Question
Add to the code in c++ #include DynamicString.h #include #include using std::out_of_range; using std::tolower; using std::toupper; using std::ostream; using namespace std; //DynamicString() //Constructs an empty
 Add to the code in c++
Add to the code in c++
#include "DynamicString.h" #include
using std::out_of_range; using std::tolower; using std::toupper; using std::ostream; using namespace std;
//DynamicString() //Constructs an empty string. Allocating enough memory to store the null character DynamicString::DynamicString(){ cstr = new char[1]; cstr[0] = '\0'; }
//DynamicString(const char* str) //Constructs a string by copying the characters from the char array str to this object. DynamicString::DynamicString(const char* str){ int count = 0; while (str[count]) { ++count; } this->cstr = new char[count + 1]; for (int i = 0; i cstr[i] = str[i]; } this->cstr[count] = '\0'; } //int len() const //returns the length of this string int DynamicString::len() const{ int count = 0; while (cstr[count]) { ++count; } return count; }
//const char* c_str() const // returns a pointer to the underlying char array const char* DynamicString::c_str() const{ return cstr;
}
//char char_at(int position) const // returns the char at the specified position char DynamicString::char_at(int position) const{ return cstr[position]; }
//char& operator[](int position) // returns the char at the specified position char& DynamicString::operator[](int position){ return cstr[position]; }
//bool startsWith(const DynamicString& other) const //True if other is a prefix of this string bool DynamicString::startsWith(const DynamicString& other) const{ if (other.len()
//bool endsWith(const DynamicString& other) const //True if other is a suffix of this string bool DynamicString::endsWith(const DynamicString& other) const{ int len1 = len(); int len2 = other.len(); if (len2
//int compare(const DynamicString& other) const // negative if this is smaller than other, 0 if this is equal to other, positive if this is larger than other int DynamicString::compare(const DynamicString& other) const{ // Get size of this string int size1 = this->len(); // Get size of other string int size2 = other.len();
int i = 1; // Iterate through the characters while ((i != size1) || (i != size2)) { // If this is less than other if (this->cstr[i] cstr[i] > other.cstr[i]) { return 1; } i++; }
// If this is equal to other return 0; }
//int iCompare(const DynamicString& other) const // same as compare but is case-insensetive int DynamicString::iCompare(const DynamicString& other) const { // Get size of this string int size1 = this->len(); // Get size of other string int size2 = other.len();
int i = 1; // Iterate through the characters while ((i != size1) || (i != size2)) { // Compare each character after converting to lower case to make it case insensitive comparison.
// If this is less than other if (tolower(this->cstr[i]) cstr[i]) > tolower(other.cstr[i])) { return 1; } i++; }
// If this is equal to other return 0; }
//DynamicString& toLower() // converts the string to lowercase DynamicString& DynamicString::toLower() { // Iterate through the characters of this string for (int i = 0; i
//DynamicString& toUpper() // converts the string to uppercase DynamicString& DynamicString::toUpper() { // Iterate through the characters of this string for (int i = 0; i
//DynamicString& replace(char old, char new) //replace all instances of old with new DynamicString& DynamicString::replace(char old, char newCh){ char letter; for (int i = 0; i
//int find(char needle, int start = 0) const //return the first index of the specified char or -1 if the char is not found starting from index start. int DynamicString::find(char c, int start) const{ for (int i = start; i
//int reverseFind(char needle, int start) const //return the right-most index (less than or equal to start) of the specified char or -1 if the char is not found. int DynamicString::reverseFind(char c, int start) const{ for (int i = start; i >= 0; i--) { if (cstr[i] == c) { return i; } } return -1; }
int DynamicString::reverseFind(char c) const { int lastIndex = len() - 1; for (int i = lastIndex; i >= 0; --i) { if (cstr[i] == c) { return i; } } return -1; }
//Copy constructor for the DynamicString. This creates a deep copy of the char array by allocating a new array and copy each character over. DynamicString::DynamicString(const DynamicString& other) {
int len = other.len();
this->cstr = new char[len + 1]; for (int i = 0; i cstr[i] = other.cstr[i];
} this->cstr[len] = '\0'; } //Assignment operator. Like the copy-constructor, this method creates a deep copy of the char array. //However, it also needs to clean up previous memory allocations as well as check for self-assignment. DynamicString& DynamicString::operator=(const DynamicString& other) {
int len = other.len(); this->cstr = new char[len + 1]; for (int i = 0; i cstr[i] = other.cstr[i]; } this->cstr[len] = '\0';
// delete the space. delete[] other.cstr; } //Destructor frees up (deletes) any dynamically allocated memory used be the class (i.e. the char array) DynamicString::~DynamicString() { delete[] this-> cstr; }
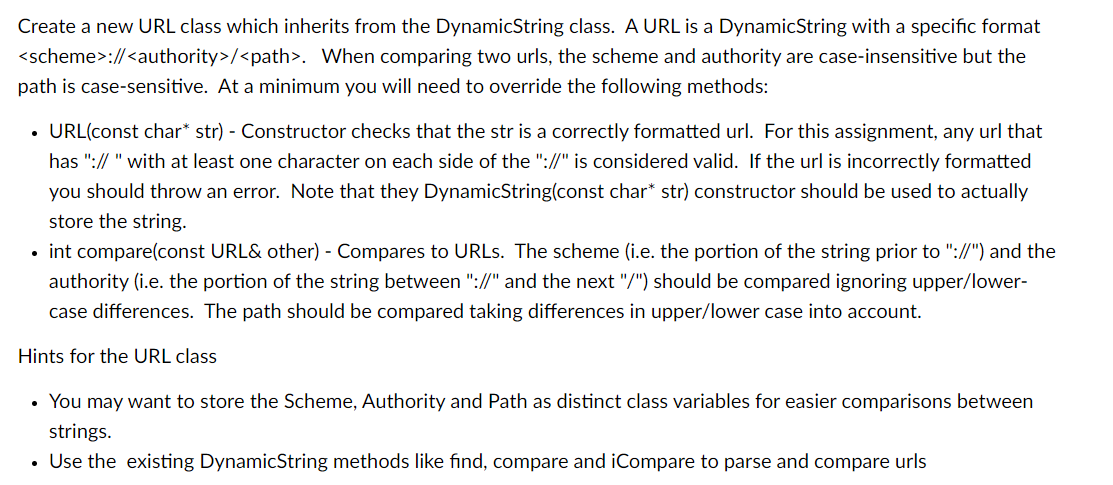
ostream& operator Create a new URL class which inherits from the DynamicString class. A URL is a Dynamic String with a specific format
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


