Kinesin-1 contains two identical heavy chains and therefore has two identical motor domains. In contrast, kinesin-5 contains
Question:
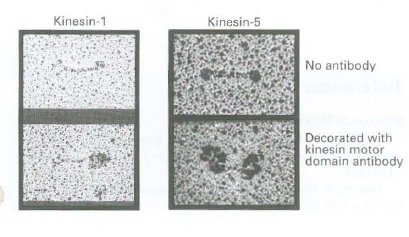
b. To determine if kinesin-5 is a (+) or (-) end microtubule motor, polarity-marked microtubules are generated by assembling short microtubules from brightly fluorescent tubulin and then elongating those short, bright microtubules using less fluorescent tubulin. As a result, the microtubules are very fluorescent at one end and less fluorescent along most of their length. A perfusion chamber is then coated with purified kinesin-5, which becomes immobilized on the glass surface. The chamber is then perfused with the polarity-labeled microrubules and ATP, and microtubule gliding with respect to the immobilized kinesin-5 is observed. The following sequence of images is obtained. Which end of these microtubules, the bright or the less-bright end, is the (+) end? Do these microrubules glide on kinesin-5 with their (+) or (-) end leading? Based on these data, is kinesin-5 a (+) or (-) end microtubule motor?
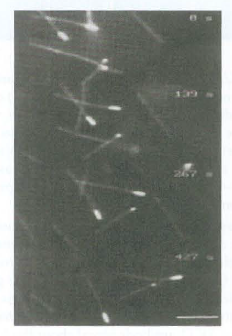
c. Kinesin-5 can cross-bridge adjacent microtubules. Polarity-marked microtubules are assembled in which rubulin attached to a red fluorescent dye is assembled to form short red microrubules, which are then elongated with tubulin attached to a green fluorescent dye. The microtubules are mixed with kinesin-5 and observed by fluorescence microscopy as A TP is added. The following images show a time sequence of two overlapping and cross-bridged microtubules as A TP is added. The arrowhead is in a fixed position. Can you explain what happens when A TP is added to microtubules cross-bridged by kinesin-5?

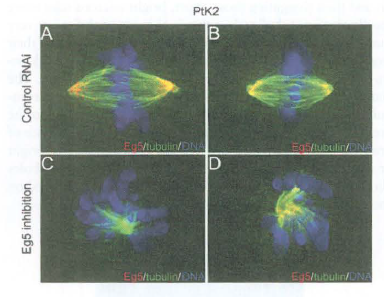
d. Eg5 is a kinesin-5 family member in Xenopus. To understand Eg5 function in vivo, cells are transfected with RNAi directed against this motor. The following images are obtained of mitotic cells. What function might Eg5 play in cells?
Step by Step Answer:

Molecular Cell Biology
ISBN: 978-1429234139
7th edition
Authors: Harvey Lodish, Arnold Berk, Chris A. Kaiser, Monty Krieger, Anthony Bretscher, Hidde Ploegh, Angelika Amon, Matthew P. Scott





