Question: Answer the following 1. It is defined as the velocity of an object in the rest frame of another object. A. relative motion B. relative


Answer the following



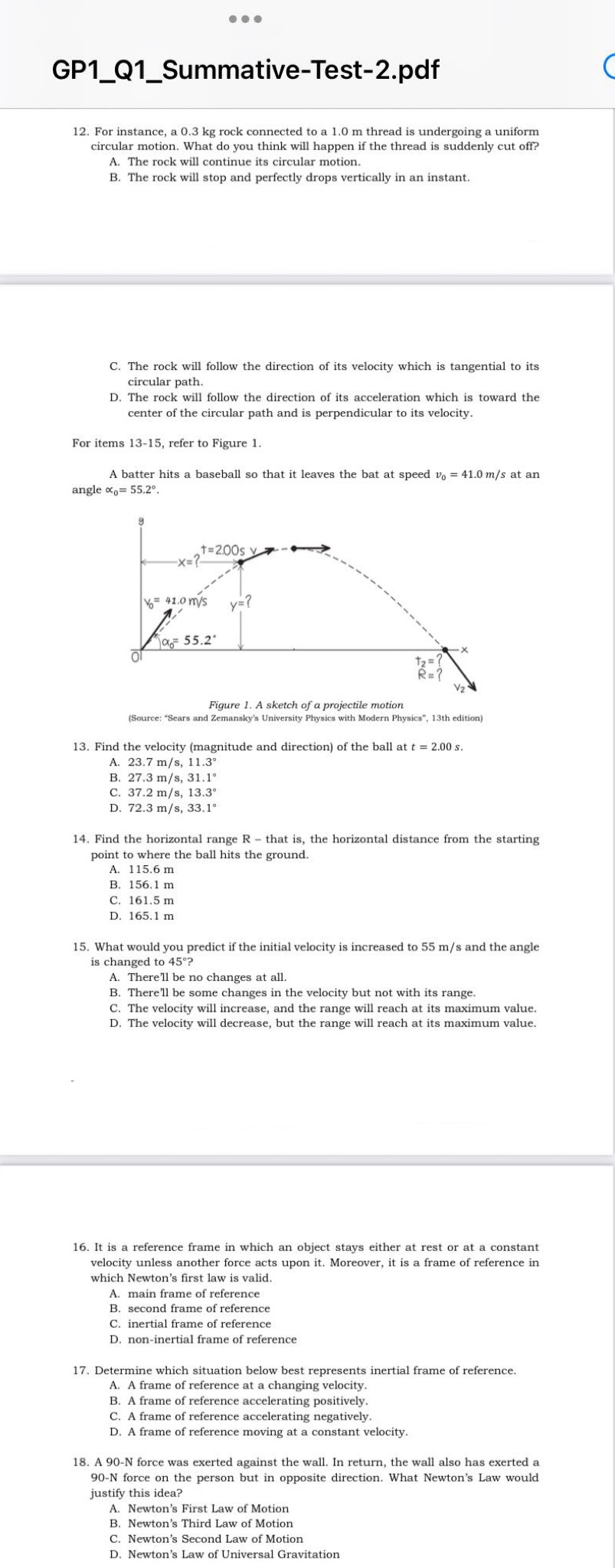
1. It is defined as the velocity of an object in the rest frame of another object. A. relative motion B. relative velocity C. instantaneous velocity D. instantaneous acceleration 2. Two trains, A and B are travelling towards east with velocities V, = 1.5 m/s and Vb = 2.5 m/s . What is the velocity of train B with respect to train A? A. +1.0 m/s B. -1.0 m/s C. +3.5 m/s D. -3.5 m/s 3. Considering that two cars are travelling on the same direction with Vg = 4.5 m/s. In this instance, the velocity of A with respect to B is VAS = +2.0m/s. Which car has greater velocity? A. car A B. car B C. both have the same velocity D. relative velocities cannot be solved 4. Any object undergoing projectile motion would always have a constant downward acceleration equal to: A. 0 m/s2 B. +9.8 m/s2 C. -9.8 m/ s2 D. +15.0 m/ s2 5. How would you describe the motion of an object which supposed to be undergoing projectile motion but with no downward force due to gravity? A. The object won't move. B. The object would maintain its vertical motion. C. The object would maintain its horizontal motion. D. The object would still move parabolically even with no downward force due to gravity. 6. Do you agree that gravity has a great role in projectile motion? A. Yes, because it speeds up the motion of the object. B. No, because the object's horizontal acceleration is always zero anyway. C. Yes, because it is the one that influences the object's parabolic trajectory. D. No, because whether the gravity is present or not, the object would still have a downward acceleration anyway. 7. A soccer player hits the soccer ball so that it leaves at speed v. = 26.0 m/s at an angle 0. = 39.0. Solve for the maximum height, h reached by the ball. A. 0.53 m B. 2.79 m C. 13.7 m D. 27.3 m 8. By comparing the angles of projectile's initial velocity below, which one do you think would reach the highest range among them? A. 310 B. 43" C. 75 D. 85' 9. What might happen if the angle of velocity of a certain projectile is changed from 85 to 45* while the other significant values remain the same? A. The projectile's range would be shorter. B. The projectile's height would be shorter. C. The projectile's range would be at its minimum value. D. The projectile's height would be at its minimum value. 10. When a particle moves in a circle with constant speed, the motion is called A. lateral acceleration B. centripetal acceleration C. uniform circular motion D. nonuniform circular motion 11. In a carnival ride, the passengers travel at a constant speed in a circle of radius 6.0 m. They make one complete circle in 7.0 s. What is their acceleration? A. 1.3 m/s2 B. 2.7 m/ s2 C. 4.9 m/s2 D. 7.8 m/s219. Select which of the situations below is Newton's Third Law Motion most applicable? A. A bouncing hall. B. A nonmoving asteroid in the space. C. Light particles traveling in the space. D. A box of Chalk! on the teacher's table at rest. 20. Which of the following reaction forces probably has the greatest action force applied? A. -l2ON B. 434 N C. 443 N D. -I5DN 2 I. Would you agree that the situation \"a ball tied with a rope. hanging in the ceiling\" only has two forces involved? A. Yes. because if sketched through. only,r tension force and weight is involved. B. Yes. because if sketched through FBD. only normal force and kinetic friction is involved C. No. because if sketched through FED. there are three forces involved. namely tension force. weight. and normal force. D. No. because if sketched through FBD. there are four forces involved, namely normal force. kinetic friction. tension force. and weight. For items 2223. please refer to the problem and Figure 2 below. Three sleds are being pulled horizontally on a frictionless horizontal ice using ropes. 30.0 kg 20.0 kg 10.0 kg Pull #3:: Figure 2. Three sleds pulled together [Smircez 'Sem and Zemansky's University Physics with Modern Physics\". 13th edition) 22. Draw the freebody diagram [FBD] of the 10kg sled. A. B. 7 \"lo a . C 7'4 P s \"In\" 7 "u a . D. Tl '\"sn 23. Draw the free-body diagram (FBD) of the three sleds taken as a composite object D. T. 24. What would you infer from a free-body diagram (FBD) that shows only normal force directed upward and a weight directed downward? A. Something with mass is at rest on top of a surface. B. Something with mass is accelerating to the right direction. C. Something with mass is connected to a thread and is hanged from the ceiling. D. Something with mass is connected to a thread and is accelerating to the left direction. 25. According to the Newton's First Law of Motion, "An object at rest, remains at rest and an object in motion, remains in motion, unless acted upon by a net external force." Which of the following situation would best apply to this law? A. a bird flying in the air B. a fish swimming in the pond C. a person walking on the road D. a person hitting the windshield of the car after it crashed 26. A 2.5 kg mass is hanged in the rope and tied in the ceiling. Find the tension in the rope. A. 9.8 N B. 19.6 N C. 24.5 N D. 29.4 N 27. A 0.7 kg box sits on top of the table. Solve for the normal force exerted by the table on the box. A. 6.86 N B. 8.68 N C. 68.8 N D. 86.6 N 28. Jason compares which of two, Yamaha Mio Aerox's or Honda XRM's wheel is better on a muddy road. What frictional force is involved in this kind of situation? A. Gravitational force B. static frictional force C. rolling frictional force D. kinetic frictional force 29. Select which of the situations below is static friction applicable? A. A frictional force between an accelerating bus and a road. B. A frictional force between an accelerating bicycle and a road. C. A frictional force between a moving box and the surface of the table. D. A frictional force needed to overcome for a refrigerator to be transferred by pushing against the floor. 30. Select which of the situations below is kinetic friction applicable? A. A frictional force between an accelerating bus and a road. B. A frictional force between an accelerating bicycle and a road. C. A frictional force between a moving box and the surface of the table. D. A frictional force needed to overcome for a refrigerator to be transferred by pushing against the floor.GP1_Q1_Summative-Test-2.pdf 12. For instance, a 0.3 kg rock connected to a 1.0 m thread is undergoing a uniform circular motion. What do you think will happen if the thread is suddenly cut off? A. The rock will continue its circular motion. B. The rock will stop and perfectly drops vertically in an instant. C. The rock will follow the direction of its velocity which is tangential to its circular path. D. The rock will follow the direction of its acceleration which is toward the center of the circular path and is perpendicular to its velocity. For items 13-15, refer to Figure 1. A batter hits a baseball so that it leaves the bat at speed vo = 41.0 m/s at an angle = 55.2'. T=2.00s v -X= Vo# 41.0 m/s y=? 12=? R = ? Figure 1. A sketch of a projectile motion (Source: "Sears and Zemansky's University Physics with Modern Physics", 13th edition) 13. Find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the ball at t = 2.00 s. A. 23.7 m/s, 11.3 B. 27.3 m/s, 31.1 C. 37.2 m/s, 13.3. D. 72.3 m/s, 33.1' 14. Find the horizontal range R - that is, the horizontal distance from the starting point to where the ball hits the ground. A. 115.6 m B. 156.1 m C. 161.5 m D. 165.1 m 15. What would you predict if the initial velocity is increased to 55 m/s and the angle is changed to 45'? A. There'll be no changes at all. B. There'll be some changes in the velocity but not with its range. C. The velocity will increase, and the range will reach at its maximum value. D. The velocity will decrease, but the range will reach at its maximum value. 16. It is a reference frame in which an object stays either at rest or at a constant velocity unless another force acts upon it. Moreover, it is a frame of reference in which Newton's first law is valid. A. main frame of reference B. second frame of reference C. inertial frame of reference D. non-inertial frame of reference 17. Determine which situation below best represents inertial frame of reference. A. A frame of reference at a changing velocity. B. A frame of reference accelerating positively. C. A frame of reference accelerating negatively. D. A frame of reference moving at a constant velocity. 18. A 90-N force was exerted against the wall. In return, the wall also has exerted a 90-N force on the person but in opposite direction. What Newton's Law would justify this idea? A. Newton's First Law of Motion B. Newton's Third Law of Motion C. Newton's Second Law of Motion D. Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


