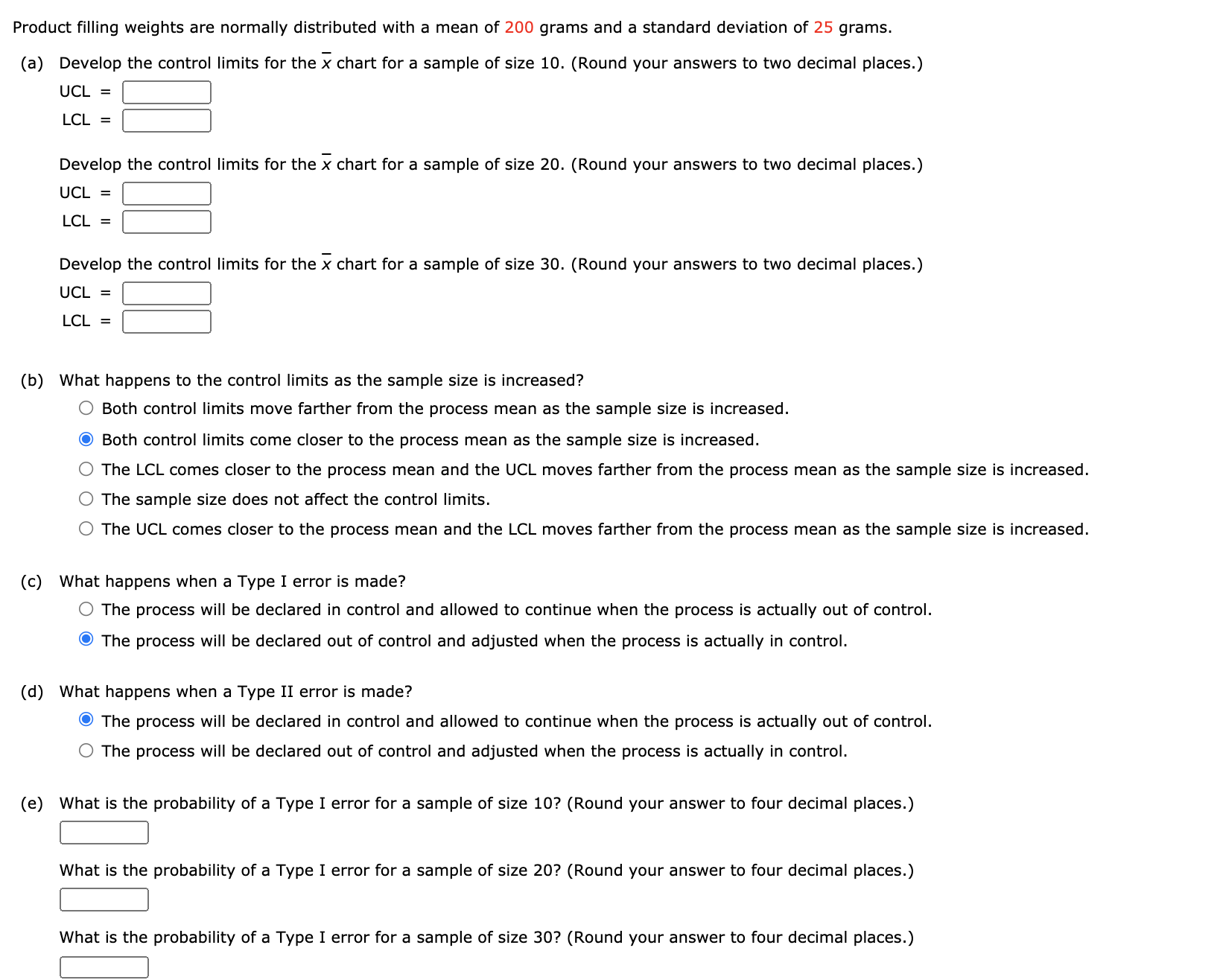
This is for statistics. thank you!
Consider the following time series data. III-EH Hanna Using the naive method (most recent value) as the forecast for the next week, compute the following measures of forecast accuracy. (a) mean absolute error (b) mean squared error (c) mean absolute percentage error (Round your answer to two decimal places.) MAPE = :1 % (d) What is the forecast for week 7? [:1 Product lling weights are normally distributed with a mean of 200 grams and a standard deviation of 25 grams. (a) Develop the control limits for the )7 chart for a sample of size 10. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) um: Develop the control limits for the )7 chart for a sample of size 20. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) new: Develop the control limits for the )7 chart for a sample of size 30. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) um: mm: (b) What happens to the control limits as the sample size is increased? 0 Both control limits move farther from the process mean as the sample size is increased. Both control limits come closer to the process mean as the sample size is increased. 0 The LCL comes closer to the process mean and the UCL moves farther from the process mean as the sample size is increased. 0 The sample size does not affect the control limits. 0 The UCL comes closer to the process mean and the LCL moves farther from the process mean as the sample size is increased. (c) What happens when a Type I error is made? 0 The process will be declared in control and allowed to continue when the process is actually out of control. The process will be declared out of control and adjusted when the process is actually in control. (d) What happens when a Type II error is made? The process will be declared in control and allowed to continue when the process is actually out of control. 0 The process will be declared out of control and adjusted when the process is actually in control. (e) What is the probability ofa Type I error for a sample of size 10? (Round your answer to four decimal places.) U What is the probability of a Type I error for a sample of size 20? (Round your answer to four decimal places.) H What is the probability of a Type I error for a sample of size 30? (Round your answer to four decimal places.) H