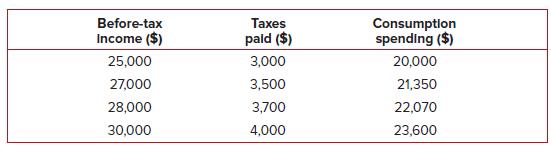
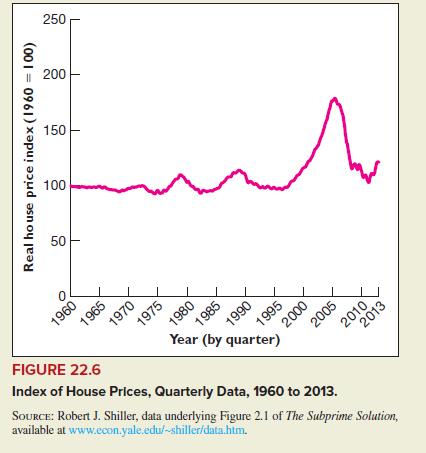
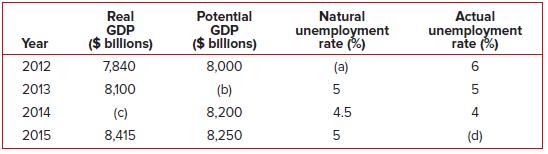
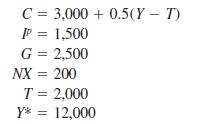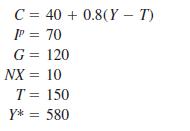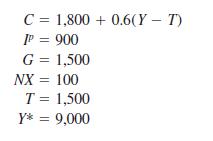Principles Of Economics 6th Edition Robert H. Frank, Ben Bernanke Professor, Kate Antonovics, Ori Heffetz - Solutions
Discover comprehensive solutions for "Principles of Economics 6th Edition" by Robert H. Frank, Ben Bernanke, Kate Antonovics, and Ori Heffetz. Access our extensive collection of solved problems and step-by-step answers, ideal for mastering the material. Dive into our online resources, including a detailed solutions manual and free PDF downloads of chapter solutions. Enhance your learning with our test bank and instructor manual, offering valuable insights and answers key for each chapter. Whether you're seeking a textbook companion or a complete guide to questions and answers, our platform is your gateway to understanding economics effortlessly.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()