Advanced: Financial evaluation of implementing a quality management programme Bushworks Ltd convert synthetic slabs into com ponents
Question:
Advanced: Financial evaluation of implementing a quality management programme Bushworks Ltd convert synthetic slabs into com¬ ponents AX and BX for use in the car industry. Bushworks Ltd is planning a quality management programme at a cost of £250000. The following information relates to the costs incurred by Bush¬ works Ltd both before and after the implementation of the quality management programme:
1. Synthetic slabs Synthetic slabs cost £40 per hundred. On average 2.5% of synthetic slabs received are returned to the supplier as scrap because of deterioration in stores. The supplier allows a credit of £1 per hundred slabs for such returns. In addition, on receipt in stores, checks to ensure that the slabs received conform to specification costs £14000 per annum.
A move to a just-in-time purchasing system will eliminate the holding of stocks of synthetic slabs. This has been negotiated with the supplier who will deliver slabs of guaran¬ teed design specification for £44 per hundred units, eliminating all stockholding costs.
2. Curing/moulding process The synthetic slabs are issued to a curing/holding process which has variable conversion costs of £20 per hundred slabs input. This process produces sub-components A and B which have the same cost structure. Losses of 10% of input to the process because of incorrect temperature control during the process are sold as scrap at £5 per hundred units. The quality programme will rectify the temperature control problem thus reducing losses to 1% of input to the process.
3. Finishing process The finishing process has a bank of machines which perform additional operations on type A and B sub-components as required and converts them into final components AX and BX respectively. The variable conversion costs in the finishing process for AX and BX are £15 and £25 per hundred units respec¬ tively. At the end of the finishing process 15% of units are found to be defective. Defective units are sold for scrap at £10 per hundred units. The quality programme will convert the finishing process into two dedicated cells, one for each of component types AX and BX. The dedicated cell variable costs per hundred sub¬ components A and B processed will be £12 and £20 respectively. Defective units of components AX and BX are expected to fall to 2.5% of the input to each cell. Defective components will be sold as scrap as at present.
4. Finished goods A finished goods stock of components AX and BX of 15 000 and 30000 units respect¬ ively is held throughout the year in order to allow for customer demand fluctuations and free replacement of units returned by cus¬ tomers due to specification faults. Customer returns are currently 2.5% of components delivered to customers. Variable stock holding costs are £15 per thousand component units.
The proposed dedicated cell layout of the finishing process will eliminate the need to hold stocks of finished components, other than sufficient to allow for the free replace¬ ment of those found to be defective in cus¬ tomer hands. This stock level will be set at one month’s free replacement to customers which is estimated at 500 and 1000 units for types AX and BX respectively. Variable stock¬ holding costs will remain at £15 per thousand component units.
5.Quantitative data Some preliminary work has already been carried out in calculating the number of units of synthetic slabs, sub-components A and B and components AX and BX which will be required both before and after the implementation of the quality management programme, making use of the information in the question. Table 1 summarises the rel¬ evant figures.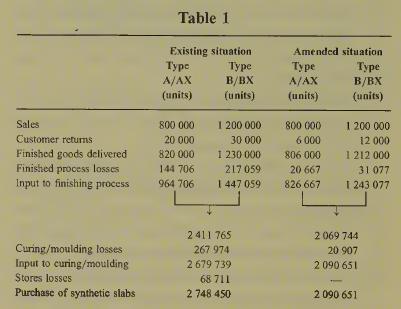
Required:
(a) Evaluate and present a statement showing the net financial benefit or loss per annum of implementing the quality management programme, using the information in the question and the data in Table 1.
{All relevant workings must be shown)
(27 marks)
(b) Explain the meaning of the terms internal failure costs, external failure costs, appraisal costs and prevention costs giving examples of ea°h. (8 marks)
Step by Step Answer:






