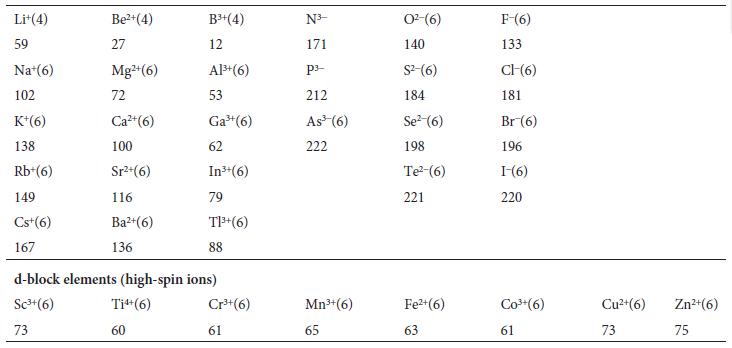
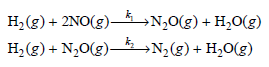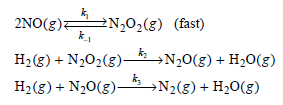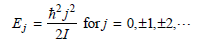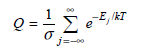Physical Chemistry Thermodynamics And Kinetics 10th Edition Peter Atkins, Julio De Paula - Solutions
Dive into the world of "Physical Chemistry Thermodynamics and Kinetics 10th Edition" by Peter Atkins and Julio De Paula with our comprehensive online resources. Unlock the full potential of your studies with our answers key and solutions manual, available in solutions pdf format. Tackle solved problems with ease, utilizing our step-by-step answers and detailed chapter solutions. Explore our questions and answers section, enriched with a test bank and instructor manual for an in-depth understanding. Whether you're using the textbook or seeking additional support, our free download options make mastering this subject accessible and straightforward.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()