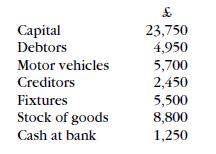
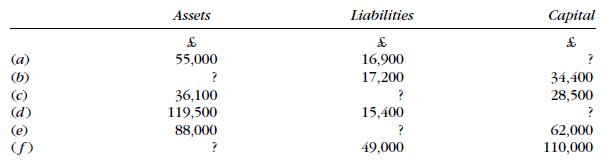
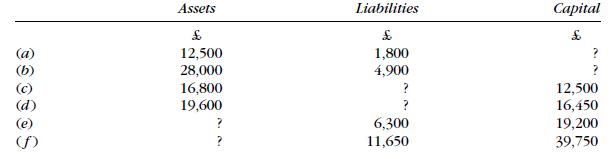
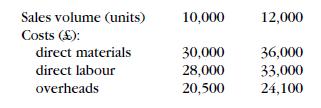
Frank Woods A Level Accounting Gce Year 2 4th Edition Alan Sangster - Solutions
Discover comprehensive solutions for "Frank Woods A Level Accounting GCE Year 2 4th Edition" with our expert resources. Access the online answers key for a deeper understanding of complex topics. Our solution manual provides detailed, step-by-step answers to solved problems, ensuring clarity and understanding. Whether you're looking for questions and answers, a test bank, or chapter solutions, our resources have you covered. Download the solutions PDF for a convenient and accessible study experience. With our instructor manual and textbook insights, excel in your studies effortlessly. Enjoy the free download of essential accounting solutions today.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()