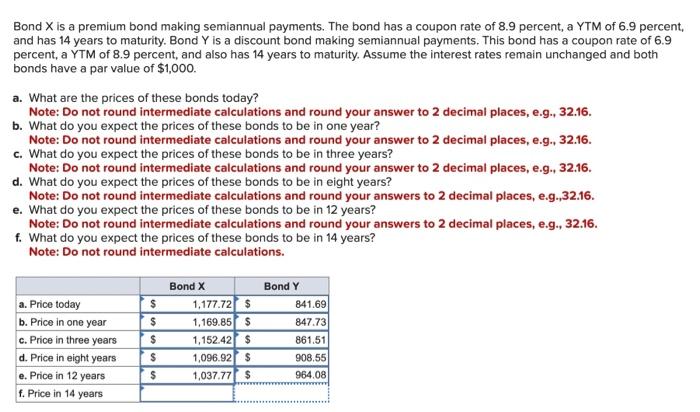
The YTM on a bond is the interest rate you earn on your investment if interest rates don't change. If you actually sell the bond before it matures, your realized return is known as the holding period yield (HPY). a. Suppose that today you buy an annual coupon bond with a coupon rate of 8 percent for $900. The bond has 9 years to maturity and a par value of $1,000. What rate of return do you expect to earn on your investment? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16 . b-1. Two years from now, the YTM on your bond has declined by 1 percent, and you decide to sell. What price will your bond sell for? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. b-2. What is the HPY on your investment? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16 . Bond X is a premium bond making semiannual payments. The bond has a coupon rate of 8.9 percent, a YTM of 6.9 percer and has 14 years to maturity. Bond Y is a discount bond making semiannual payments. This bond has a coupon rate of 6.9 percent, a YTM of 8.9 percent, and also has 14 years to maturity. Assume the interest rates remain unchanged and both bonds have a par value of $1,000. a. What are the prices of these bonds today? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. b. What do you expect the prices of these bonds to be in one year? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. c. What do you expect the prices of these bonds to be in three years? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. d. What do you expect the prices of these bonds to be in eight years? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answers to 2 decimal places, e.g.,32.16. e. What do you expect the prices of these bonds to be in 12 years? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answers to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. f. What do you expect the prices of these bonds to be in 14 years? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. The YTM on a bond is the interest rate you earn on your investment if interest rates don't change. If you actually sell the bond before it matures, your realized return is known as the holding period yield (HPY). a. Suppose that today you buy an annual coupon bond with a coupon rate of 8 percent for $900. The bond has 9 years to maturity and a par value of $1,000. What rate of return do you expect to earn on your investment? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16 . b-1. Two years from now, the YTM on your bond has declined by 1 percent, and you decide to sell. What price will your bond sell for? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. b-2. What is the HPY on your investment? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16 . Bond X is a premium bond making semiannual payments. The bond has a coupon rate of 8.9 percent, a YTM of 6.9 percer and has 14 years to maturity. Bond Y is a discount bond making semiannual payments. This bond has a coupon rate of 6.9 percent, a YTM of 8.9 percent, and also has 14 years to maturity. Assume the interest rates remain unchanged and both bonds have a par value of $1,000. a. What are the prices of these bonds today? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. b. What do you expect the prices of these bonds to be in one year? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. c. What do you expect the prices of these bonds to be in three years? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. d. What do you expect the prices of these bonds to be in eight years? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answers to 2 decimal places, e.g.,32.16. e. What do you expect the prices of these bonds to be in 12 years? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answers to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. f. What do you expect the prices of these bonds to be in 14 years? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations