Chemistry A Molecular Approach 5th Edition Nivaldo Tro - Solutions
Explore comprehensive solutions for "Chemistry: A Molecular Approach 5th Edition" by Nivaldo Tro with our online answers key and solution manual. Access detailed answers and solutions in PDF format, featuring solved problems and step-by-step explanations for each chapter. Our test bank and instructor manual provide an extensive collection of questions and answers, making it a valuable textbook resource. Discover chapter solutions and benefit from free downloads to enhance your understanding. Perfect for students and educators, our content ensures you have the support needed to excel in your chemistry studies.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


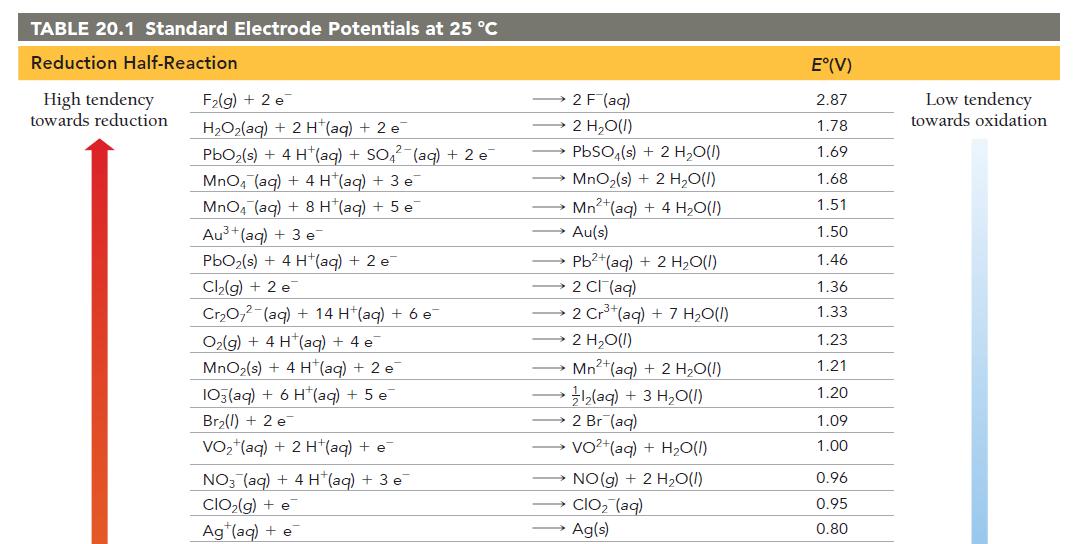
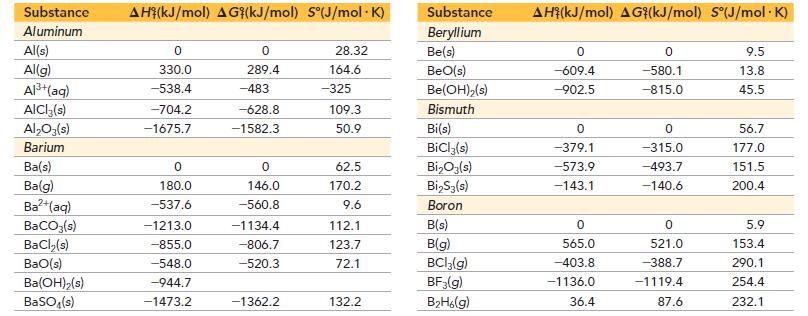
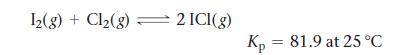
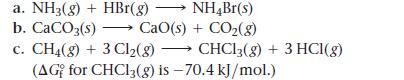
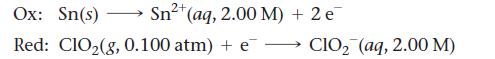
![[B+] 1.00 1.00 1.0 x 10-4 3.54 x 10-3 [A+] 1.00 1.00 x 10-4 1.0 1.0 Ecell AGxn](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1700/5/4/4/240655c3ef0c1c651700544237676.jpg)
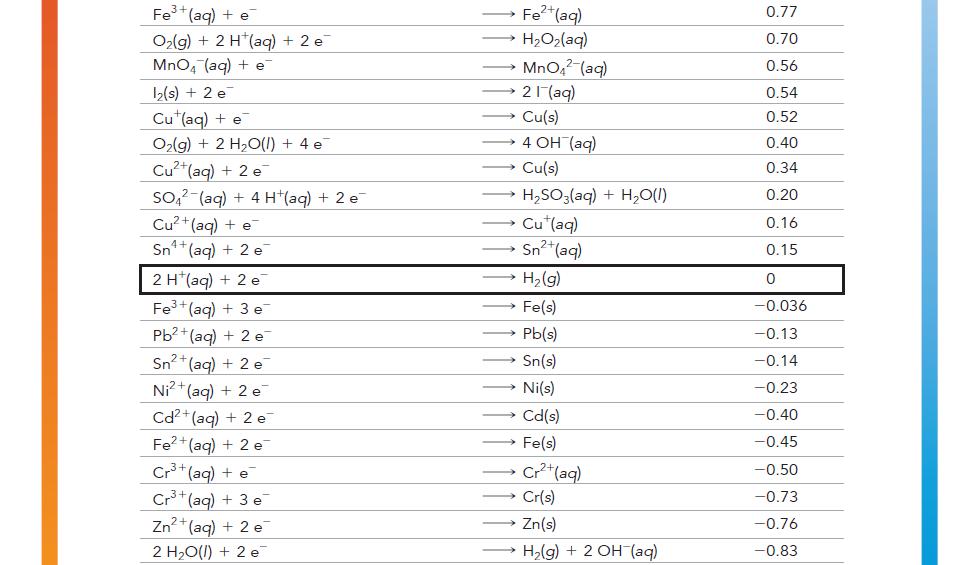
![[Cd+] 1.00 1.00 1.00 x 10-5 4.18 x 10-4 [Cr+] 1.00 1.00 x 10-5 1.00 1.00 Ecell A Grxn](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1700/5/4/4/273655c3f119499d1700544271990.jpg)
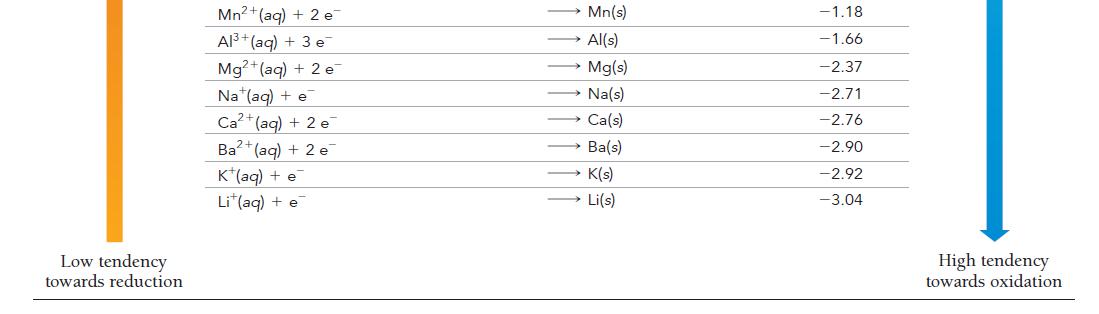
![[Cu+] 0.100 0.200 0.300 0.400 Voltage (V) 0.310 0.319 0.325 0.328 [Cu+] 0.500 0.700 1.00 Voltage (V) 0.331](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1700/5/4/6/612655c4834881241700546610129.jpg)
