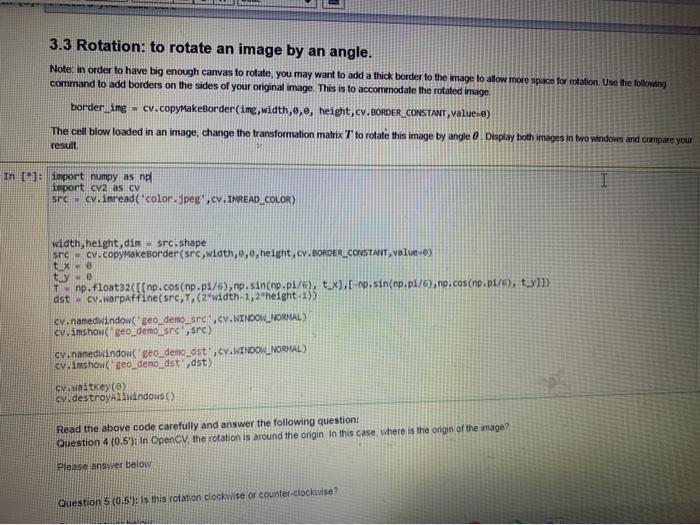
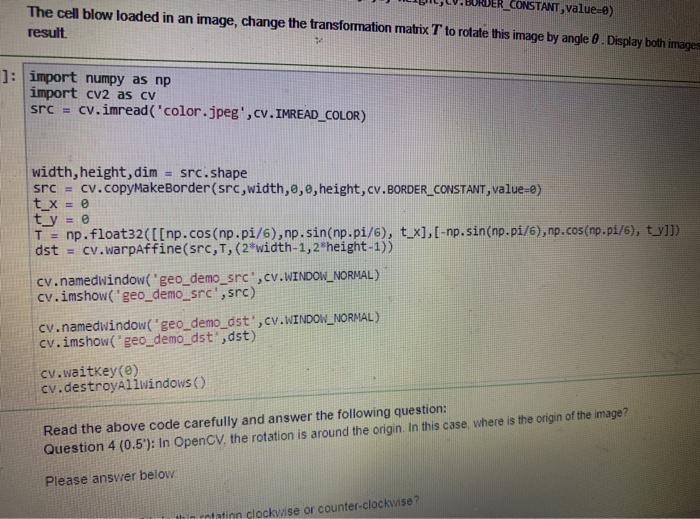
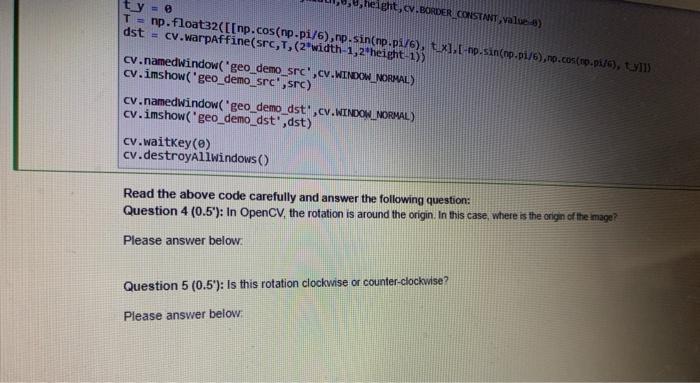
3.3 Rotation: to rotate an image by an angle. Note: in order to have big enough canvas to rotate, you may want to add a thick border to the image to allow more space for rotation. Use the following command to add borders on the sides of your original image. This is to accommodate the rotated image borderling cv.copyMakeBorder(img,width,,e, height, cv.BORDER_CONSTANT, Value:e) The cell blow loaded in an image, change the transformation matrix T to rotate this image by angle 0 Display both images in two windows and compare your result In : import numpy as ng import cv2 as c src cv. inread('color.Jpeg',cv. IMREAD_COLOR) width, height, din src.shape srev.copyMakeborder(src, width,0,0,height, cv.BORDER_CONSTANT, valves tux tly we Tnp. float32([[np.cos(np.p1/6), np. sin(np.pi/6), tux), np.sin(np.ps/@,no.cos(np.pt/6), t_y11) dst cv.worpaffine(src, T. (R"width 1,2"height:133 cv.namedwindow.geo_demo_srcscv.WINDOW_NORMAL) cuimshow geb_demolirere) cv.nanedidindow("geo_demo_dst. C. WINDOW_NORMAL) Cumshow seo demo dst, dst c.waitkey (e) c.destroyAllwindows) Read the above code carefully and answer the following question: Question 4 (0.5): In OpenCV, the rotation is around the origin In this case, where is the ongin of the image? Please answer below Question 5 (0.5'). Is this rotation clockwise or counter-clockwise? CONSTANT, value=0) The cell blow loaded in an image, change the transformation matrix T to rotate this image by angle. Display both images result ]: import numpy as np import cv2 as cv src = cv.imread('color.jpeg',cv. IMREAD_COLOR) width, height, dim = src.shape src = cv.copyMakeBorder(src,width,0,0,height, cv.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=) t_x = 0 ty = 0 T = np.float32([[np.cos(np.pi/6), np.sin(np.pi/6), t_x], [-np.sin(np.pi/6), np.cos(np.pi/6), ty]]) dst cv.warpaffine(src,T, (2*width-1,2"height-1)) cv.namedwindow('geo_demo_src',CV.WINDOW_NORMAL) cv.imshow'geo_demo_src',src) cv.namedwindow('geo_demo_ast',cv.WINDOW_NORMAL) cv.imshow("geo_demo_dst, dst) cv.waitKey(0) cv.destroyAllwindows) Read the above code carefully and answer the following question: Question 4 (0.5"): In OpenCV. the rotation is around the origin. In this case where is the origin of the image? Please answer below Thin natinn clockwise or counter-clockwise? het... BORDER CONSTANT,Value) ty = 8 T = np.float32([[np.cos(np-pi/6), np.sin(np.pi/6), tx], [-hp.sin(np.p1/6),no.cos(np.p:/4), UM dst = cv.Warpaffine(src,1,(2*width-1,2 height-1)) cv.namedWindow("geo_demo_src",cv.WINDOW_NORMAL) cy.imshow('geo_demo_src" src) cv.namedwindow("geo_demo_dst.cv.WINDOW_NORMAL) cv.imshow('geo_demo_dst',dst) cv.destroyAllwindows() Read the above code carefully and answer the following question: Question 4 (0.5"): In OpenCV, the rotation is around the origin. In this case, where is the origin of the image? Please answer below Question 5 (0.5'): Is this rotation clockwise or counter-clockwise? Please answer below