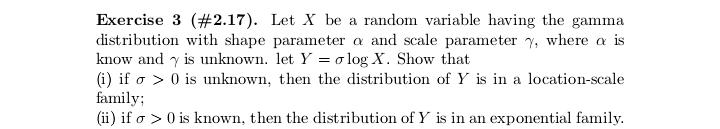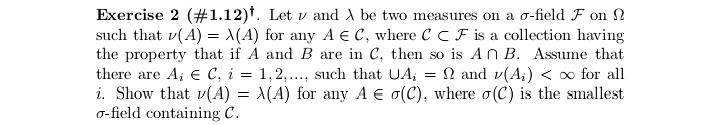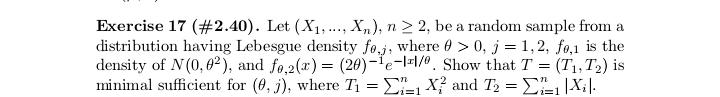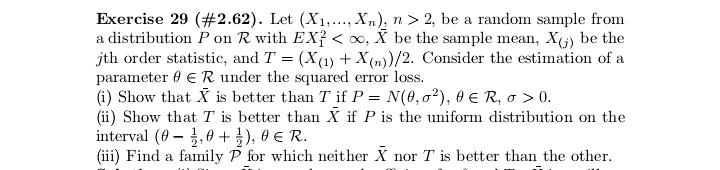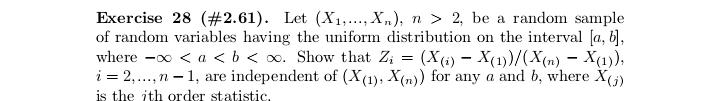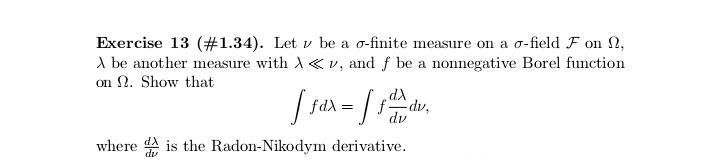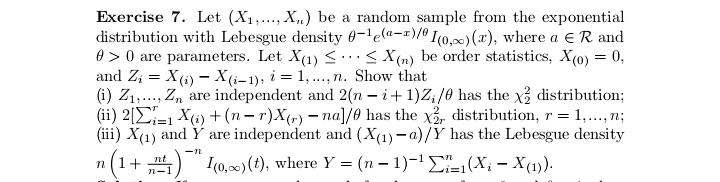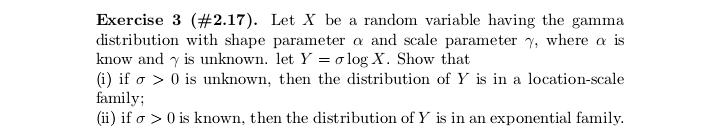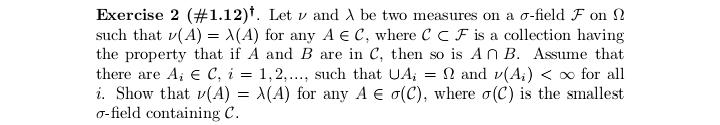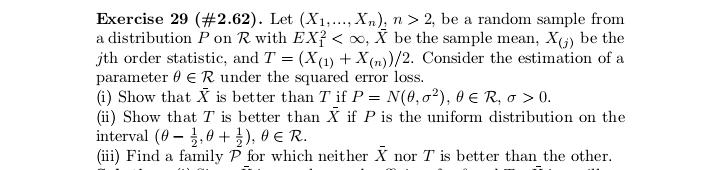

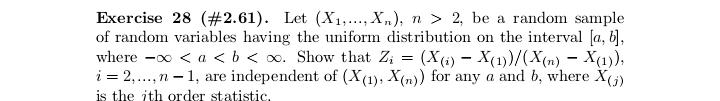
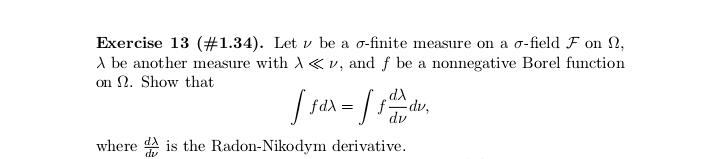

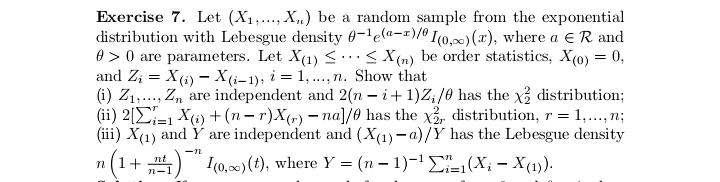
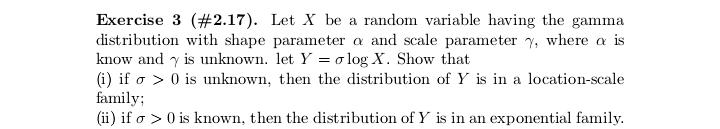

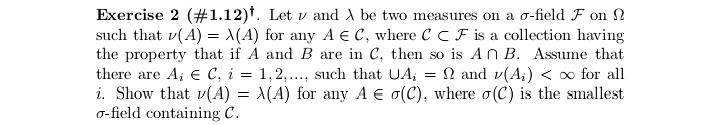
Statistics and probability, help.
Exercise 17 (#2.40). Let (X1. .... X,), n > 2, be a random sample from a distribution having Lebesgue density fo,,, where # > 0, j = 1, 2, fo,1 is the density of N(0, 02), and fo.2(x) = (20)-le-Izl/". Show that T = (Ti, T2 ) is minimal sufficient for (0, j), where 71 = SR, X? and 72 = CM, Xil.Exercise 29 (#2.62). Let (X1...., X,), n > 2, be a random sample from a distribution Pon R with EX? 0. (ii) Show that T is better than X if P is the uniform distribution on the interval (8 - 3.0 + }), DER. (iii) Find a family P for which neither X nor T is better than the other.Exercise 13 (#2.30). Let X and Y be two random variables such that Y has the binomial distribution with size / and probability # and, given Y = y, X has the binomial distribution with size y and probability p. (i) Suppose that p E (0, 1) and # 6 (0, 1) are unknown and N is known. Show that (X, Y) is minimal sufficient for (p. "). (ii) Suppose that a and N are known and p e (0, 1) is unknown. ShowExercise 28 (#2.61). Let (X1,.... X,), n > 2, be a random sample of random variables having the uniform distribution on the interval [o, b], where -co 1; (ii) any estimator of the form X + b is inadmissible, where b / 0 is a constant.Exercise 7. Let (X1..... X,,) be a random sample from the exponential distribution with Lebesgue density (-le(@-?)/0,3) (x), where a e R and d >0 are parameters. Let X() 0 is unknown, then the distribution of Y is in a location-scale family; (ii) if o > 0 is known, then the distribution of Y is in an exponential family.Exercise 25 (#2.56). Suppose that (X1, Yi). . ... (Xn, Y,) are indepen dent and identically distributed random 2-vectors and X, and Y, are in- dependently distributed as N(u, of ) and N(A, ov), respectively, with 8 = (M. OK. Of) E R x (0, co) x (0, co). Let X and So be the sample mean and variance for Xy's and Y and So be the sample mean and variance for Y's. Show that T = (X, Y, S, S ) is minimal sufficient for # but T is not boundedly complete.Exercise 2 (#1.12)'. Let v and A be two measures on a o-field F on ! such that v( A) = A(A) for any A e C, where C C F is a collection having the property that if A and B are in C, then so is An B. Assume that there are A; E C, i = 1, 2...., such that UA, = 0 and (A,)