Refer to the situation in Example 1. (a) What is the probability your friend will be between
Question:
Refer to the situation in Example 1.
(a) What is the probability your friend will be between 10 and 20 minutes late?
(b) It is 10 a.m. There is a 20% probability your friend will arrive within the next ______ minutes.
Approach Use the graph of the density function in Figure 1 to find the solutions.
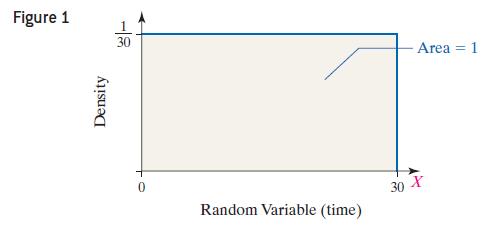
Data from Example 1
Imagine that a friend of yours is always late. Let the random variable X represent the time from when you are supposed to meet your friend until he shows up. Suppose your friend could be on time (x = 0) or up to 30 minutes late (x = 30), with all intervals of equal time between x = 0 and x = 30 being equally likely. For example, your friend is just as likely to be 3–4 minutes late as he is to be 25–26 minutes late. The random variable X can be any value in the interval from 0 to 30, that is, 0 ≤ x ≤ 30. Because any two intervals of equal length between 0 and 30, inclusive, are equally likely, the random variable X is said to follow a uniform probability distribution.
Step by Step Answer:

Statistics Informed Decisions Using Data
ISBN: 9781292157115
5th Global Edition
Authors: Michael Sullivan





