Question
Question 2. Consider the state-transition-diagram for the Stop-and-Wait ARQ in Fig. 5.12. Assume that the transmission times of a frame and an ACK are t_f
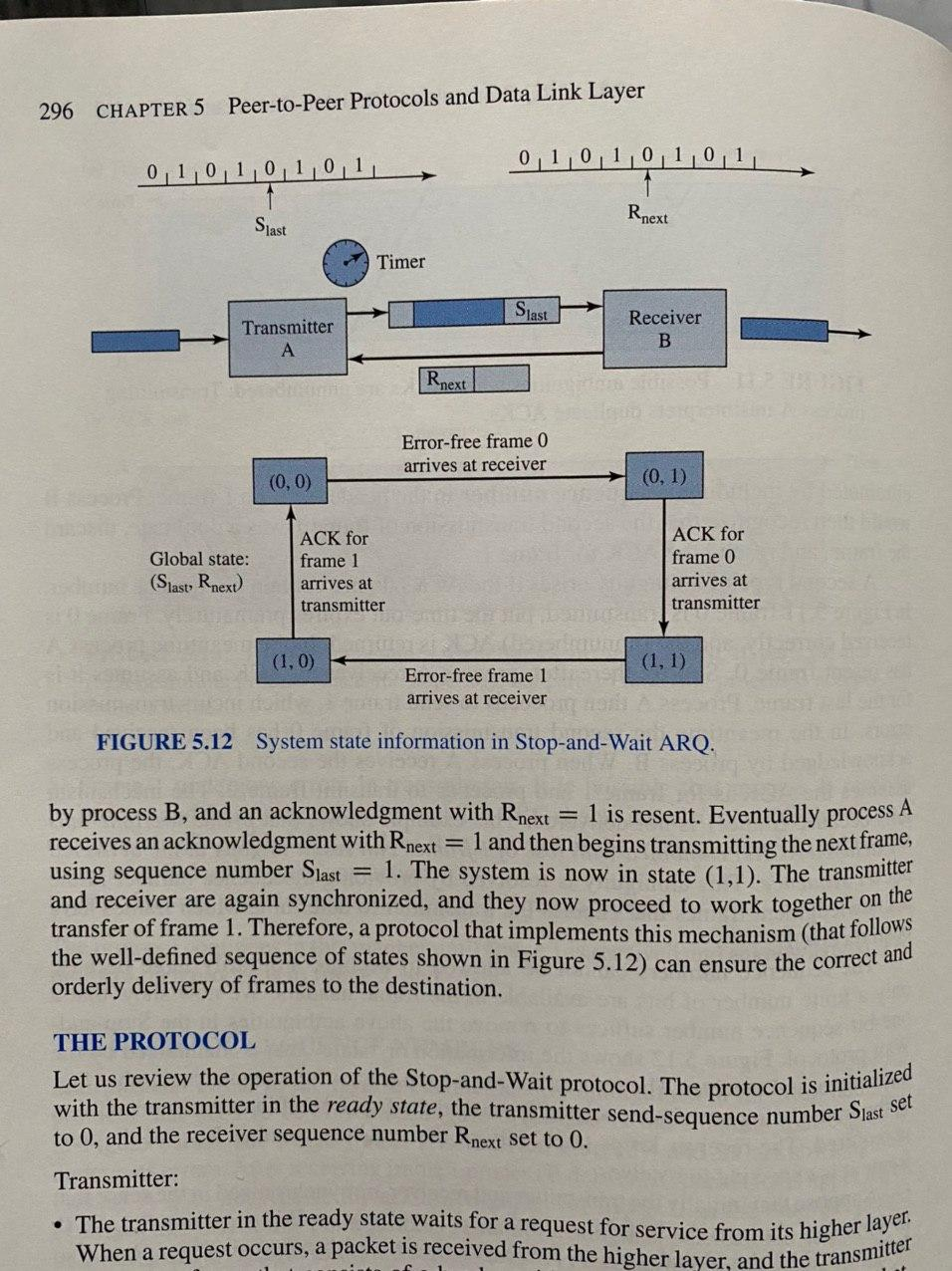 Question 2. Consider the state-transition-diagram for the Stop-and-Wait ARQ in Fig. 5.12. Assume that the transmission times of a frame and an ACK are t_f and t_a sec. respectively and processing and propagation delays are negligible. Let P_f denote the probability that an information frame will be received in error in a transmission and P_a probability that an ACK will be received in error. Determine, Probability distribution of the number of times that the frame will need to be transmitted for the system to make the transition from state (0, 0) to (0, 1). Probability distribution of the number of times that ACK will need to be transmitted for the system to make the transition from state (0, 0) to (1, 1). Average time that it will take for the system to make the transition from state (0, 0) to state (1, 1).
Question 2. Consider the state-transition-diagram for the Stop-and-Wait ARQ in Fig. 5.12. Assume that the transmission times of a frame and an ACK are t_f and t_a sec. respectively and processing and propagation delays are negligible. Let P_f denote the probability that an information frame will be received in error in a transmission and P_a probability that an ACK will be received in error. Determine, Probability distribution of the number of times that the frame will need to be transmitted for the system to make the transition from state (0, 0) to (0, 1). Probability distribution of the number of times that ACK will need to be transmitted for the system to make the transition from state (0, 0) to (1, 1). Average time that it will take for the system to make the transition from state (0, 0) to state (1, 1).
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


