3. Compute seasonal index by dividing average season demand (step 1) over total average demand (step 2).
Question:
3. Compute seasonal index by dividing average season demand (step 1) over total average demand (step 2). For example, March seasonal index equals 85>110 = 0.77.
Table 4.4 shows the weekly demand for Eurospeed, a Europe-wide parcel delivery company. It measures demand, on a weekly basis, in terms of the number of parcels that it is given to deliver (irrespective of the size of each parcel). Each week, the next week’s demand is forecast by taking the moving average of the previous four weeks’ actual demand. Thus if the forecast demand for week t is Ft and the actual demand for week t is At,
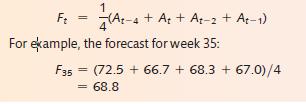
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Operations And Process Management Principles And Practice For Strategic Impact
ISBN: 978-1292350066
6th Edition
Authors: Alistair Brandon-Jones
Question Posted:






