Question: This is a java code problem using eclipse, there are two codes below. The purpose is to work the BinaryTreeTest code, and get a score
This is a java code problem using eclipse, there are two codes below.
The purpose is to work the BinaryTreeTest code, and get a score of 100.
CODE Below:
import java.util.Arrays;
/** * A binary search tree for Comparable objects such as Strings, Integers, etc. * For each node n, all nodes to the left have data which is less than n.data * and all nodes to the right have data which is greater than n.data. * * @param
public void add(T d) { int comp = d.compareTo(data); if (comp == 0) return; // Already in tree if (comp (); left.data = d; } else { left.add(d); } } else { // Greater than if (right == null) { right = new Node(); right.data = d; } else { right.add(d); } } }
public boolean contains(T d) { int comp = d.compareTo(data); if (comp == 0) return true; // Already in tree if (comp
}
public void print(int indent) { if (right != null) right.print(indent + 1); char[] spaces = new char[indent * 2]; Arrays.fill(spaces, ' '); System.out.println(new String(spaces) + data); if (left != null) left.print(indent + 1); }
/** * The number of nodes of this subtree. * @return Number of nodes */ public int size() { // We know there is a node here int total = 1; // This node may have left children if (left != null) total = total + left.size(); // This node may have right children if (right != null) total = total + right.size(); // The total size of the tree from this point... return total; }
/** * Delete this node. * * @return The new root of this subtree (null if this node had no * children, also known as a leaf) */ public Node
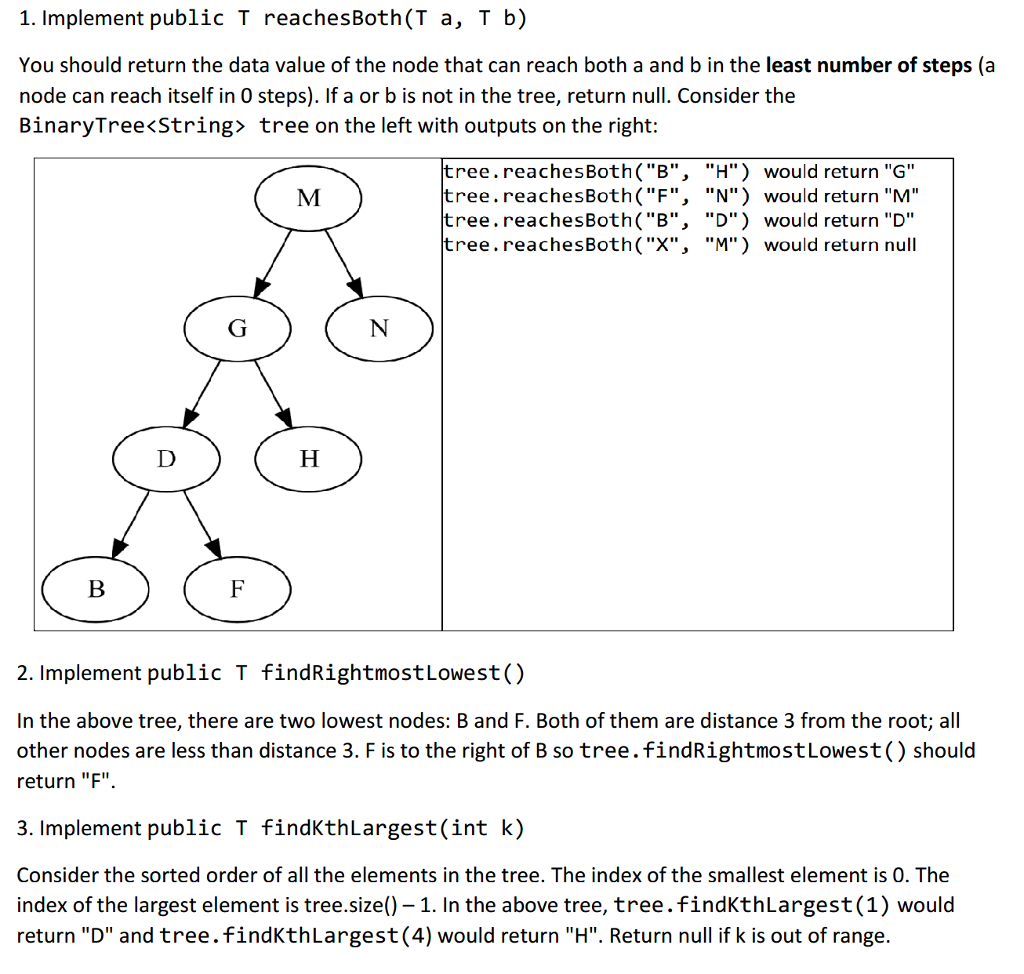
/** * Deletes the node containing d if it exists. * * @param d * @return A valid BinaryTree that doesn't have d in it but does have * everything else. */ public Node private Node public BinaryTree() { root = null; } /** * Adds data to the tree if it didn't already contain it. * * @param data */ public void add(T data) { if (root == null) { root = new Node(); root.data = data; } else { root.add(data); } } /** * Returns true if the tree contains data, false otherwise * * @param data * Does the tree contain this? * @return true if it does */ public boolean contains(T data) { if (root == null) return false; return root.contains(data); } /** * Prints out a representation of the tree (rotate your head 90 degrees * left) */ public void print() { if (root != null) root.print(0); } /** * Gets the number of nodes of the tree in O(n) time. * * @return number of nodes */ public int size() { if (root == null) return 0; return root.size(); } /** * Delete the node containing data from the tree, if it exists. * * @param data */ public void delete(T data) { root = root.delete(data); } /** * Returns the data value of the node that can reach both a and b in the * least number of steps. If the tree doesn't contain both a and b, return * null. * * @param a * @param b * @return data value */ public T reachesBoth(T a, T b) { // TODO: Implement. return null; } /** * Among all the nodes which are farthest from the root, find the one which * is farthest to the right. * * @return data value of said node */ public T findRightmostLowest() { // TODO: Implement. return null; } /** * Return the kth largest element according to the Comparable sorted order * of the tree. The leftmost node has index 0 and the rightmost node has * index size() - 1. * * @param k * index * @return element, or null if k is out of range. */ public T findKthLargest(int k) { // TODO: Implement. return null; } /** * EXTRA CREDIT: Balance the tree. The new root should be the * findKthLargest(size()/2) node. Recursively, the root of each subtree * should also be the size/2-largest node (indexed from 0) of that subtree. * This method should not call new and should execute in O(n log n) time for * full credit. */ public void balance() { // TODO: Implement for extra credit. } } TEST CODE Below: import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.PrintStream; import java.security.MessageDigest; import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException; import java.util.Arrays; public class BinaryTreeTest { public static public static public static public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException { int reachesBothScore = 0, findRightmostLowestScore = 0, findKthLargestScore = 0; int ecScore = 0; try { String[] letters = { "M", "G", "N", "D", "H", "B", "F" }; BinaryTree BinaryTree }
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


