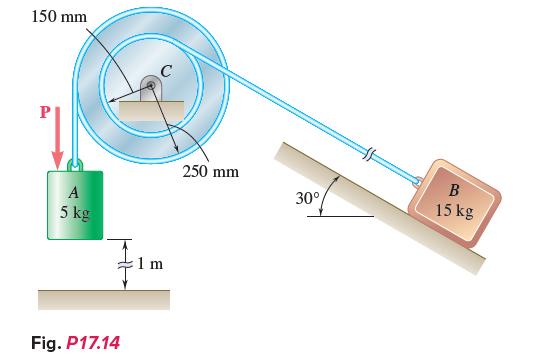
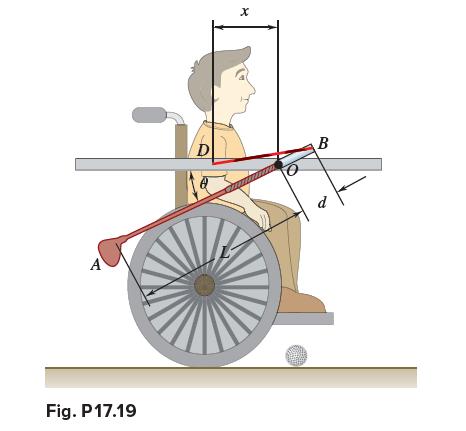
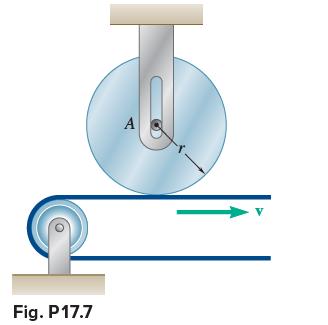
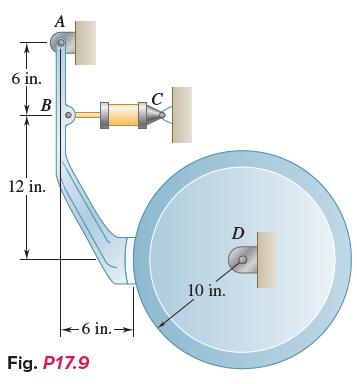
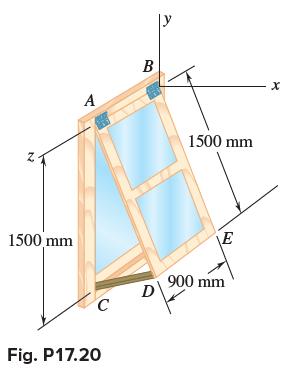
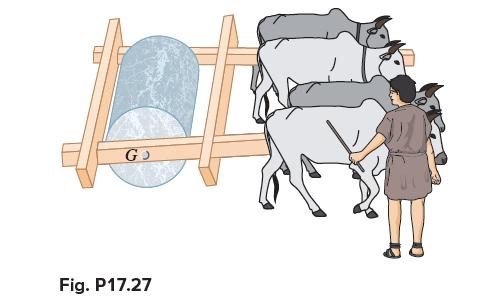
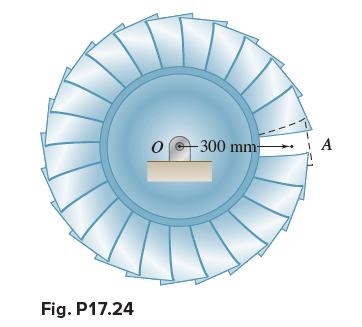
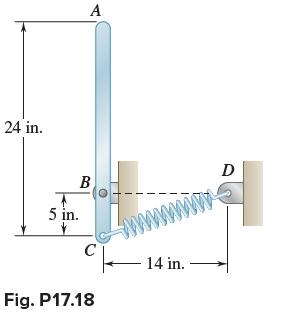
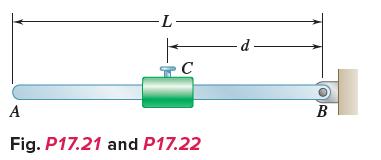
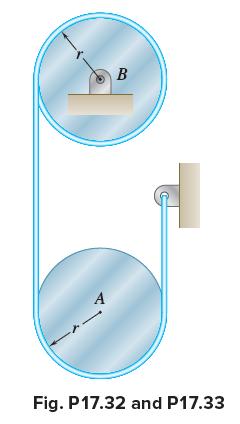
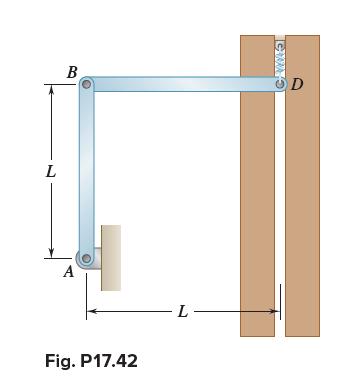
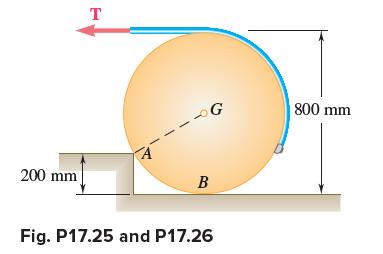
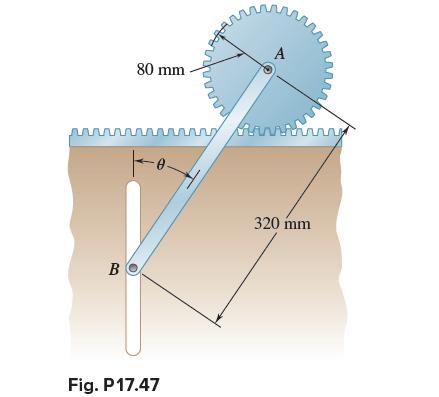
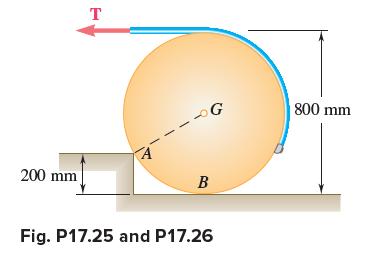
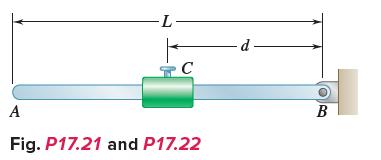
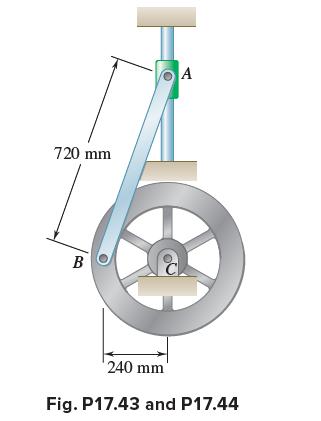
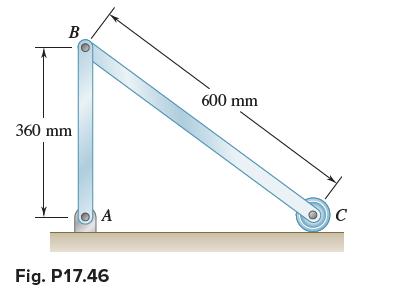
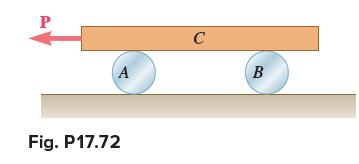
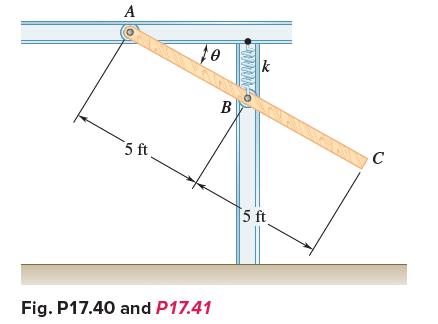
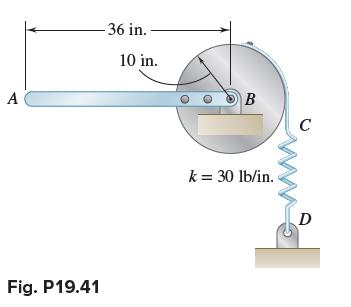
Vector Mechanics For Engineers Statics And Dynamics 12th Edition Phillip J Cornwell, E Russell Jr Johnston, David Mazurek, E Russell Johnston Jr, Ferdinand P Beer, Brian - Solutions
Discover comprehensive solutions for "Vector Mechanics For Engineers: Statics and Dynamics, 12th Edition" by Phillip J. Cornwell and others, available online. Access the answers key and detailed solutions pdf to tackle challenging problems with ease. Our platform offers step-by-step answers, a complete solution manual, and solved problems to aid your understanding. Benefit from the test bank and instructor manual for in-depth chapter solutions. Whether you're seeking questions and answers from the textbook or a free download of essential resources, our collection ensures a seamless learning experience for engineering students.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()