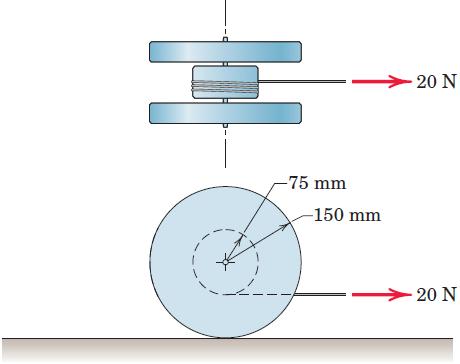
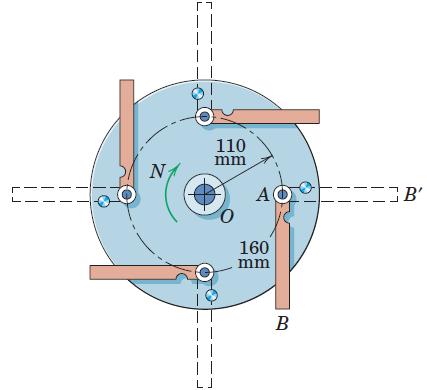
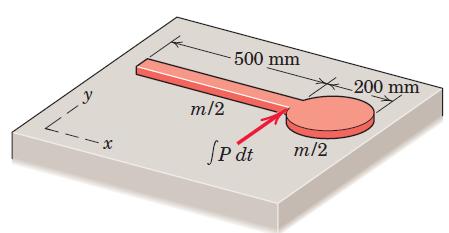
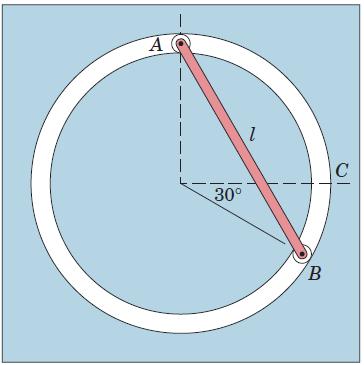
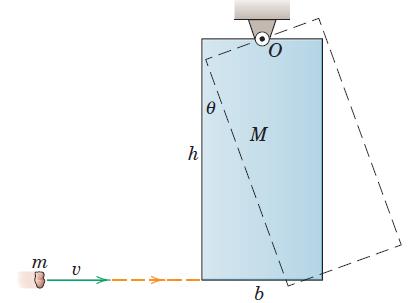
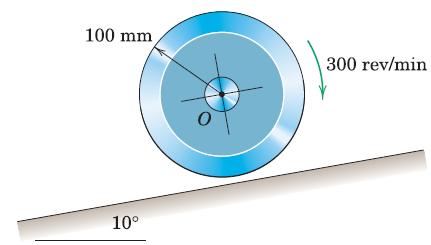
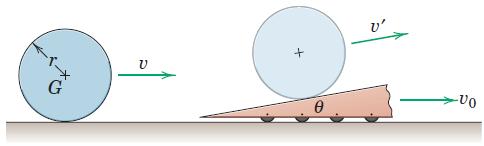
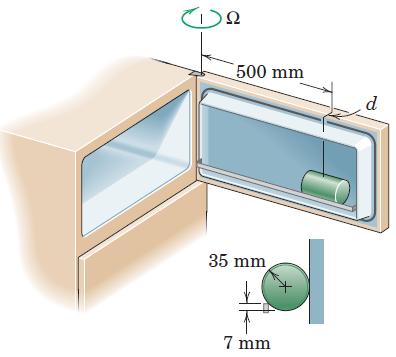
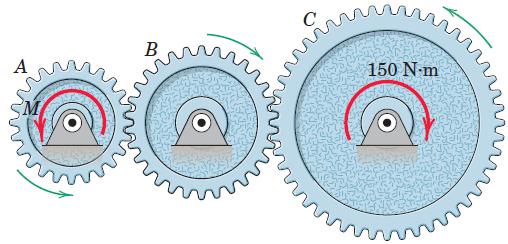
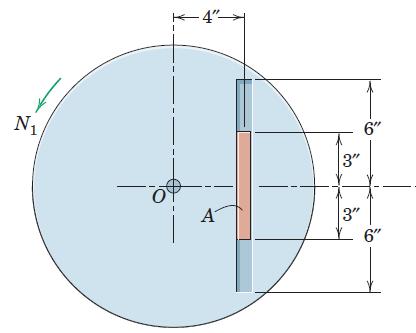
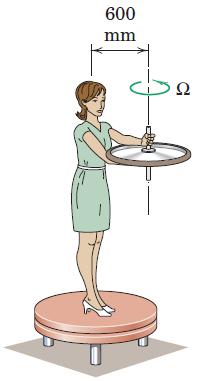
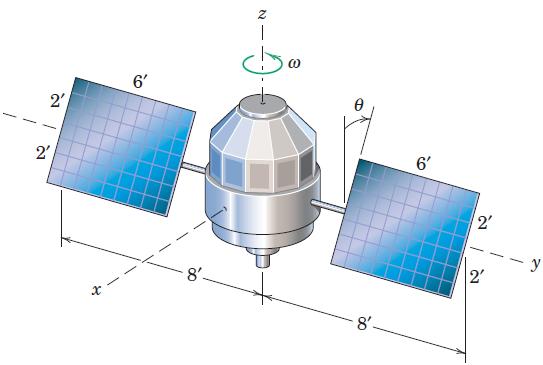
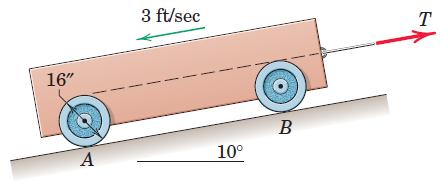
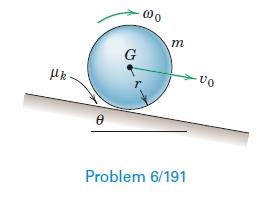
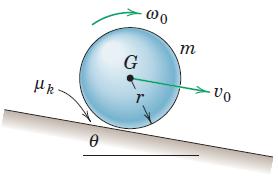
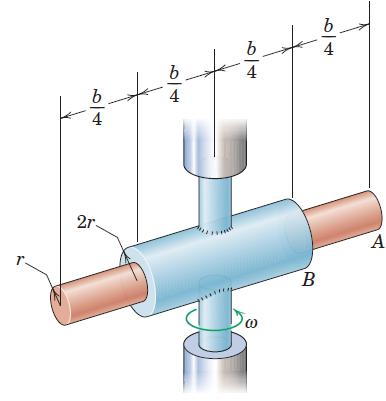
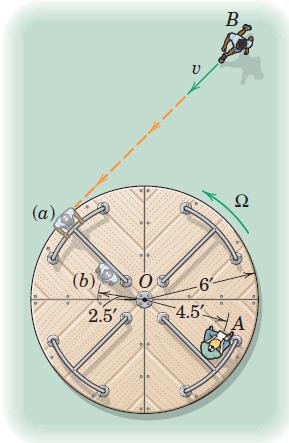
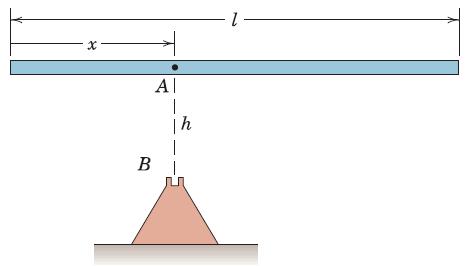
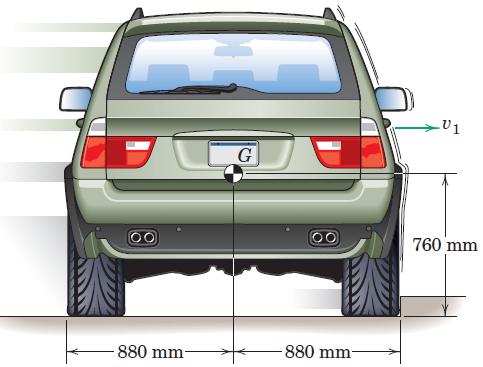
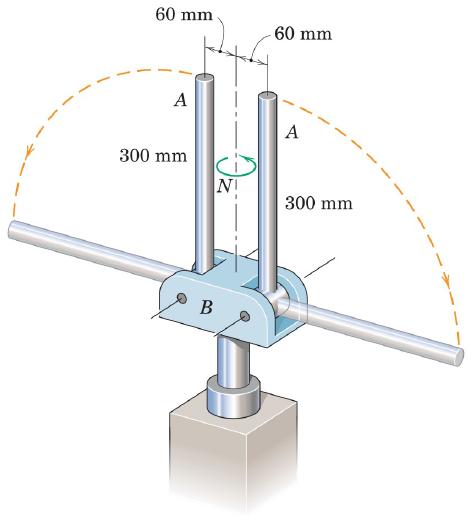
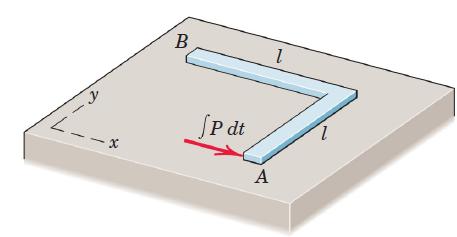
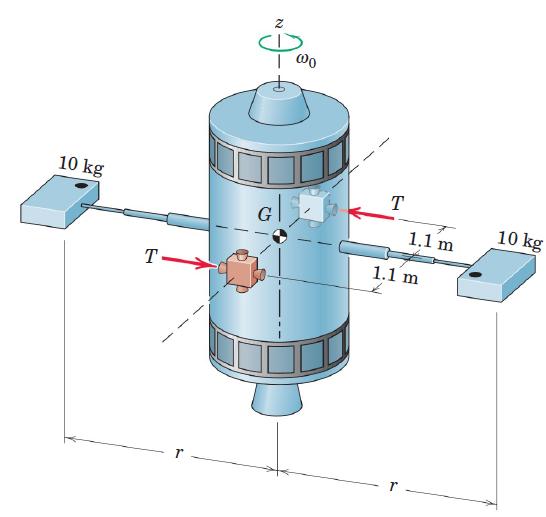
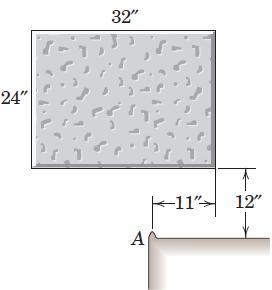
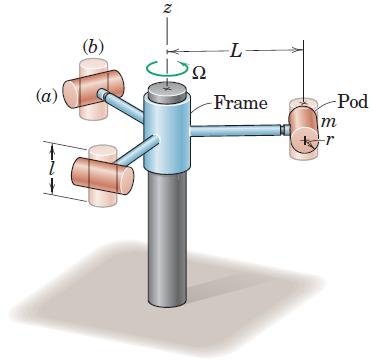
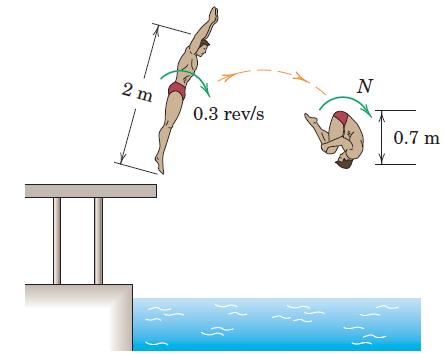
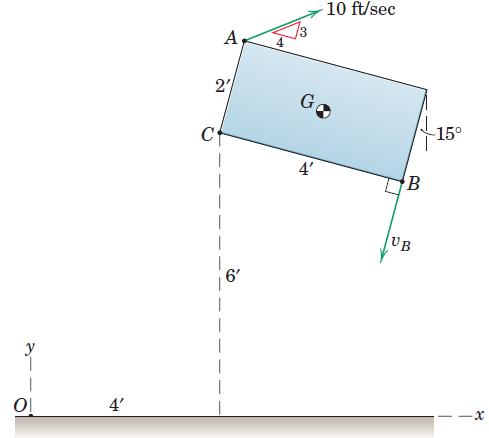
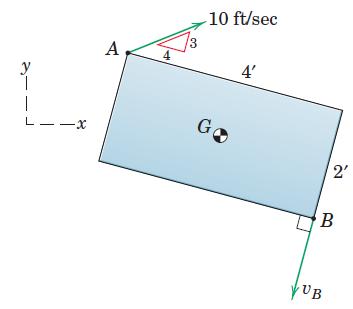
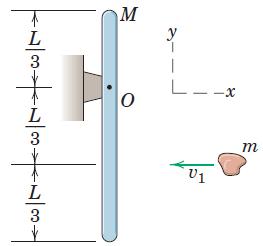
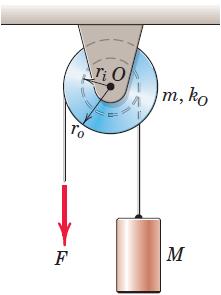
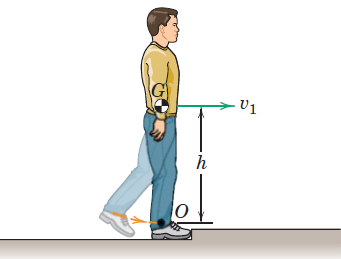
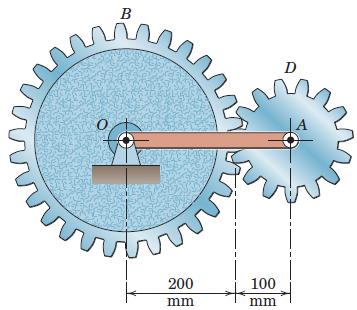
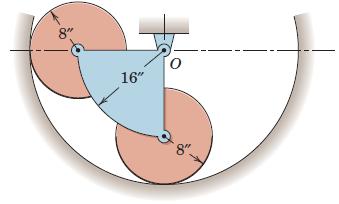
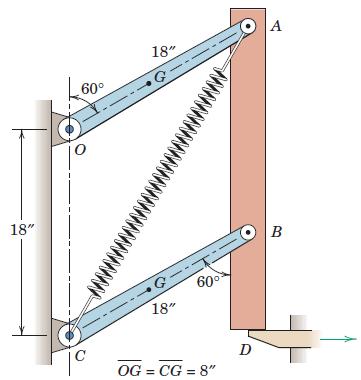
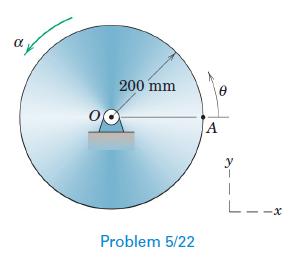
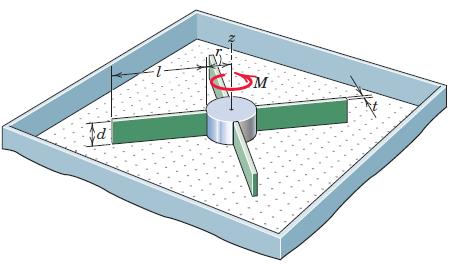
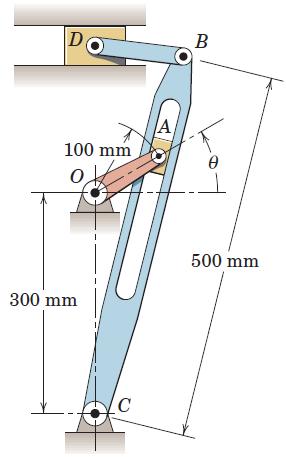
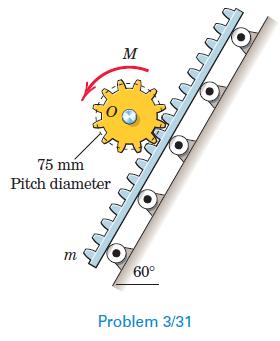
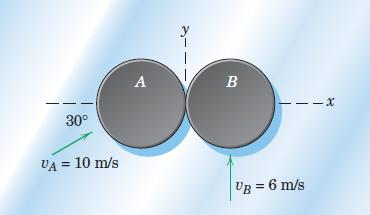
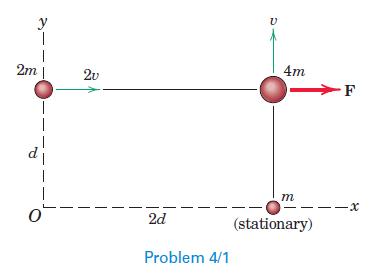
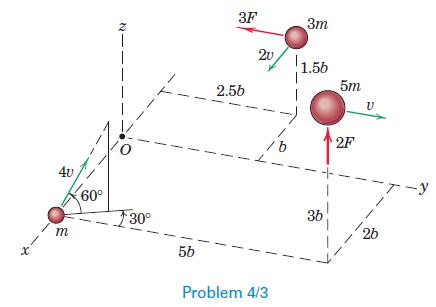
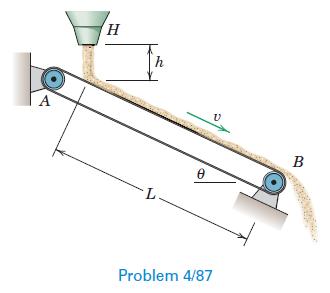
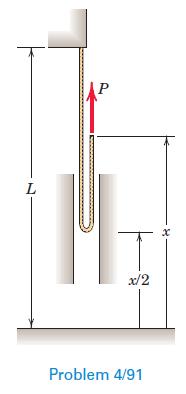
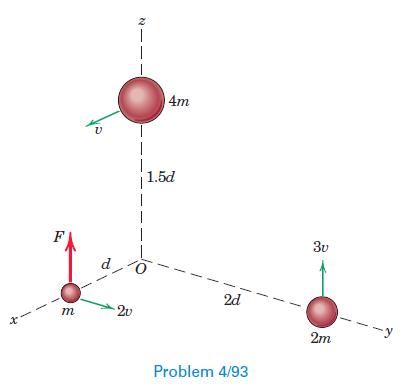
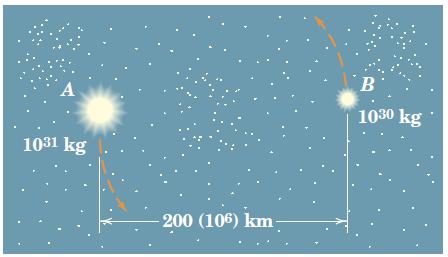
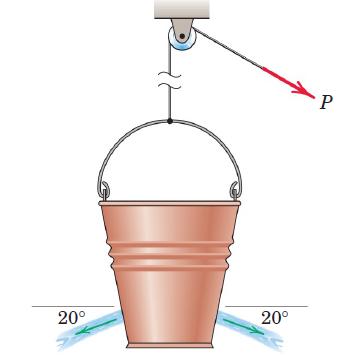
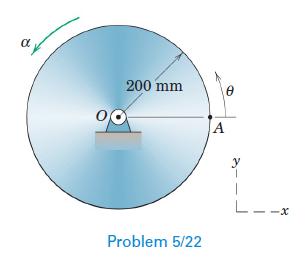
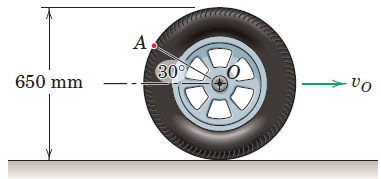
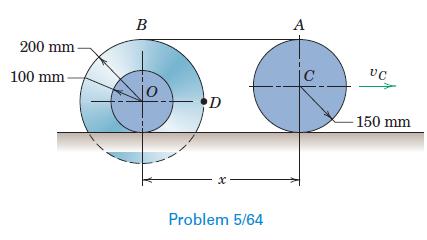
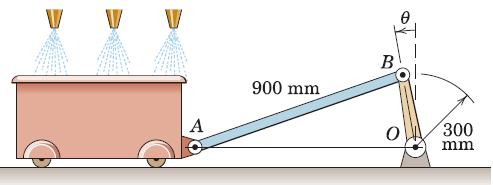
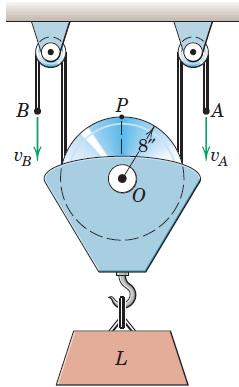
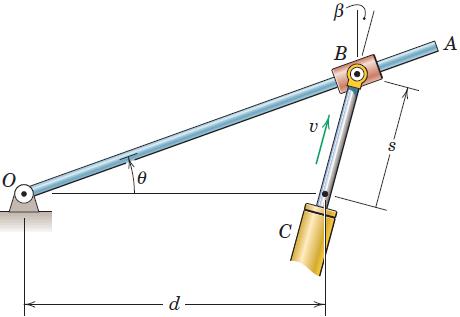
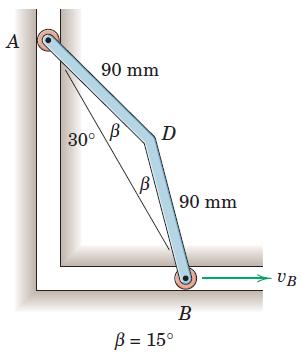
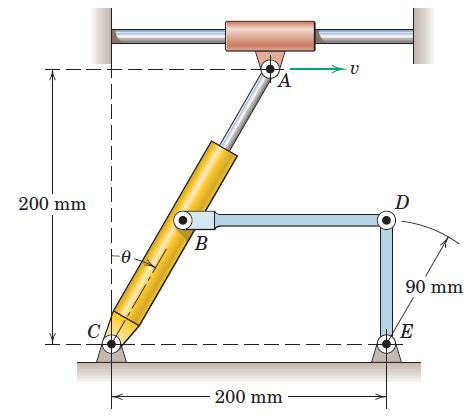
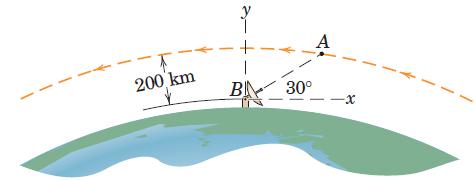
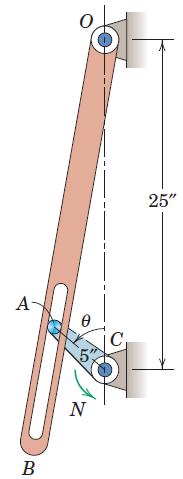
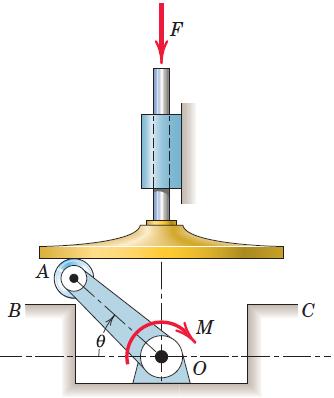
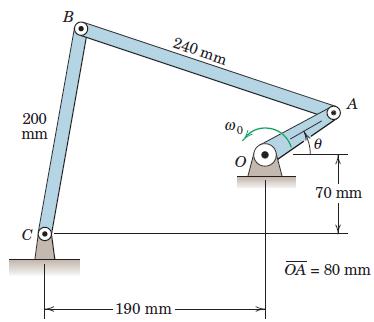
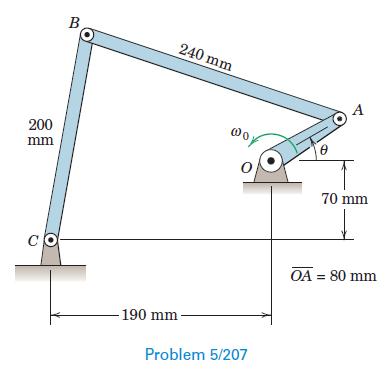
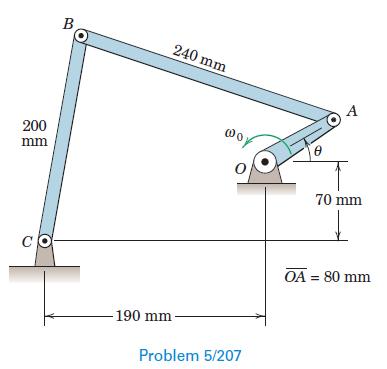
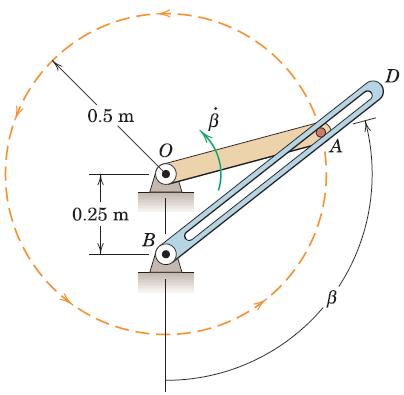
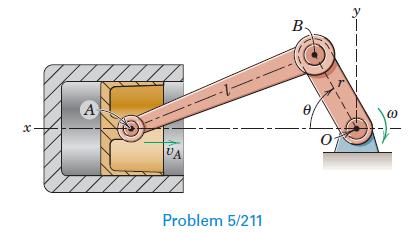
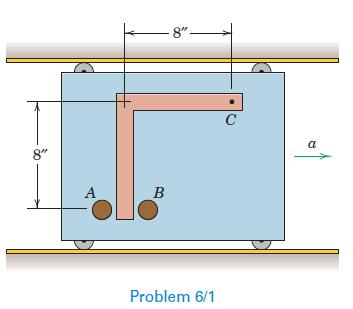
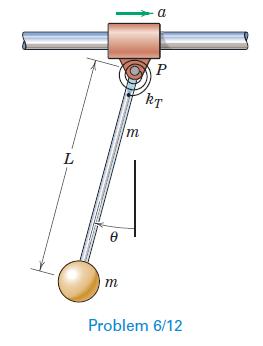
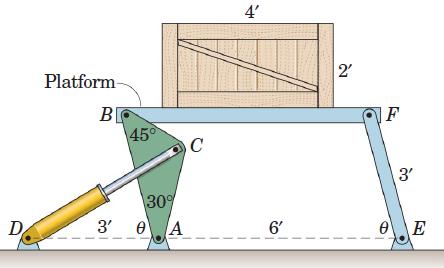
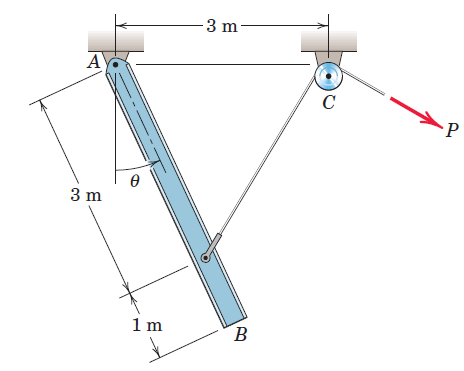
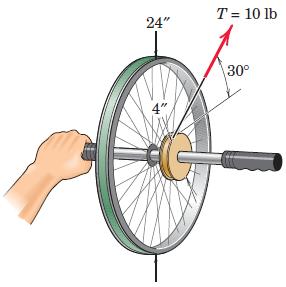
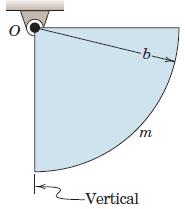
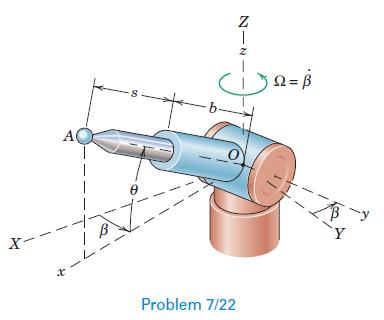
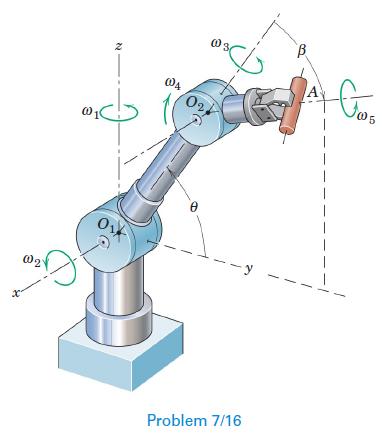
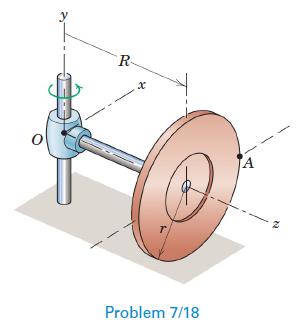
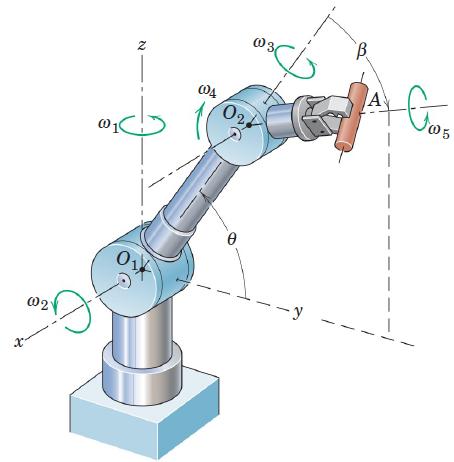
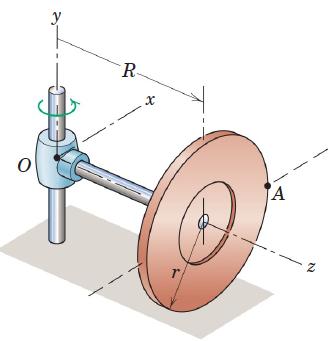
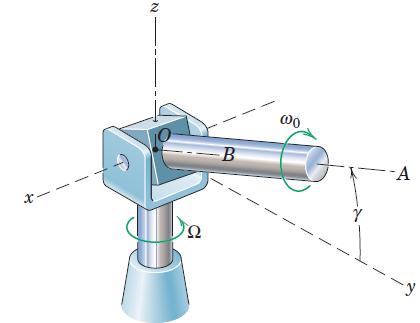
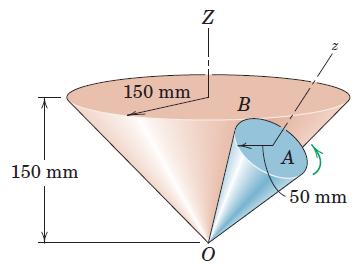
Engineering Mechanics Dynamics 8th Edition James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton - Solutions
Discover comprehensive solutions to the challenging problems in "Engineering Mechanics Dynamics 8th Edition" by James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, and J. N. Bolton. Access the complete answers key and solutions manual for a thorough understanding of each concept. Dive into the solved problems and step-by-step answers to enhance your learning experience. Our resource includes a detailed test bank and chapter solutions, providing a solid foundation for your studies. The instructor manual and textbook materials are available for free download in PDF format, ensuring you have everything you need to succeed.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()