Figure 40.27a modeled a hydrogen atom as a finite potential well with rectangular edges. A more realistic
Question:
Figure 40.27a modeled a hydrogen atom as a finite potential well with rectangular edges. A more realistic model of a hydrogen atom, although still a one-dimensional model, would be the electron + proton electrostatic potential energy in one dimension:
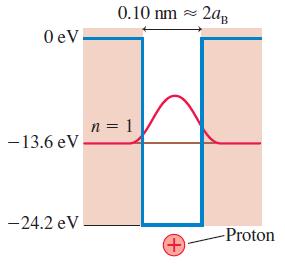
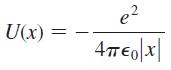
a. Draw a graph of U(x) versus x. Center your graph at x = 0.
b. Despite the divergence at x = 0, the Schrödinger equation can be solved to find energy levels and wave functions for the electron in this potential. Draw a horizontal line across your graph of part a about one-third of the way from the bottom to the top. Label this line E2, then, on this line, sketch a plausible graph of the n = 2 wave function.
c. Redraw your graph of part a and add a horizontal line about two-thirds of the way from the bottom to the top. Label this line E3, then, on this line, sketch a plausible graph of the n = 3 wave function.
Step by Step Answer:

Physics For Scientists And Engineers A Strategic Approach With Modern Physics
ISBN: 9780321740908
3rd Edition
Authors: Randall D. Knight





