Q4
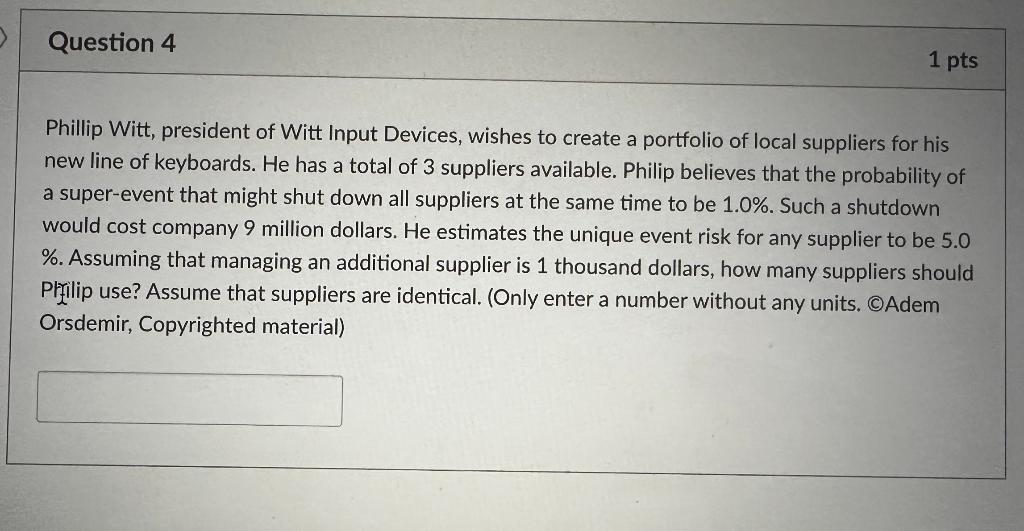
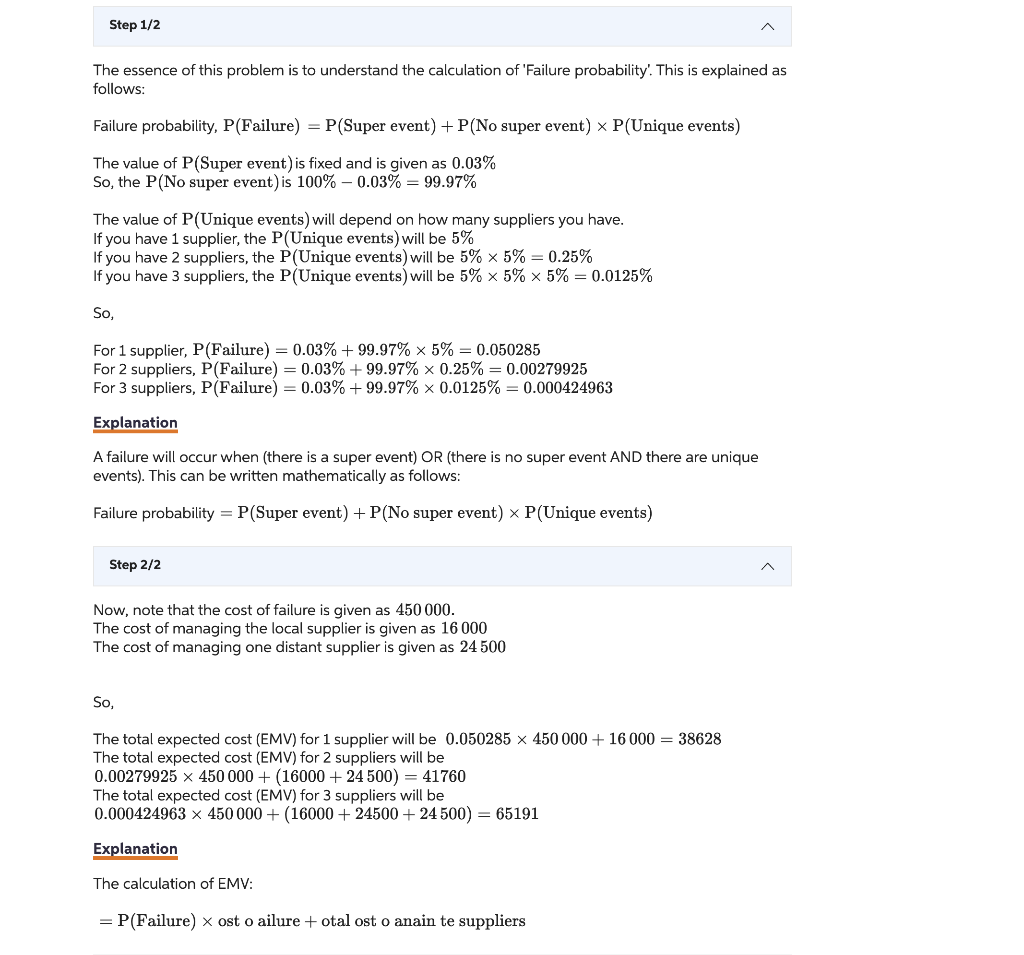
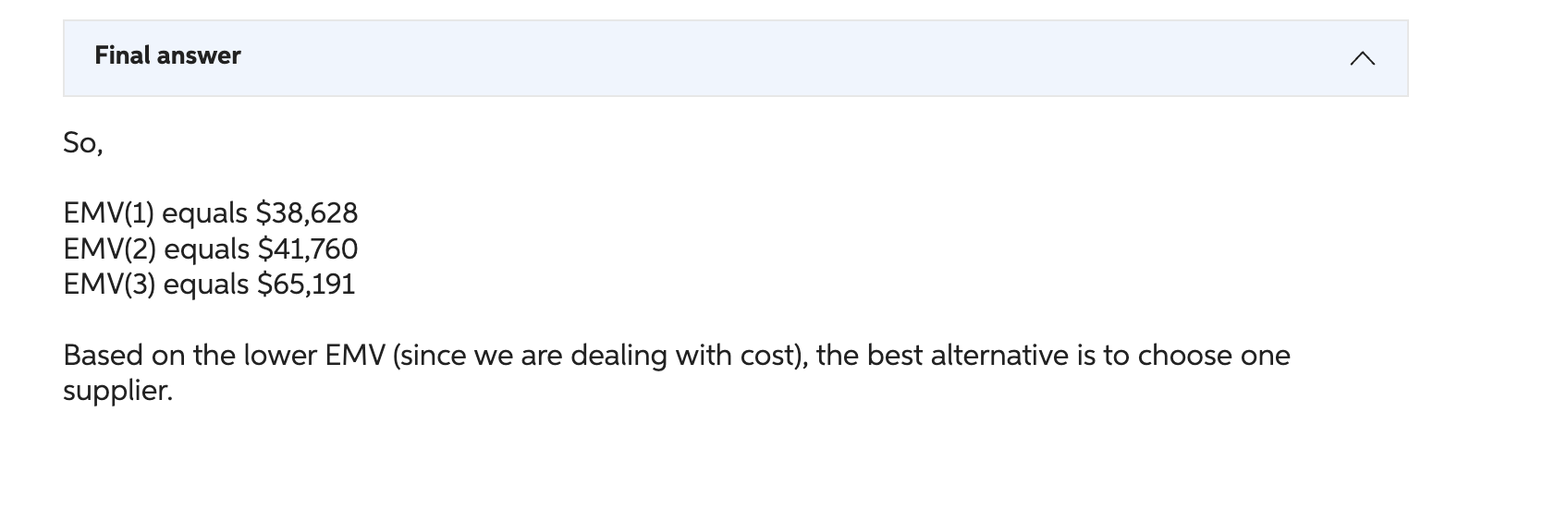
Phillip Witt, president of Witt Input Devices, wishes to create a portfolio of local suppliers for his new line of keyboards. He has a total of 3 suppliers available. Philip believes that the probability of a super-event that might shut down all suppliers at the same time to be 1.0%. Such a shutdown would cost company 9 million dollars. He estimates the unique event risk for any supplier to be 5.0 \%. Assuming that managing an additional supplier is 1 thousand dollars, how many suppliers should Prilip use? Assume that suppliers are identical. (Only enter a number without any units. (OAdem Orsdemir, Copyrighted material) Step 1/2 The essence of this problem is to understand the calculation of 'Failure probability'. This is explained as follows: Failure probability, P( Failure )=P( Super event )+P( No super event )P( Unique events ) The value of P (Super event) is fixed and is given as 0.03% So, the P (No super event) is 100%0.03%=99.97% The value of P (Unique events) will depend on how many suppliers you have. If you have 1 supplier, the P( Unique events) will be 5% If you have 2 suppliers, the P (Unique events) will be 5%5%=0.25% If you have 3 suppliers, the P (Unique events) will be 5%5%5%=0.0125% So, For 1 supplier, P( Failure )=0.03%+99.97%5%=0.050285 For 2 suppliers, P (Failure) =0.03%+99.97%0.25%=0.00279925 For 3 suppliers, P( Failure )=0.03%+99.97%0.0125%=0.000424963 Explanation A failure will occur when (there is a super event) OR (there is no super event AND there are unique events). This can be written mathematically as follows: Failure probability =P( Super event )+P( No super event )P( Unique events ) Step 2/2 Now, note that the cost of failure is given as 450000 . The cost of managing the local supplier is given as 16000 The cost of managing one distant supplier is given as 24500 So, The total expected cost (EMV) for 1 supplier will be 0.050285450000+16000=38628 The total expected cost (EMV) for 2 suppliers will be 0.00279925450000+(16000+24500)=41760 The total expected cost (EMV) for 3 suppliers will be 0.000424963450000+(16000+24500+24500)=65191 Explanation The calculation of EMV: =P( Failure ) ost o ailure + otal ost o anain te suppliers So, EMV(1) equals $38,628 EMV(2) equals $41,760 EMV(3) equals $65,191 Based on the lower EMV (since we are dealing with cost), the best alternative is to choose one supplier. Phillip Witt, president of Witt Input Devices, wishes to create a portfolio of local suppliers for his new line of keyboards. He has a total of 3 suppliers available. Philip believes that the probability of a super-event that might shut down all suppliers at the same time to be 1.0%. Such a shutdown would cost company 9 million dollars. He estimates the unique event risk for any supplier to be 5.0 \%. Assuming that managing an additional supplier is 1 thousand dollars, how many suppliers should Prilip use? Assume that suppliers are identical. (Only enter a number without any units. (OAdem Orsdemir, Copyrighted material) Step 1/2 The essence of this problem is to understand the calculation of 'Failure probability'. This is explained as follows: Failure probability, P( Failure )=P( Super event )+P( No super event )P( Unique events ) The value of P (Super event) is fixed and is given as 0.03% So, the P (No super event) is 100%0.03%=99.97% The value of P (Unique events) will depend on how many suppliers you have. If you have 1 supplier, the P( Unique events) will be 5% If you have 2 suppliers, the P (Unique events) will be 5%5%=0.25% If you have 3 suppliers, the P (Unique events) will be 5%5%5%=0.0125% So, For 1 supplier, P( Failure )=0.03%+99.97%5%=0.050285 For 2 suppliers, P (Failure) =0.03%+99.97%0.25%=0.00279925 For 3 suppliers, P( Failure )=0.03%+99.97%0.0125%=0.000424963 Explanation A failure will occur when (there is a super event) OR (there is no super event AND there are unique events). This can be written mathematically as follows: Failure probability =P( Super event )+P( No super event )P( Unique events ) Step 2/2 Now, note that the cost of failure is given as 450000 . The cost of managing the local supplier is given as 16000 The cost of managing one distant supplier is given as 24500 So, The total expected cost (EMV) for 1 supplier will be 0.050285450000+16000=38628 The total expected cost (EMV) for 2 suppliers will be 0.00279925450000+(16000+24500)=41760 The total expected cost (EMV) for 3 suppliers will be 0.000424963450000+(16000+24500+24500)=65191 Explanation The calculation of EMV: =P( Failure ) ost o ailure + otal ost o anain te suppliers So, EMV(1) equals $38,628 EMV(2) equals $41,760 EMV(3) equals $65,191 Based on the lower EMV (since we are dealing with cost), the best alternative is to choose one supplier









