(a) When the rate of oxidation of isopropyl alcohol to acetone is compared with the rate of...
Question:
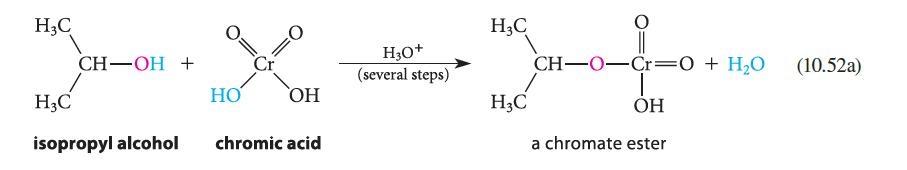
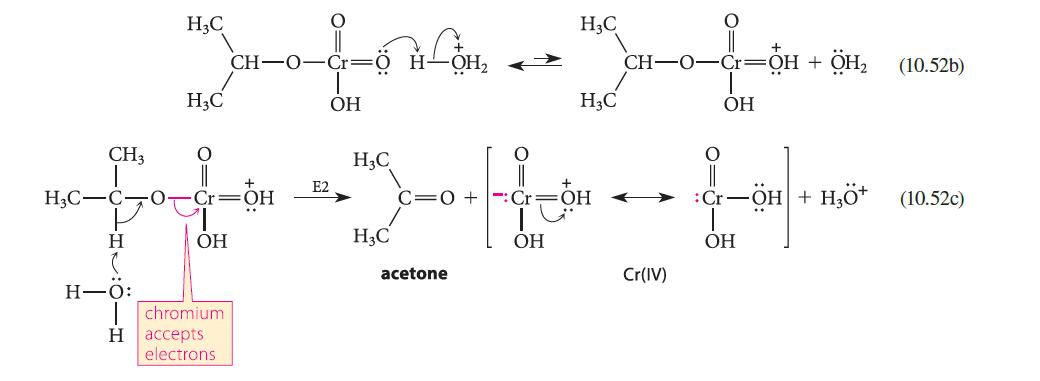
(a) When the rate of oxidation of isopropyl alcohol to acetone is compared with the rate of oxidation of a deuterated derivative, a primary isotope effect (Sec. 9.5D) is observed (see part (a) of Fig. P10.60). Assuming that the mechanism is the same as the one shown in Eqs. 10.52a–c, which step of this mechanism is rate-limiting?
(b) When either (S)- or (R)-1-deuterioethanol is oxidized with PCC in CH2Cl2, the same product mixture results and it contains significantly more of the deuterated aldehyde A than the undeuterated aldehyde B (see part (b) of Fig. P10.60). Explain why the deuterated aldehyde is the major product.
(c) Explain why, in the oxidation of (R)-1- deuterioethanol with alcohol dehydrogenase and NAD+, none of the deuterated aldehyde is obtained.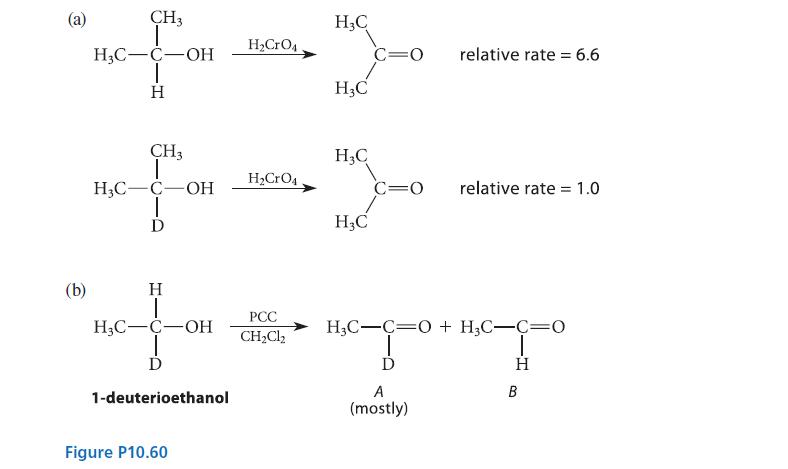
Step by Step Answer:






