The Normal approximation (a) A discrete stochastic variable (X) has expected value (mu_{X}=3) and (sigma_{X}=1.2). Use the
Question:
The Normal approximation
(a) A discrete stochastic variable \(X\) has expected value \(\mu_{X}=3\) and \(\sigma_{X}=1.2\). Use the Normal approximation to find \(P(X \leq 4)\).
(b) A continuous stochastic variable \(X\) has expected value \(\mu_{X}=3\) and \(\sigma_{X}=1.2\). Use the Normal approximation to find \(P(X \leq 4)\).
(c) A discrete stochastic variable \(X\) has expected value \(\mu_{X}=5.1\) and \(\sigma_{X}=2.2\). Use the Normal approximation to find \(P(X \in\{6,7\})\).
(d) A continuous stochastic variable \(X\) has expected value \(\mu_{X}=5.1\) and \(\sigma_{X}=2.2\). Use the Normal approximation to find \(P(X \in(5,7))\).
(e) A discrete stochastic variable \(X\) has expected value \(\mu_{X}=12.1\) and \(\sigma_{X}=4.7\). Use the Normal approximation to find
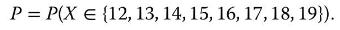
Step by Step Answer:

The Bayesian Way Introductory Statistics For Economists And Engineers
ISBN: 9781119246879
1st Edition
Authors: Svein Olav Nyberg





