Nitrogen oxides can be removed from the exhaust gases of a car engine by using a catalytic
Question:
Nitrogen oxides can be removed from the exhaust gases of a car engine by using a catalytic converter. Many catalytic converters contain metals such as platinum and rhodium. These act as heterogeneous catalysts.
a. i. What is meant by the term heterogeneous catalysis?
ii. Explain in general terms how heterogeneous catalysts work.
b. Nitrogen(IV) oxide and carbon monoxide from car exhausts can react in a catalytic converter.
NO2(g) + CO(g) → NO(g) + CO2(g)
The rate equation for this reaction is rate = k[NO2]2
Suggest a two-step reaction mechanism for this reaction that is consistent with this rate equation.
c. Nitrogen(IV) oxide is formed when nitrogen(II) oxide reacts with oxygen.
2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
The table shows the data obtained from a series of experiments to investigate the kinetics of this reaction.
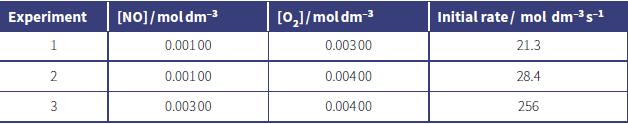
i. Deduce the order of reaction with respect to each reactant. In each case, show your reasoning.
ii. Deduce the rate equation for this reaction.
iii. State the units of the rate constant, k, for this reaction.
Step by Step Answer:

Cambridge International AS And A Level Chemistry Coursebook
ISBN: 9781316637739
2nd Edition
Authors: Lawrie Ryan, Roger Norris




