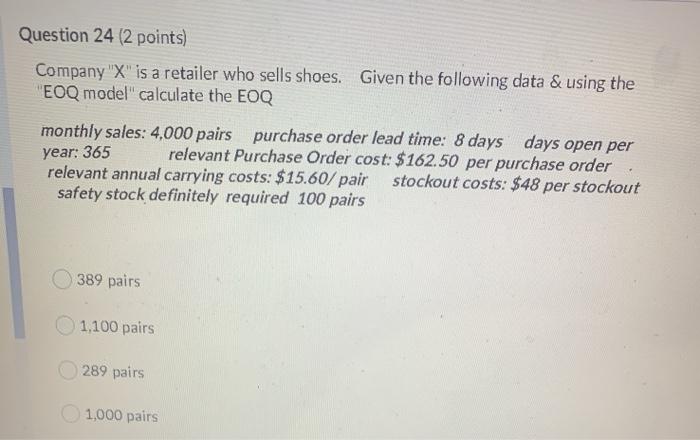
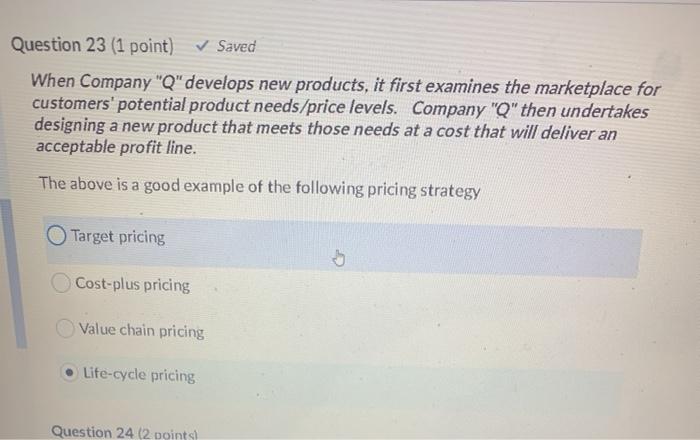
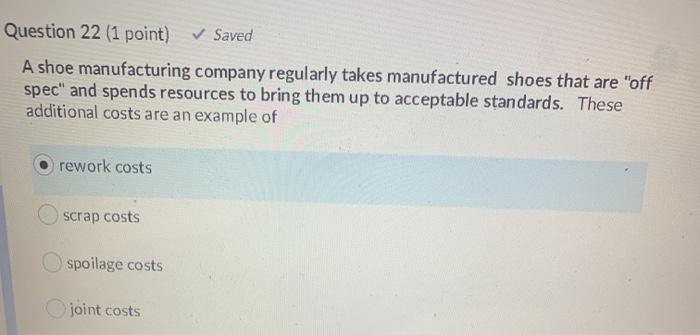
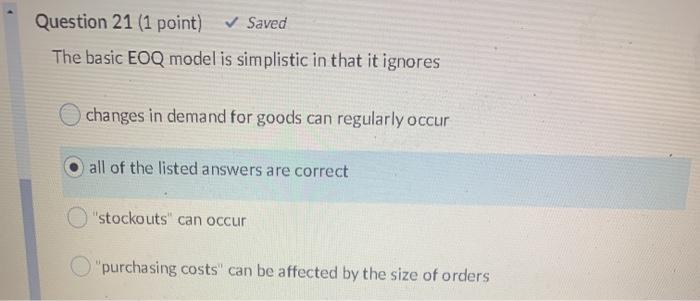
Question 24 (2 points) Company "X" is a retailer who sells shoes. Given the following data & using the "EOQ model calculate the EOQ monthly sales: 4,000 pairs purchase order lead time: 8 days days open per relevant Purchase Order cost: $162.50 per purchase order relevant annual carrying costs: $15.60/pair stockout costs: $48 per stockout safety stock definitely required 100 pairs year: 365 389 pairs 1,100 pairs 289 pairs 1,000 pairs Question 25 (2 points) In 2019, Company G sold 6,000 units for a total of $1.2 million in revenue. In 2020, Company G sold 7,000 units for a total of $1.26 million in revenue. Compared to 2019, 2020 had a "sales quantity variance of $1,000 U $1000 F $200,000 F $200,000 U Question 23 (1 point) Saved When Company "Q" develops new products, it first examines the marketplace for customers' potential product needs/price levels. Company "Q" then undertakes designing a new product that meets those needs at a cost that will deliver an acceptable profit line. The above is a good example of the following pricing strategy Target pricing Cost-plus pricing Value chain pricing Life-cycle pricing Question 24 (2 points Question 22 (1 point) Saved A shoe manufacturing company regularly takes manufactured shoes that are "off spec" and spends resources to bring them up to acceptable standards. These additional costs are an example of rework costs scrap costs spoilage costs joint costs Question 21 (1 point) Saved The basic EOQ model is simplistic in that it ignores changes in demand for goods can regularly occur all of the listed answers are correct "stockouts" can occur "purchasing costs" can be affected by the size of orders Question 20 (1 point) Saved The overall goal of "joint cost" allocation is to always allocate joint costs based on a mathematical formula provide managers with the necessary information to perform their their duties/responsibilities and those of their company always allocate joint costs based either on a "physical measure" method or "sales value at splitoft" method always allocate prices based on a mathematical formula Question 19 (1 point) Saved Life-cycle pricing strategies recognize BOTH "unit costs" and "selling prices" can change in either direction, over the life cycle of a product. True False