The standard molar enthalpy of formation of diborane, B 2 H 6 (g), cannot be determined directly
Question:
The standard molar enthalpy of formation of diborane, B2H6(g), cannot be determined directly because the compound cannot be prepared by the reaction of boron and hydrogen. It can be calculated from other enthalpy changes, however. The following enthalpy changes can be measured. 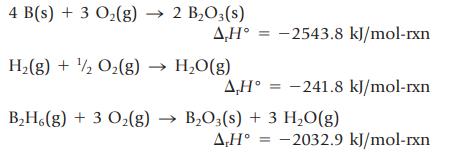
(a) Show how these equations can be added together to give the equation for the formation of B2H6(g) from B(s) and H2(g) in their standard states. Assign enthalpy changes to each reaction.
(b) Calculate ∆fH° for B2H6(g).
(c) Draw an energy level diagram that shows how the various enthalpies in this problem are related.
(d) Is the formation of B2H6(g) from its elements exo- or endothermic?
Step by Step Answer:

Chemistry And Chemical Reactivity
ISBN: 9780357001172
10th Edition
Authors: John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel





