Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
You are the manager of Short Term Capital Management (STCM). You observe that the interest rate on 4 year notes is 5.2 percent, while the
- You are the manager of Short Term Capital Management (STCM). You observe that the interest rate on 4 year notes is 5.2 percent, while the interest rate 4.25 year notes is 5.29 percent. You know for sure for sure that the two interest rates will converge in six months to some value X. You also have the ability to go short $300 million face in any note you choose. Given all this, describe your profit making arbitrage strategy. Then graph the amount of money you will make if the interest rate converges to X, X a percentage rate between 3 and 7 percent. Please make sure you dont have negative returns.
Note: If your initial calculations show a negative return, you can simply reverse the strategy.
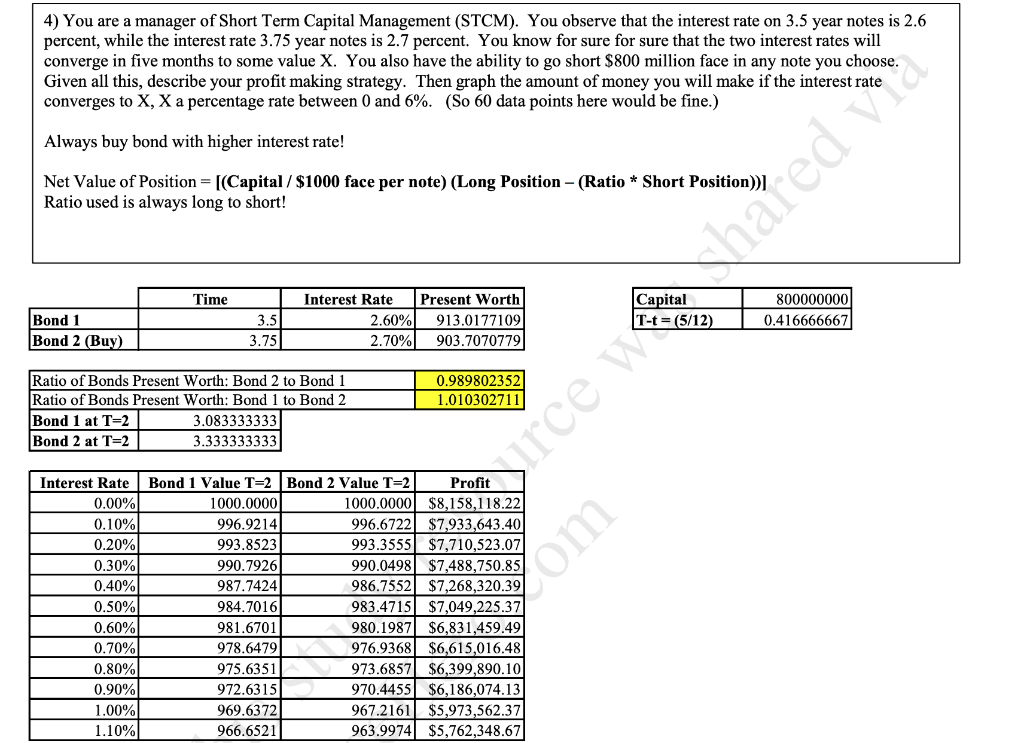
Graph 50 data points for the interest rate using EXCEL (please display the formulas used once you're done). For example, graph for interest rates would be between 3% and 7% with atleast 50 data points ( Ex 3.00%, 3.10%, 3.20%...., 6.90%, 7.00%, etc) Here's EXAMPLE on what it should look like when completed:
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


