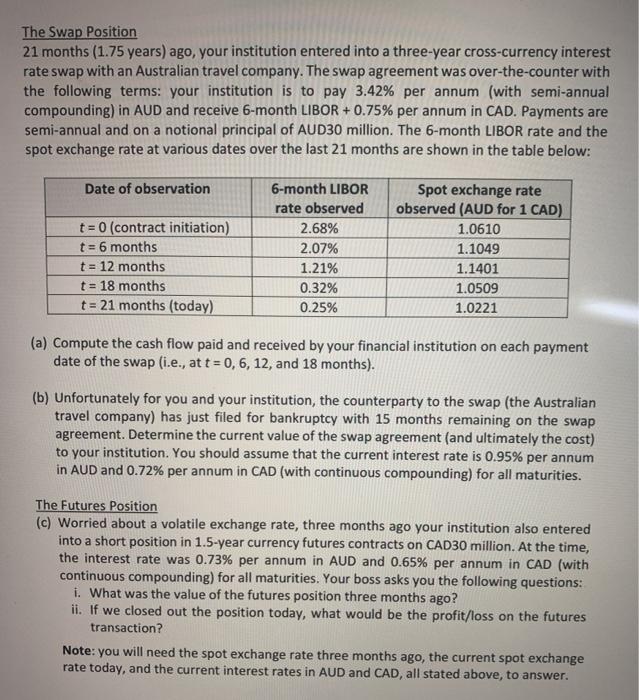
The Swap Position 21 months (1.75 years) ago, your institution entered into a three-year cross-currency interest rate swap with an Australian travel company. The swap agreement was over-the-counter with the following terms: your institution is to pay 3.42% per annum (with semi-annual compounding) in AUD and receive 6-month LIBOR +0.75% per annum in CAD. Payments are semi-annual and on a notional principal of AUD30 million. The 6-month LIBOR rate and the spot exchange rate at various dates over the last 21 months are shown in the table below: Date of observation t = 0 (contract initiation) t = 6 months t = 12 months t = 18 months t = 21 months (today) 6-month LIBOR rate observed 2.68% 2.07% 1.21% 0.32% 0.25% Spot exchange rate observed (AUD for 1 CAD) 1.0610 1.1049 1.1401 1.0509 1.0221 (a) Compute the cash flow paid and received by your financial institution on each payment date of the swap (i.e., at t=0, 6, 12, and 18 months). (b) Unfortunately for you and your institution, the counterparty to the swap (the Australian travel company) has just filed for bankruptcy with 15 months remaining on the swap agreement. Determine the current value of the swap agreement (and ultimately the cost) to your institution. You should assume that the current interest rate is 0.95% per annum in AUD and 0.72% per annum in CAD (with continuous compounding) for all maturities. The Futures Position (c) Worried about a volatile exchange rate, three months ago your institution also entered into a short position in 1.5-year currency futures contracts on CAD30 million. At the time, the interest rate was 0.73% per annum in AUD and 0.65% per annum in CAD (with continuous compounding) for all maturities. Your boss asks you the following questions: i. What was the value of the futures position three months ago? ii. If we closed out the position today, what would be the profit/loss on the futures transaction? Note: you will need the spot exchange rate three months ago, the current spot exchange rate today, and the current interest rates in AUD and CAD, all stated above, to answer. The Swap Position 21 months (1.75 years) ago, your institution entered into a three-year cross-currency interest rate swap with an Australian travel company. The swap agreement was over-the-counter with the following terms: your institution is to pay 3.42% per annum (with semi-annual compounding) in AUD and receive 6-month LIBOR +0.75% per annum in CAD. Payments are semi-annual and on a notional principal of AUD30 million. The 6-month LIBOR rate and the spot exchange rate at various dates over the last 21 months are shown in the table below: Date of observation t = 0 (contract initiation) t = 6 months t = 12 months t = 18 months t = 21 months (today) 6-month LIBOR rate observed 2.68% 2.07% 1.21% 0.32% 0.25% Spot exchange rate observed (AUD for 1 CAD) 1.0610 1.1049 1.1401 1.0509 1.0221 (a) Compute the cash flow paid and received by your financial institution on each payment date of the swap (i.e., at t=0, 6, 12, and 18 months). (b) Unfortunately for you and your institution, the counterparty to the swap (the Australian travel company) has just filed for bankruptcy with 15 months remaining on the swap agreement. Determine the current value of the swap agreement (and ultimately the cost) to your institution. You should assume that the current interest rate is 0.95% per annum in AUD and 0.72% per annum in CAD (with continuous compounding) for all maturities. The Futures Position (c) Worried about a volatile exchange rate, three months ago your institution also entered into a short position in 1.5-year currency futures contracts on CAD30 million. At the time, the interest rate was 0.73% per annum in AUD and 0.65% per annum in CAD (with continuous compounding) for all maturities. Your boss asks you the following questions: i. What was the value of the futures position three months ago? ii. If we closed out the position today, what would be the profit/loss on the futures transaction? Note: you will need the spot exchange rate three months ago, the current spot exchange rate today, and the current interest rates in AUD and CAD, all stated above, to







