Question:
The sulfate ion, SO42–, is present in a number of important minerals, including gypsum (CaSO4 · 2H2O), which is used in cement, and Epsom salts (MgSO4 · 7H2O), which is used as a purgative. Determine the dominant resonance structure of a sulfate ion from the three shown in (10a–10c) by calculating the formal charges on the atoms in each structure.
ANTICIPATE As you gain experience, you will be able to recognize the most favorable structure from the patterns of bonds and lone pairs, but until then the only way forward is to calculate the formal charges.
PLAN Follow the procedure in Toolbox 2B.2. You need do only one calculation for equivalent atoms, such as the oxygen atoms in the first diagram, because they all have the same arrangement of electrons and hence the same formal charge.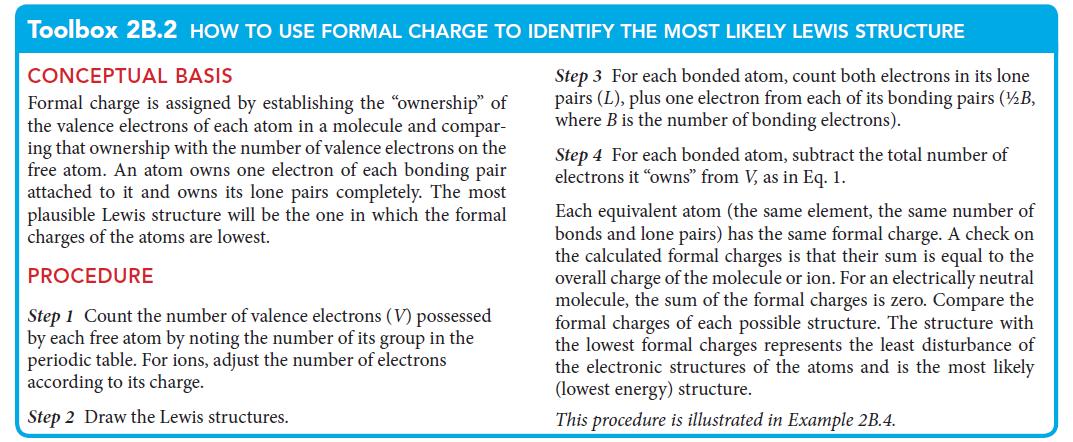
Transcribed Image Text:
Toolbox 2B.2 HOW TO USE FORMAL CHARGE TO IDENTIFY THE MOST LIKELY LEWIS STRUCTURE
CONCEPTUAL BASIS
Step 3 For each bonded atom, count both electrons in its lone
pairs (L), plus one electron from each of s bonding pairs (½/B,
where B is the number of bonding electrons).
Formal charge is assigned by establishing the "ownership" of
the valence electrons of each atom in a molecule and compar-
ing that ownership with the number of valence electrons on the
free atom. An atom owns one electron of each bonding pair
attached to it and owns its lone pairs completely. The most
plausible Lewis structure will be the one in which the formal
charges of the atoms are lowest.
PROCEDURE
Step 1 Count the number of valence electrons (V) possessed
by each free atom by noting the number of its group in the
periodic table. For ions, adjust the number of electrons
according to its charge.
Step 2 Draw the Lewis structures.
Step 4 For each bonded atom, subtract the total number of
electrons it "owns" from V, as in Eq. 1.
Each equivalent atom (the same element, the same number of
bonds and lone pairs) has the same formal charge. A check on
the calculated formal charges is that their sum is equal to the
overall charge of the molecule or ion. For an electrically neutral
molecule, the sum of the formal charges is zero. Compare the
formal charges of each possible structure. The structure with
the lowest formal charges represents the least disturbance of
the electronic structures of the atoms and is the most likely
(lowest energy) structure.
This procedure is illustrated in Example 2B.4.







