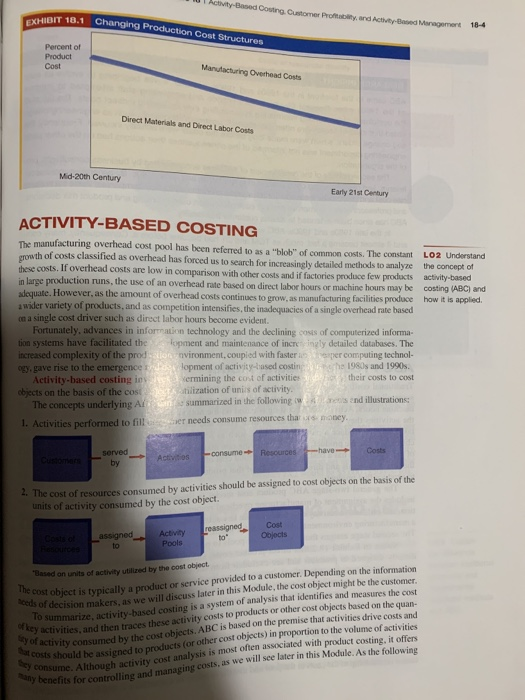
Topic Week #7 Discussion v During the last century, production cost structures have significantly changed (see Exhibit 18.1 on text page 18-4). Discuss the reasons for this trend which have resulted in Activity Based Costing (ABC) becoming such an important method for determining a product's costs. Respond to other posts on whether you agree or not. If you disagree, state your reasons. ey consume. Although activity cost analysis is most often associated with product costing, it offers y benefits for controlling and managing costs, as we will see later in this Module. As the following Activity-Based Costing. Customer Profitability, and Activity-Based Margement EXHIBIT 18.1 Changing Production Cost Structures 18-4 Percent of Product Cost Manufacturing Overhead Costs Direct Materials and Direct Labor Costs Mid-20th Century Early 21st Century ACTIVITY-BASED COSTING The manufacturing overhead cost pool has been referred to as a "blob" of common costs. The constant growth of costs classified as overhead has forced us to search for increasingly detailed methods to analyze the concept of LO2 Understand these costs. If overhead costs are low in comparison with other costs and if factories produce few products activity-based in large production runs, the use of an overhead rate based on direct labor hours or machine hours may be costing (ABC) and adequate. However, as the amount of overhead costs continues to grow, as manufacturing facilities produce how it is applied. a wider variety of products, and as competition intensifies, the inadequacies of a single overhead rate based on a single cost driver such as direct labor hours become evident. Fortunately, advances in information technology and the declining costs of computerized informa- tion systems have facilitated the lopment and maintenance of incre ingly detailed databases. The increased complexity of the prodaion vironment, coupled with faster per computing technol- og gave rise to the emergence de lopment of activity-based costinhe 1980s and 1990s. Activity-based costing in vermining the cost of activities their costs to cost cbjects on the basis of the cost tilization of units of activity mes and illustrations The concepts underlying Aron summarized in the following is 1. Activities performed to fill needs consume resources that is money Costs -have- served by Activities --consume Resources 2. The cost of resources consumed by activities should be assigned to cost objects on the basis of the units of activity consumed by the cost object. reassigned assigned to Activity Pools Cost Objects to Based on units of activity utilized by the cost object The cost object is typically a product or service provided to a customer. Depending on the information soods of decision makers, as we will discuss later in this Module, the cost object might be the customer. To summarize, activity-based costing is a system of analysis that identifies and measures the cost key activities, and then traces these activity costs to products or other cost objects based on the quan- couts should be assigned to products for other cost objects) in proportion to the volume of activities actually used first to improve cost management before in Research Insight box explains, ABC was used for product costing