Because of the massive scale of WSCs, it is very important to properly allocate network resources based
Question:
a. Using the numbers in the spreadsheet detailed in Figure 6.13, what is the oversubscription ratio at each access-layer switch? What is the impact on TCO if the oversubscription ratio is cut in half? What if it is doubled?
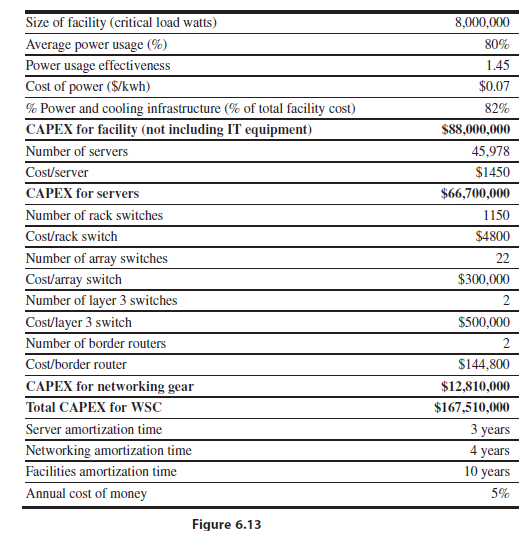
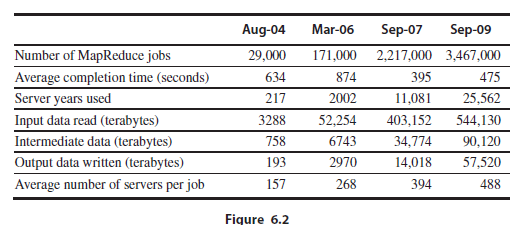
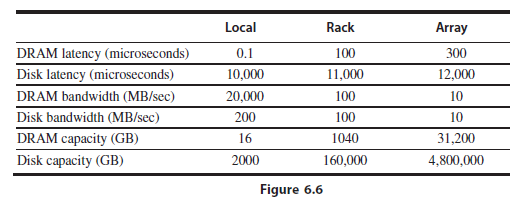
b. Reducing the oversubscription ratio can potentially improve the performance if a workload is network-limited. Assume a MapReduce job that uses 120 servers and reads 5 TB of data. Assume the same ratio of read/intermediate/ output data as in Figure 6.2, Sep-09, and use Figure 6.6 to define the bandwidths of the memory hierarchy. For data reading, assume that 50% of data is read from remote disks; of that, 80% is read from within the rack and 20% is read from within the array. For intermediate data and output data, assume that 30% of the data uses remote disks; of that, 90% is within the rack and 10% is within the array. What is the overall performance improvement when reducing the oversubscription ratio by half? What is the performance if it is doubled? Calculate the TCO in each case.
c. We are seeing the trend to more cores per system. We are also seeing the increasing adoption of optical communication (with potentially higher bandwidth and improved energy efficiency). How do you think these and other emerging technology trends will affect the design of future WSCs?
Step by Step Answer:

Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach
ISBN: 978-8178672663
5th edition
Authors: John L. Hennessy, David A. Patterson





