the occumence of ralease an be considered low. can be considered low. - Part 1: Use the risk gaph method to determine the SIL requirement for the flash distiliation process. - Part 2- Use the 3-Dimensional risk matrix method to determine the Sil resuirement and compare it with that from the risk graph method. - Part 3: Draw an event tree to determine whether the exioting safety tystems meet the safety requirement of 'probabity of release to the atmosphere to be not peater than 10-4 per year'. - Part 4 : Draw a n event tree with an addtional StS with SIL obtained usire the rigk gragh or tisk matrix method to determine whether the modified process will meet the safuty requirement. - Part 5: Camment on whether a dike will be helplul to meet the salety requirement. Case 2: Based on the above salety requirment you are mucned to design a sis for the flant distiliation process. - Part 1: abentify the ses and the coriqupending sir your in inplenent ta provert ever pressurization of the wesel, Expleit your selected 515. - Part 2: isentify the required alements of the 515 . determine the required configuration of the SIS to meet the desired st of the sufety function fuse the sirpiled eauatisnd function zuse the simplitied equations). Additional infsmation: 1. From a fautt tree analyis, the probabilitr of over-pressuriation of the ressel =m. determined as b.1. 2. The failure rate of the alarm system, oserator and uafety relief walke are 102,102, and 10t, respettively. 3. The MTTt ef valves and presbure transmitten are so year. 4. You cin astume a teit interval of 2 years. ENGI 9121: Advanced Safety, Risk and Reliability Engineering Important points: - You can make appropriate assumptions about the data you believe missing as long as the assumptions are clearly stated. - Assignment due date: Thursday, February 23, 2023, at 11:59 PM NST Questions: Case 1: Consider the flash distillation problem as illustrated below. The liquid and vapor under consideration are flammable. A high level of liquid in the vessel may result in overpressurization of the vessel. - The following basic process control systems are implemented in the process: - Transmitter L1 measures the level and manipulates the outlet flow valve (valve V1) to maintain the level. Transmitters F4 and P1 measure the overhead line flow and pressure respectively and manipulate the overhead outlet flow valve (valve V2 ) to maintain the flow and pressure - A high-pressure alarm (not shown in the diagram) is also implemented to alert the operator to take appropriate action. - If the operator fails to respond, a pressure relief valve is installed (not shown in the diagram) to release the materials in the vessel to the atmosphere and thus prevent the vessel's failure. The management specifies the safety target level as the "probability of release to the atmosphere to be not greater than 104 per year". The release into the atmosphere can cause serious permanent injury to one or more persons and can result in the death of one person as well as causing temporary damage to the environment. The vessel is not isolated, and plant personnel are always exposed to possible accidents. There are no other measures in place to avoid or minimize the exposure of plant personnel. The frequency of the occurrence of release can be considered low. - Part 1: Use the risk graph method to determine the SIL requirement for the flash distillation process. - Part 2: Use the 3-Dimensional risk matrix method to determine the SIL requirement and compare it with that from the risk graph method. - Part 3: Draw an event tree to determine whether the existing safety systems meet the safety requirement of 'probability of release to the atmosphere to be not greater than 10-4 per year'. - Part 4: Draw an event tree with an additional SIS with SIL obtained using the risk graph or risk matrix method to determine whether the modified process will meet the safety requirement. - Part 5: Comment on whether a dike will be helpful to meet the safety requirement. Figure 1: Preliminary design of a flash distillation column. Case 2: Based on the above safety requirement you are assigned to design a SIS for the flash distillation process. - Part 1: Identify the SIS and the corresponding SIF you will implement to prevent overpressurization of the vessel. Explain your selected SIS. - Part 2: Identify the required elements of the SIS. - Part 3: Using the ISA guidelines (posted on the course Brightspace section for Module 3), determine the required configuration of the SIS to meet the desired SIL of the safety function (use the simplified equations). Additional information: 1. From a fault tree analysis, the probability of over-pressurization of the vessel was determined as 0.1. 2. The Failure rate of the alarm system, operator and safety relief valve are 102,101, and 101, respectively. 3. The MTTF of valves and pressure transmitters are 50 years. 4. You can assume a test interval of 2 years