
 Question: Assume that in 2023 Johnny Bravo Company reported a pretax operating loss of P100,000. There were no other temporary or permanent differences in tax and book income for 2023. Prepare the journal entry to record income tax expense for 2023. It is probable that Johnny Bravo Company will return to profitability in 2024. (With solutions)
Question: Assume that in 2023 Johnny Bravo Company reported a pretax operating loss of P100,000. There were no other temporary or permanent differences in tax and book income for 2023. Prepare the journal entry to record income tax expense for 2023. It is probable that Johnny Bravo Company will return to profitability in 2024. (With solutions)
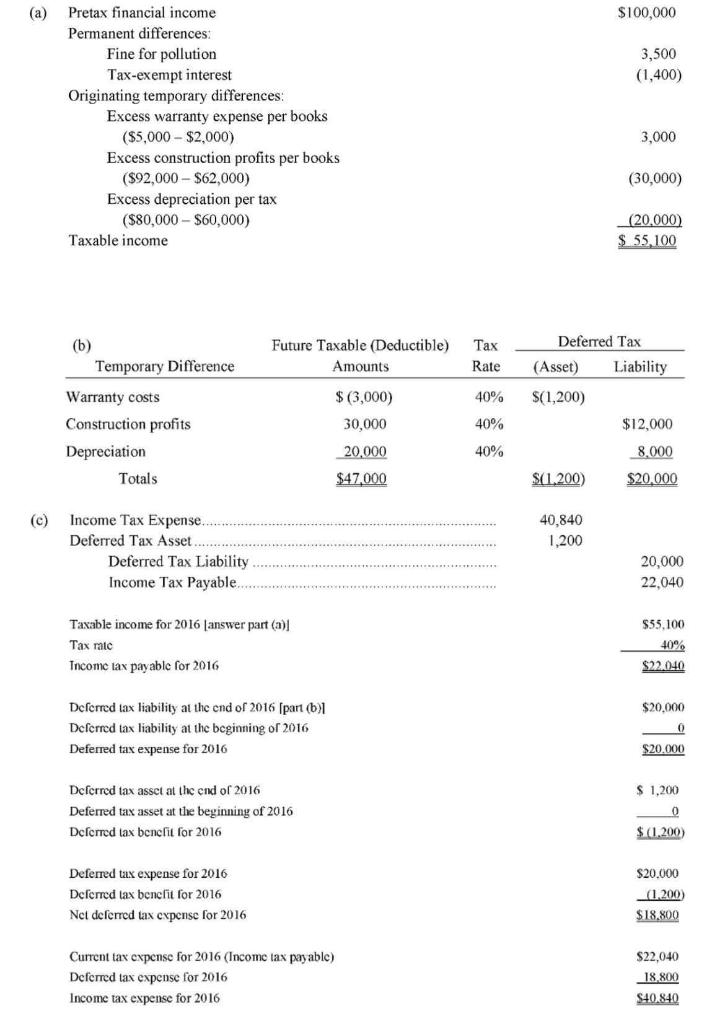
Johnny Bravo Company began operations in 2016 and has provided the following information. Pretax financial income for 2016 is $100,000. The tax rate enacted for 2016 and future years is 40%. Differences between the 2016 income statement and tax return are listed below: Warranty expense accrued for financial reporting purposes amounts to $5,000. Warranty deductions per the tax return amount to $2,000. Gross profit on construction contracts using the percentage-of-completion method for book purposes amounts to $92,000. Gross profit on construction contracts for tax purposes amounts to $62,000. Depreciation of property, plant, and equipment for financial reporting purposes amounts to $60,000. Depreciation of these assets amounts to $80,000 for the tax return. A $3,500 fine paid for violation of pollution laws was deducted in computing pretax financial income. Interest revenue earned on an investment in tax-exempt municipal bonds amounts to $1,400. Taxable income is expected for the next few years. (a) $100,000 3,500 (1,400) Pretax financial income Permanent differences: Fine for pollution Tax-exempt interest Originating temporary differences: Excess warranty expense per books ($5,000 - $2,000) Excess construction profits per books ($92,000 - $62,000) Excess depreciation per tax ($80,000 - $60,000) Taxable income 3,000 (30,000) (20.000) $ 55,100 (b) Temporary Difference Future Taxable (Deductible) Amounts Tax Rate Deferred Tax (Asset) Liability 40% $(1,200) $ (3,000) 30,000 40% $12,000 Warranty costs Construction profits Depreciation Totals 20,000 40% 8.000 $47.000 $(1.200) $20.000 (c) 40,840 1,200 Income Tax Expense. Deferred Tax Asset Deferred Tax Liability Income Tax Payable... 20,000 22.040 Taxable income for 2016 (answer part (a) Tax rate Income tax payable for 2016 $55.100 40% $22.040 $20.000 Deferred tax liability at the end of 2016 (part (b)| Deferred tax liability at the beginning of 2016 Deferred tax expense for 2016 0 $20.000 Deferred tax asset at the end of 2016 Deferred tax asset at the beginning of 2016 Deferred lax bencfit for 2016 $ 1,200 0 $ (1.200) Deferred tax expense for 2016 Deferred lax benefit for 2016 Net deferred tax expense for 2016 $20.000 (1.200) $18.800 $22,040 Current tax expense for 2016 (Income tax payable) Deferred tax expense for 2016 Income tax expense for 2016 18.800 S40.840 (d) $100,000 Income before income taxes Income tax expense Current Deferred $22.040 18.800 40.840 $ 59.160 Net income


 Question: Assume that in 2023 Johnny Bravo Company reported a pretax operating loss of P100,000. There were no other temporary or permanent differences in tax and book income for 2023. Prepare the journal entry to record income tax expense for 2023. It is probable that Johnny Bravo Company will return to profitability in 2024. (With solutions)
Question: Assume that in 2023 Johnny Bravo Company reported a pretax operating loss of P100,000. There were no other temporary or permanent differences in tax and book income for 2023. Prepare the journal entry to record income tax expense for 2023. It is probable that Johnny Bravo Company will return to profitability in 2024. (With solutions)





