Question: A continuous-time LTI system is represented by the ordinary differential equation where x(t) is the input and y(t) the output. (a) Determine the frequency response
A continuous-time LTI system is represented by the ordinary differential equation
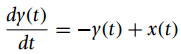
where x(t) is the input and y(t) the output.
(a) Determine the frequency response H(jΩ) of this system by considering the steady-state output of the system to inputs of the form x(t)=ejΩt, for ˆ’ˆž < Ω < ˆž.
(b) Carefully sketch the magnitude, |H(jΩ)|, and the phase, ˆ H(jΩ), frequency responses of the system. Indicate the magnitude and phase at frequencies of 0, ±1, and ±ˆž rad/sec.
(c) If the input to this LTI is x(t) = sin(t)/(Ï€t), determine and carefully plot the magnitude response |Y(Ω)|of the output, indicating the values at frequencies 0, ±1, and ±ˆž rad/sec.
dy(t) dt = -y(t) + x(t) %|
Step by Step Solution
3.46 Rating (162 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a According to the eigenvalue property for xt e jt the output in the steadystate would ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


