Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
System of equilibrium equations: Forces acting on Gears T = Ft xr Fitano cos Fa= Fttan Fcoso Fr FBD: = - Ft cos Forces

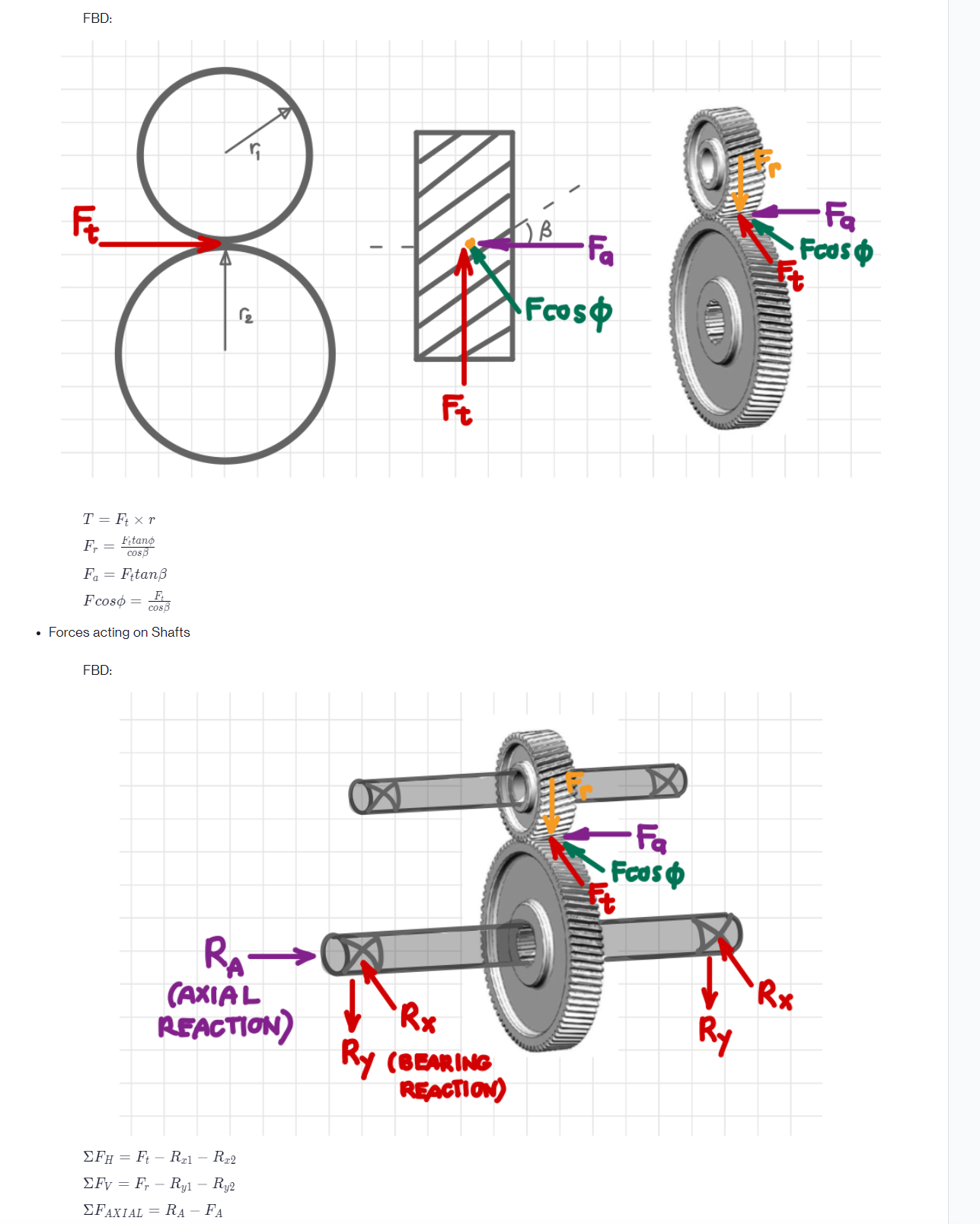

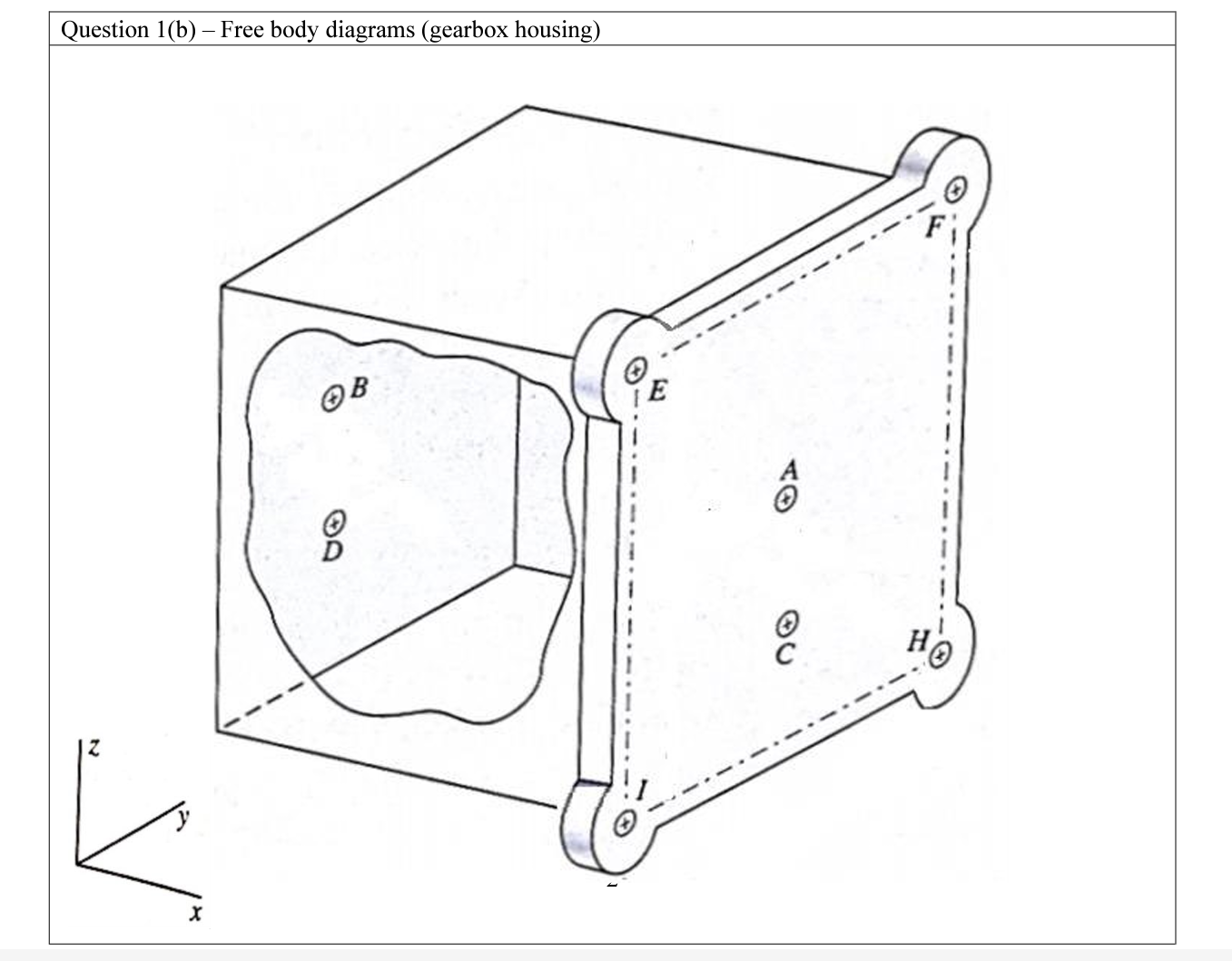
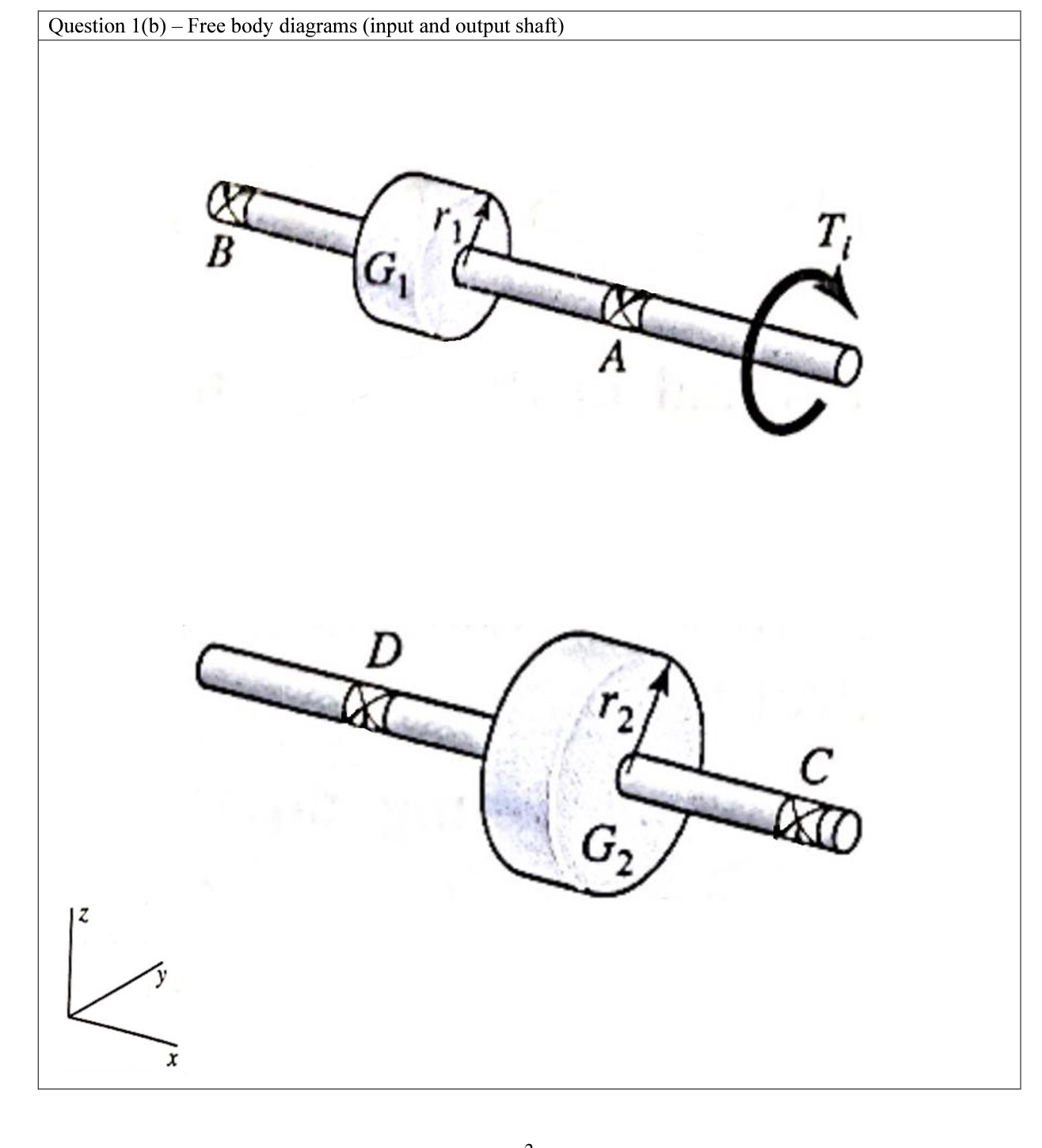
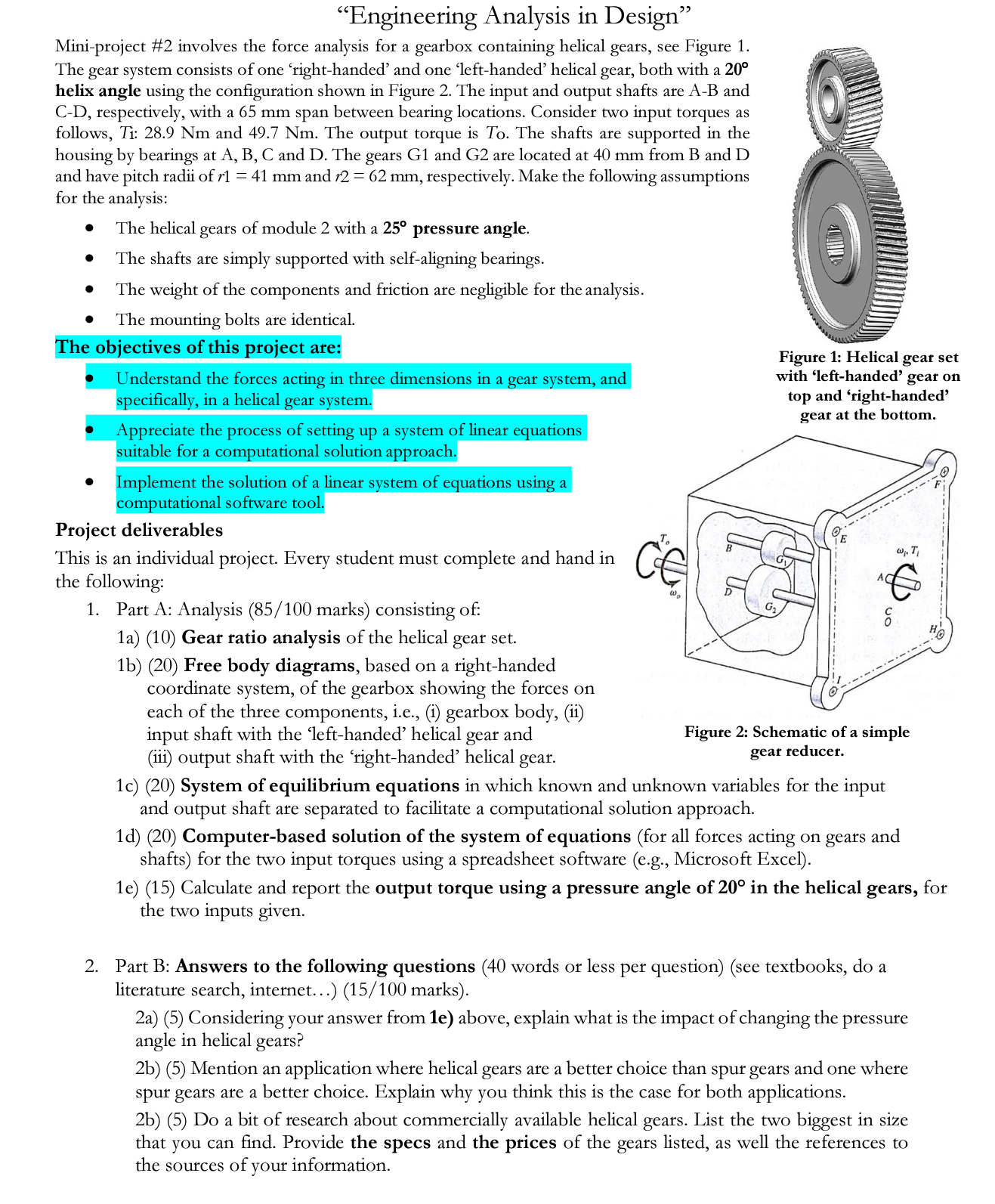
System of equilibrium equations: Forces acting on Gears T = Ft xr Fitano cos Fa= Fttan Fcoso Fr FBD: = - Ft cos Forces acting on Shafts FBD: FH = Ft R1 - Rx2 Fy Fr Ry1 - Ry2 = FAXIAL = RA - FA FBD: 8 T = Ft xr Fitano Fr cos Fa Fitan Fcoso Forces acting on Shafts FBD: = F cos RA (AXIAL REACTION) FH = Ft R1 - Rx2 Fy Fr Ryl - Ry2 FAXIAL = RA - FA OXI Ft Rx Ry (BEARING REACTION) B Fa Frost Fa Fcos Ry Rx Fa Foos Gear ratio = Explanation: Gear ratio analysis Step 1: The gear ratio of helical gear is: Gear ratio N N where N is the number of teeth. 59 39 N Step 2: Calculate the number of teeth from the given pitch radii, module and helix angle. Gear, G ( = 41 mm, m = 2, helix angle = 20) = N N = - = : 1.51 = Dcos mn N N = 38.53 39teeth = mn 2x41mmxcos 20 2mm/teeth Gear, G (r = 62 mm, m=2, helix angle = 25) Dcos mn 2r1 cos - - 2x62mmxcos20 2mm/teeth N = 58.26 59teeth 2rcos mn Step 3: Solve for the gear ratio: 59 Gear ratio 1.51 39 = Question 1(b) - Free body diagrams (gearbox housing) E HO Question 1(b) - Free body diagrams (input and output shaft) X B G D (X A G T IXO "Engineering Analysis in Design" Mini-project #2 involves the force analysis for a gearbox containing helical gears, see Figure 1. The gear system consists of one right-handed' and one left-handed' helical gear, both with a 20 helix angle using the configuration shown in Figure 2. The input and output shafts are A-B and C-D, respectively, with a 65 mm span between bearing locations. Consider two input torques as follows, Ti: 28.9 Nm and 49.7 Nm. The output torque is To. The shafts are supported in the housing by bearings at A, B, C and D. The gears G1 and G2 are located at 40 mm from B and D and have pitch radii of r1 = 41 mm and r2 = 62 mm, respectively. Make the following assumptions for the analysis: The helical gears of module 2 with a 25 pressure angle. The shafts are simply supported with self-aligning bearings. The weight of the components and friction are negligible for the analysis. The mounting bolts are identical. The objectives of this project are: Understand the forces acting in three dimensions in a gear system, and specifically, in a helical gear system. Appreciate the process of setting up a system of linear equations suitable for a computational solution approach. Implement the solution of a linear system of equations using a computational software tool. Project deliverables This is an individual project. Every student must complete and hand in the following: 1. Part A: Analysis (85/100 marks) consisting of: 1a) (10) Gear ratio analysis of the helical gear set. 1b) (20) Free body diagrams, based on a right-handed coordinate system, of the gearbox showing the forces on each of the three components, i.e., (i) gearbox body, (ii) input shaft with the 'left-handed' helical gear and (iii) output shaft with the 'right-handed' helical gear. CE @ Figure 1: Helical gear set with 'left-handed' gear on top and 'right-handed gear at the bottom. o 1c) (20) System of equilibrium equations in which known and unknown variables for the input and output shaft are separated to facilitate a computational solution approach. w. T Figure 2: Schematic of a simple gear reducer. 1d) (20) Computer-based solution of the system of equations (for all forces acting on gears and shafts) for the two input torques using a spreadsheet software (e.g., Microsoft Excel). 2. Part B: Answers to the following questions (40 words or less per question) (see textbooks, do a literature search, internet...) (15/100 marks). 1e) (15) Calculate and report the output torque using a pressure angle of 20 in the helical gears, for the two inputs given. 2a) (5) Considering your answer from 1e) above, explain what is the impact of changing the pressure angle in helical gears? 110 2b) (5) Mention an application where helical gears are a better choice than spur gears and one where spur gears are a better choice. Explain why you think this is the case for both applications. H! 2b) (5) Do a bit of research about commercially available helical gears. List the two biggest in size that you can find. Provide the specs and the prices of the gears listed, as well the references to the sources of your information.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


