Question: CHEM 6 SPRING 2023 (Problem #1) A helium-neon laser emits an intense monochromatic light beam with a wavelength of 6328 . Calculate the angles

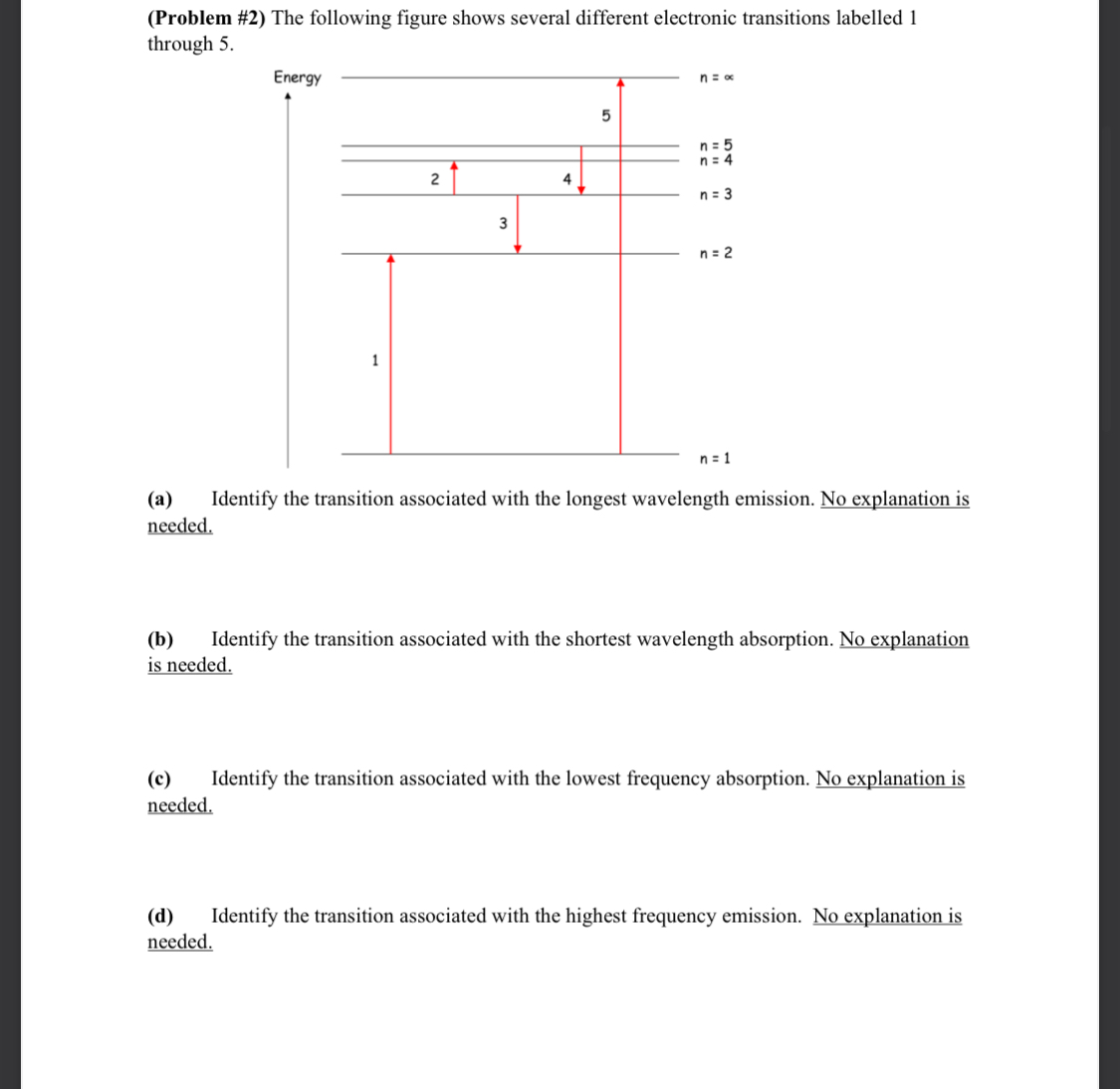








CHEM 6 SPRING 2023 (Problem #1) A helium-neon laser emits an intense monochromatic light beam with a wavelength of 6328 . Calculate the angles at which the first- and second-order diffractions will be observed using a diffraction grating with 13,400 lines/inch. Make sure to take care with units in this problem. (Problem #2) The following figure shows several different electronic transitions labelled 1. through 5. Energy 1 2 3 n = x 5 n = 5 n = 4 4 n = 3 n = 2 n = 1 (a) needed. Identify the transition associated with the longest wavelength emission. No explanation is (b) Identify the transition associated with the shortest wavelength absorption. No explanation is needed. (c) needed. Identify the transition associated with the lowest frequency absorption. No explanation is (d) needed. Identify the transition associated with the highest frequency emission. No explanation is CHEM 6 SPRING 2023 (Problem #3) (a) An electron in a one-dimensional box requires the absorption of a photon with a wavelength of 8080 nm to excite it from the n = 2 to the n = 3 energy level. Calculate the length of this box. Show your work and express your final answer in nanometers. (b) An electron in a 10.0 nm one-dimensional box is excited from the ground state into a higher energy state by absorbing a photon of electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength of 1.374 105 m. Determine the final energy state (i.e., quantum number) for this electronic transition. (c) For a particle in the n = 3 state of a one-dimensional box of length L, what is the total probability of finding the particle between x = 0 and x = L/6. Show your work and rationalize your approach to receive full credit. (Problem #4) The orange-yellow light of sodium vapor lamps is emitted when the valence electron of sodium makes a transition from an excited state back to the ground state of the atom. The light emitted is produced by transitions from two different excited states. One of these transitions emits a photon with a wavelength of 589.00 nm, while the other transition emits a photon with a wavelength of 589.59 nm. (a) Draw an energy level diagram showing the relative energies of the ground state and the two excited states -- this diagram need not be to scale. (b) On your diagram, label and show which change of energy level -- i.e., which transition produces the photon with wavelength 589.00 nm. (c) On your diagram, label and show which change of energy level -- i.e., which transition produces the photon with wavelength 589.59 nm. (d) Calculate the energy of each excited state relative to the ground state. Express your answer in kJ mol-1. (e) Calculate the energy difference between the two excited states. Express your answer in kJ mol-1. (Problem #5) Using the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, calculate the uncertainty in position, Ax, for: (a) an electron with Avx = 0.100 m/s. How does your answer compare with the size of a hydrogen atom? (b) a baseball (mass = 145 g) with Avx = 0.100 m/s. How does your answer compare with the size of a baseball? (Problem #6) (a) When electromagnetic radiation with wavelength = 2000 is incident on a clean tungsten plate in a vacuum, the maximum kinetic energy observed amongst the electrons ejected is 1.64 eV. Calculate the threshold wavelength above which it will not be possible to eject electrons from tungsten metal. Show your work and express your answer in nm. (b) The maximum kinetic energy observed amongst electrons ejected from potassium metal by electromagnetic radiation with frequency v = 1.63 1015 s-1 is 7.2 x 10-19 J. Calculate the wavelength associated with the motion of an ejected electron that has this maximum kinetic energy. Show your method clearly and express your answer in nm.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


