The density and specific heat of a particular material are known (p = 1200 kg/m 3
Question:
The density and specific heat of a particular material are known (p = 1200 kg/m3 ∙ c p = 1250 J/kg ∙ K), but its thermal conductivity is unknown. To determine the thermal conductivity, a long cylindrical specimen of diameter D = 40 mm is machined, and a thermo couple is inserted through a small hole drilled along the centerline.
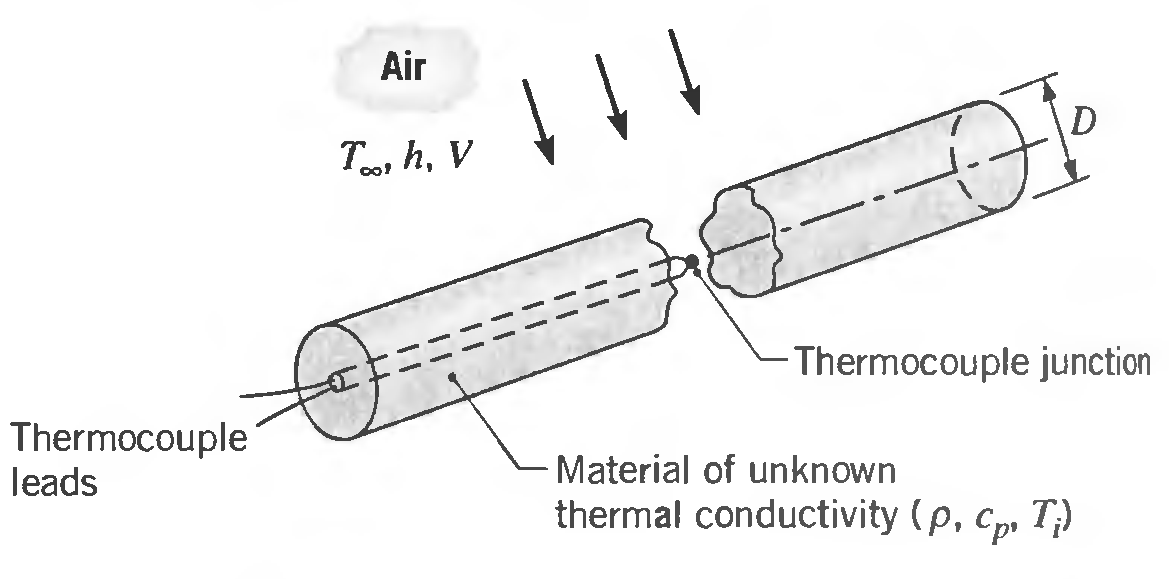
The thermal conductivity is determined by performing an experiment in which the specimen is heated to a uniform temperature of Tj = 100°C and then cooled by passing air at T∞ = 25°C in cross flow over the cylinder. For the prescribed air velocity, the convection coefficient is h = 55 W/m 2 ∙ K.
(a) If a centerline temperature of T (0, t) = 40°C is recorded after t = 1136 s of cooling, verify that the material has a thermal conductivity of k = 0.30 W/m ∙ K.
(b) For air in cross-flow over the cylinder, the prescribed value of h = 55 W/m2 ∙ K corresponds to a velocity of V = 6.8 m/s. If h = CV0.618, where the constant C has units of W ∙ s 0.618/m2.618 ∙ K, how does the centerline temperature at t = 1136 s vary with velocity for 3 < V < 20 m/s? Determine the centerline temperature histories for 0 < t < 1500 s and velocities of 3, 10, and 20 m/s.
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
ISBN: 978-0471457282
6th Edition
Authors: Incropera, Dewitt, Bergman, Lavine





