Phosphoglycerate mutase catalyzes the interconversion of (R)-3-phosphoglycerate and (R)-2-phosphoglycerate, as shown in reaction (1) of Fig. P25.35.
Question:
Phosphoglycerate mutase catalyzes the interconversion of (R)-3-phosphoglycerate and (R)-2-phosphoglycerate, as shown in reaction (1) of Fig. P25.35. The enzyme contains a histidine residue in its active site, and the reaction involves a phosphohistidine intermediate, as shown in reaction (2) of Fig. P25.35.
(a) Assuming the presence of acidic and basic groups in the active site of the enzyme as needed, draw a curved-arrow mechanism for the transformation of 3-phosphoglycerate to 2-phosphoglycerate that is consistent with the information given.
(b) Suppose that an enantiomerically pure 2-phosphoglycerate derivative containing an isotopically chiral phosphate group is subjected to this reaction. Would the isotopically chiral 3-phosphoglycerate formed have the same configuration at phosphorus, the opposite configuration at phosphorus, or equal amounts of the two configurations? Explain your reasoning.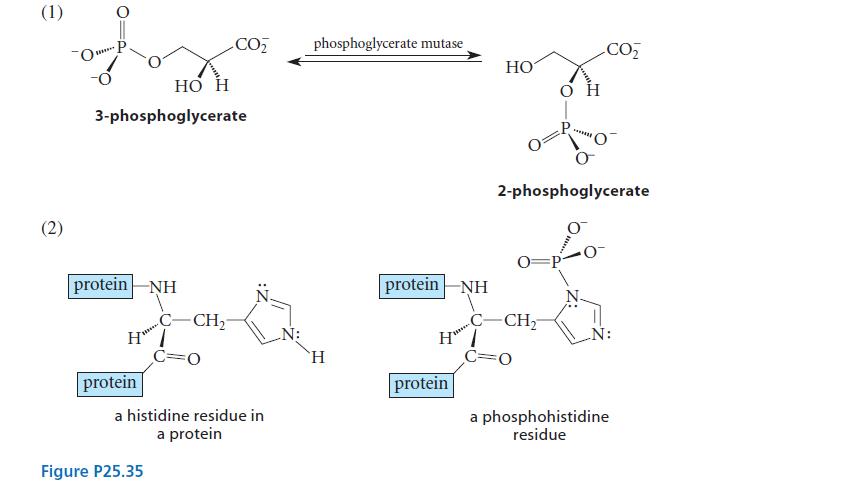
Step by Step Answer:






