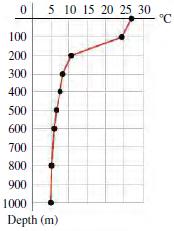
If the power plant uses a Carnot cycle and the desired theoretical efficiency is 6.5%, from what
Question:
(a) 100 m;
(b) 400 m;
(c) 800 m;
(d) deeper than 1000 m.
Ocean thermal energy conversion is a process that uses the temperature difference between the warm surface water of tropical oceans and the cold deep ocean water to run a heat engine. The graph shows a typical decrease of temperature with depth below the surface in tropical oceans. In the heat engine, the warmer surface water vaporizes a low-boiling-point fluid, such as ammonia. The heat of vaporization of ammonia is 260 cal/g at 27°C, the surface-water temperature. The vapor is used to turn a turbine and is then condensed back into a liquid by means of cold water brought from deep below the surface through a large intake pipe. A power plant producing 10 MW of useful power would require a cold seawater flow rate of about 30,000 kg/s.
Step by Step Answer:

University Physics with Modern Physics
ISBN: 978-0133977981
14th edition
Authors: Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman





